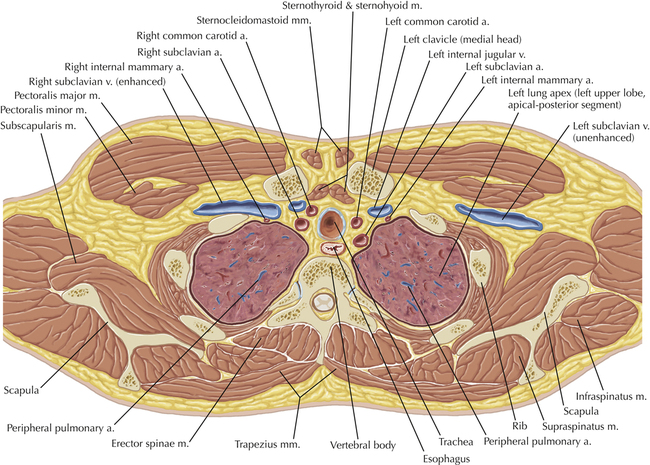
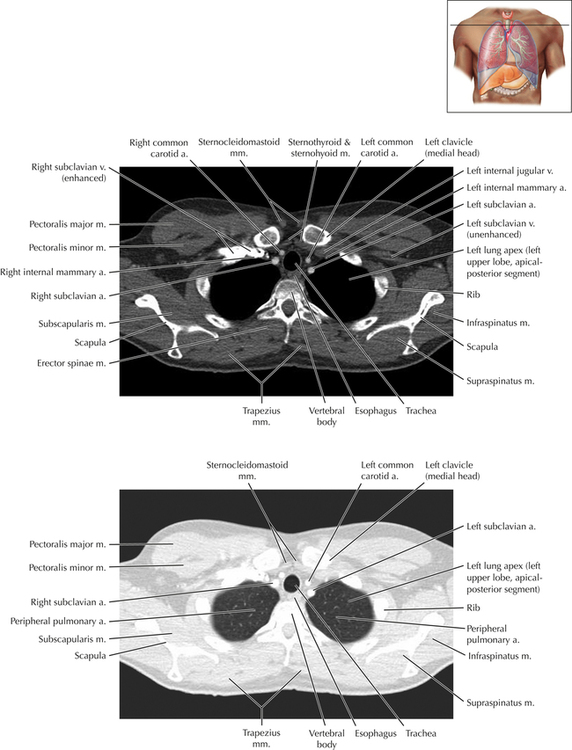
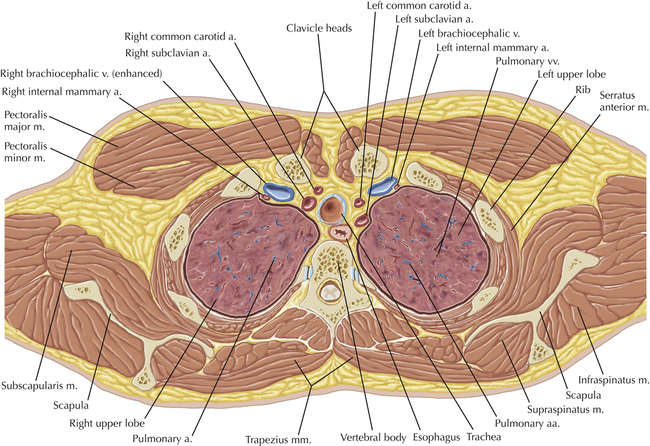
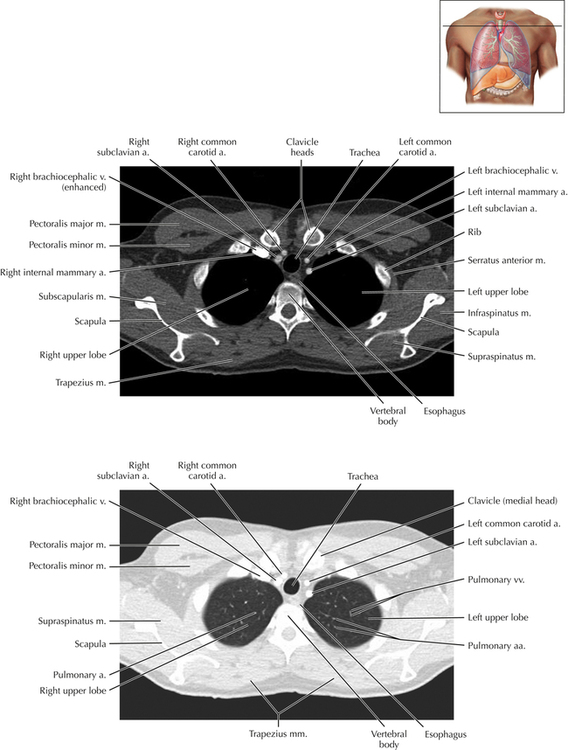
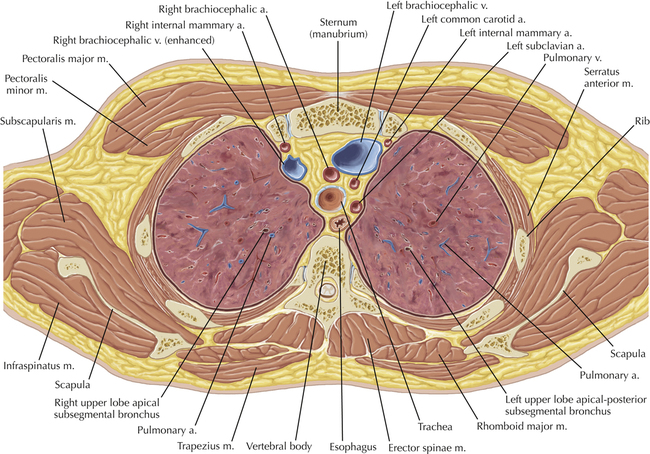
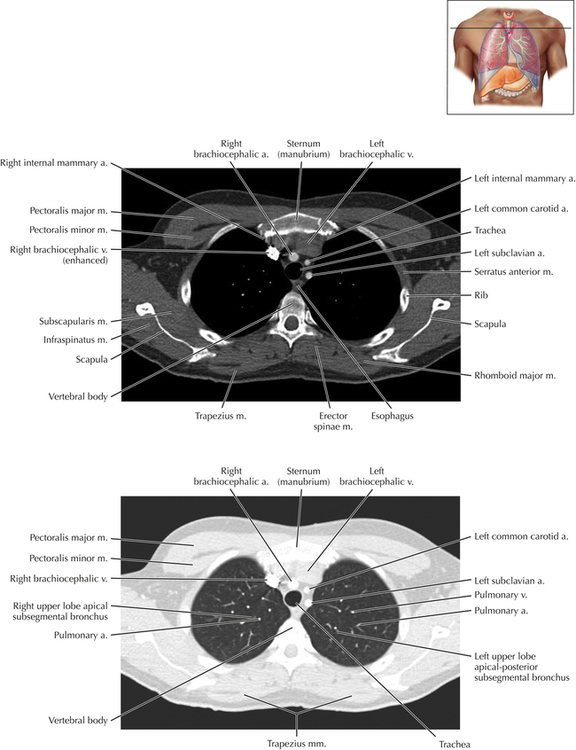
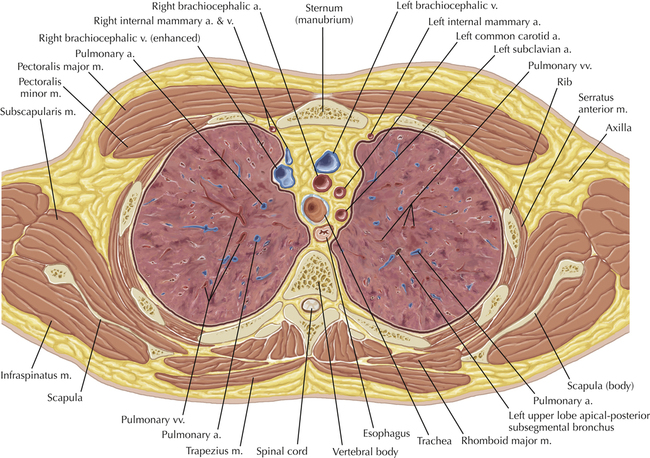
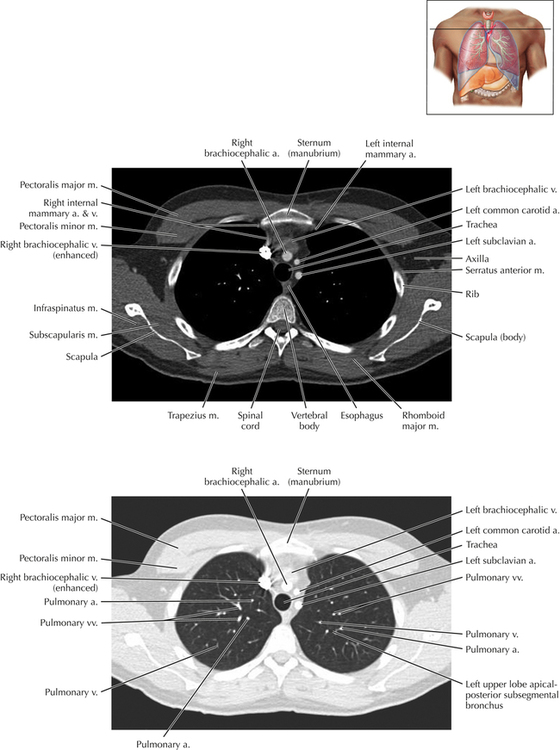
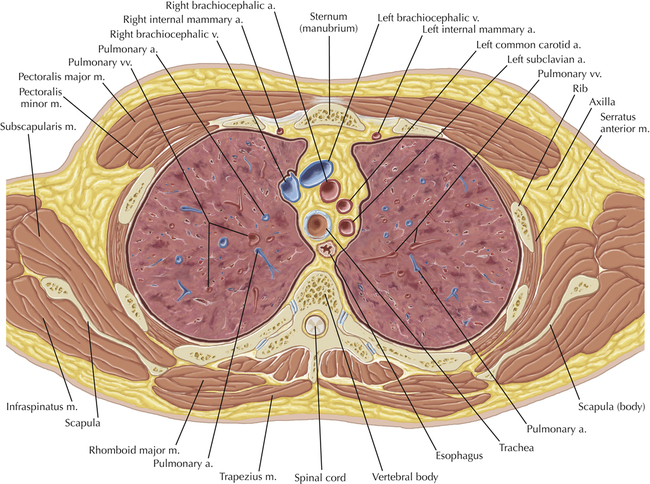
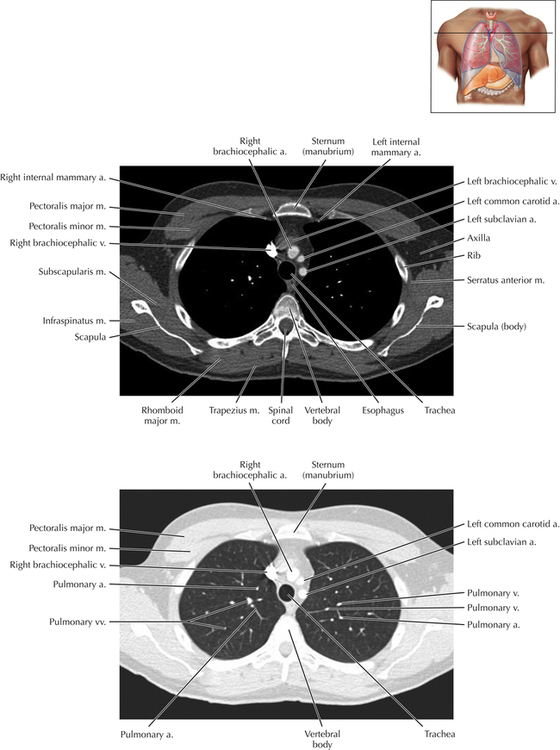
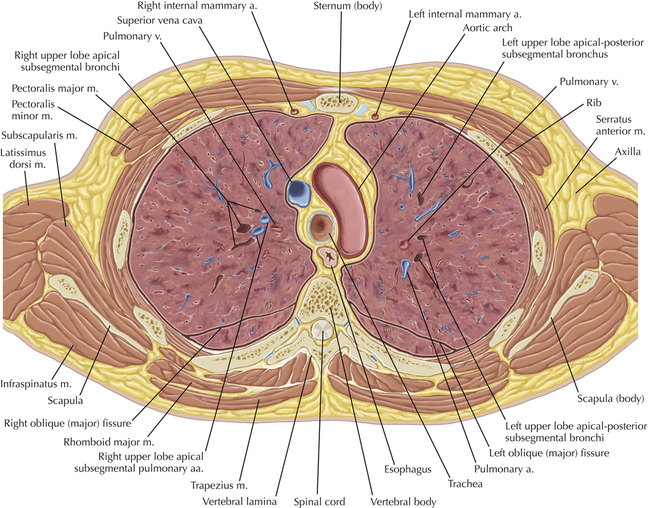
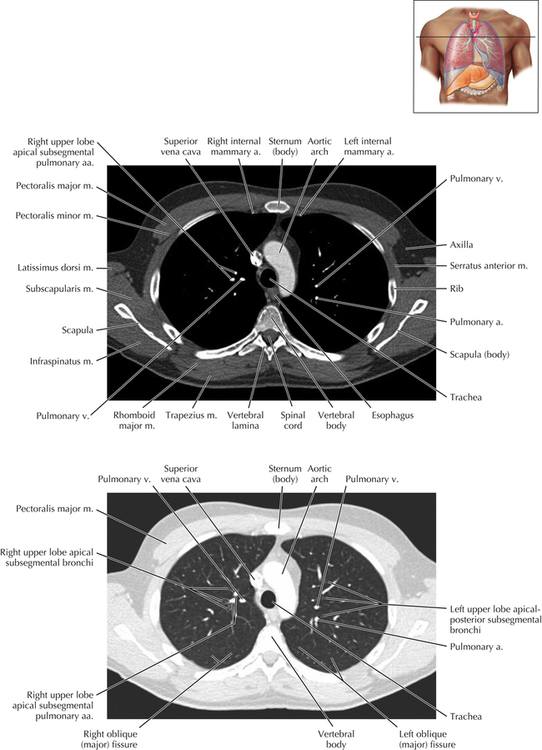
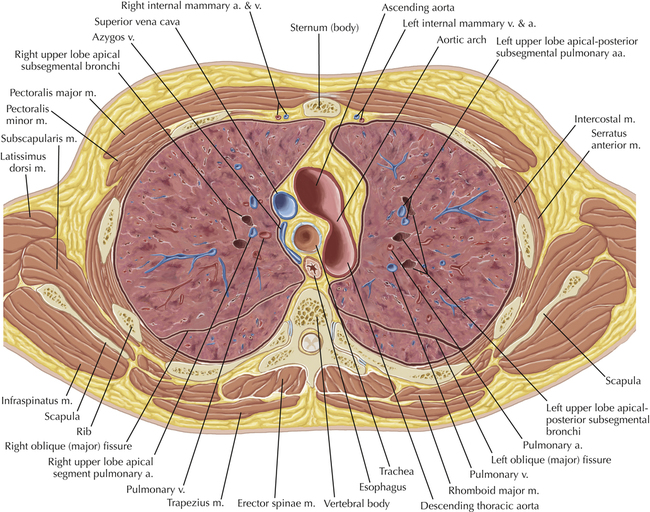
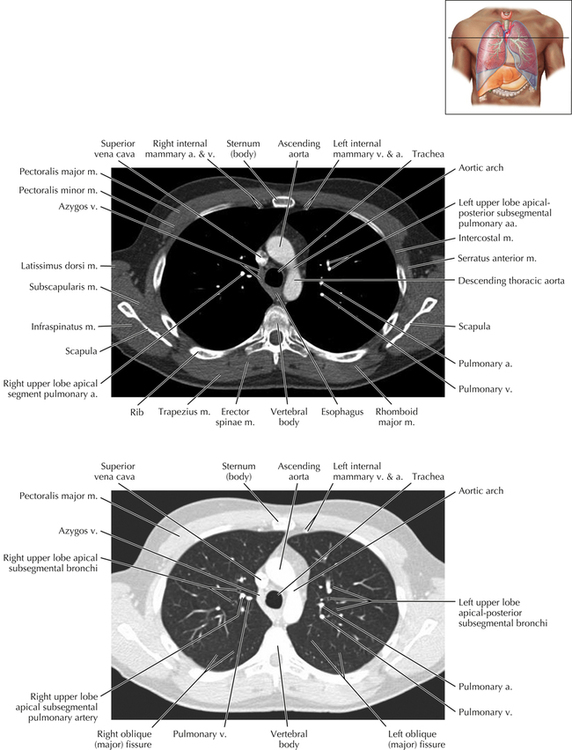
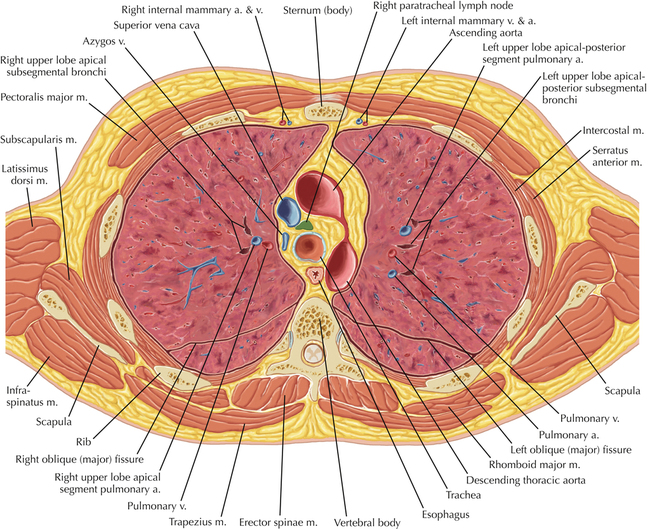
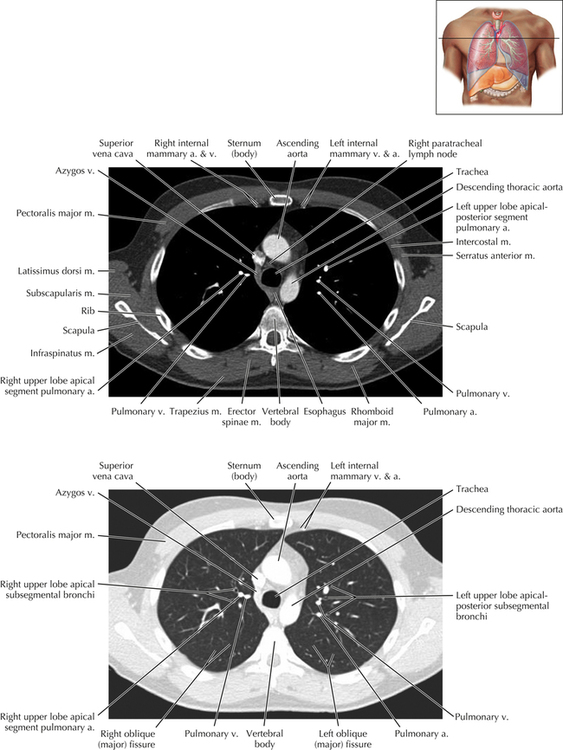
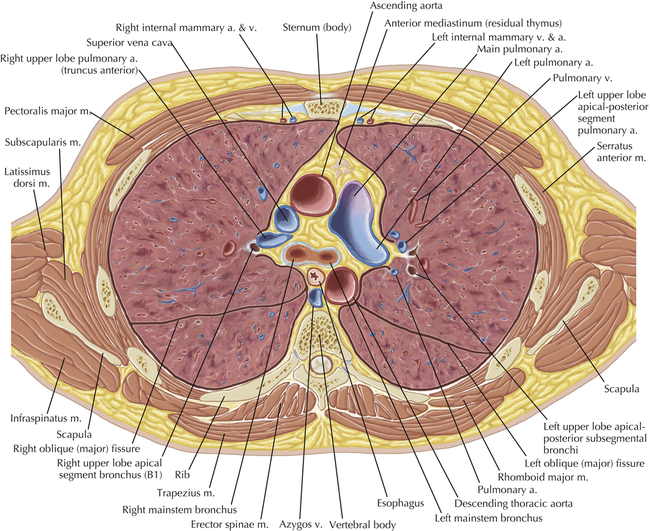
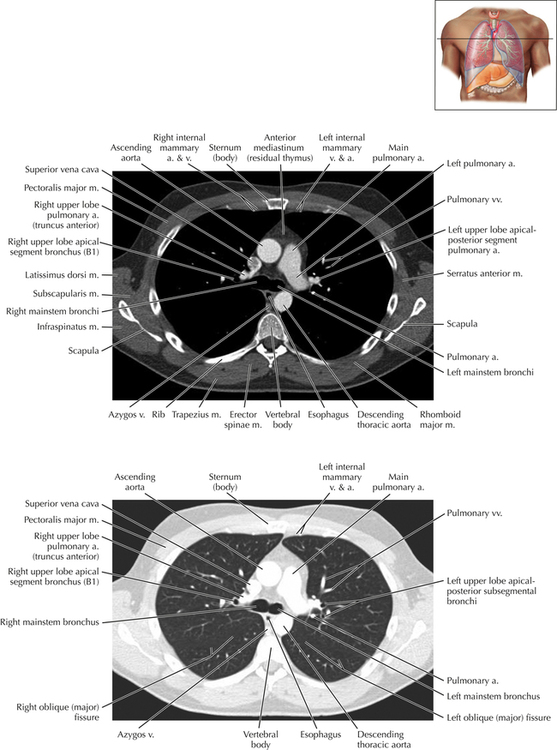
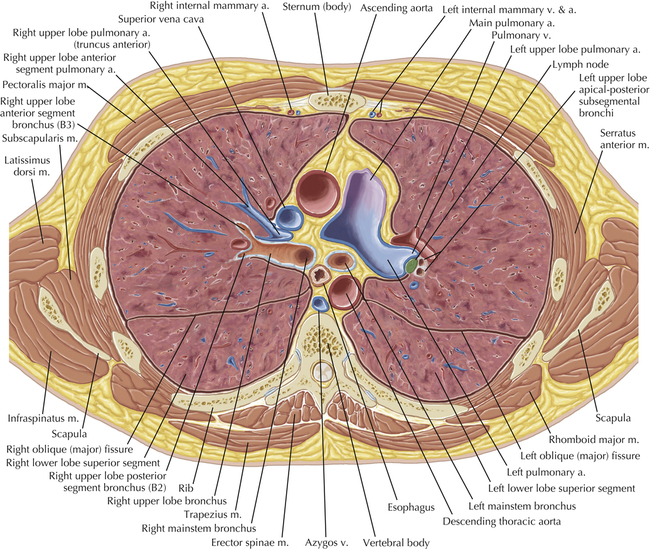
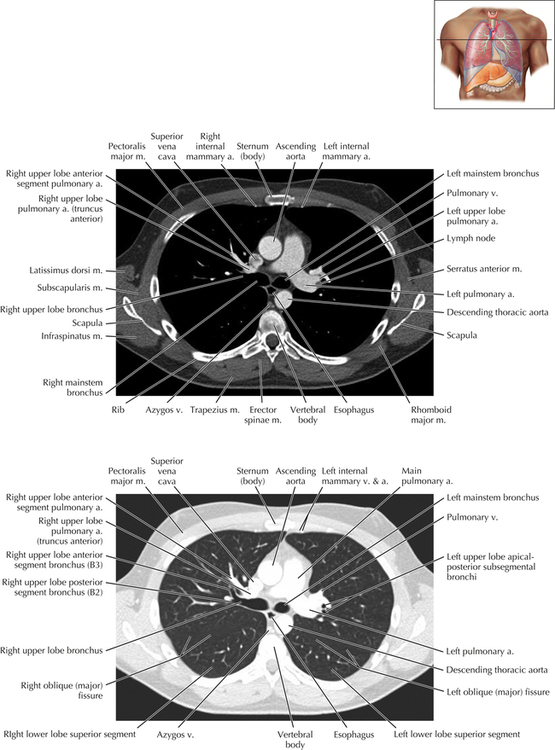
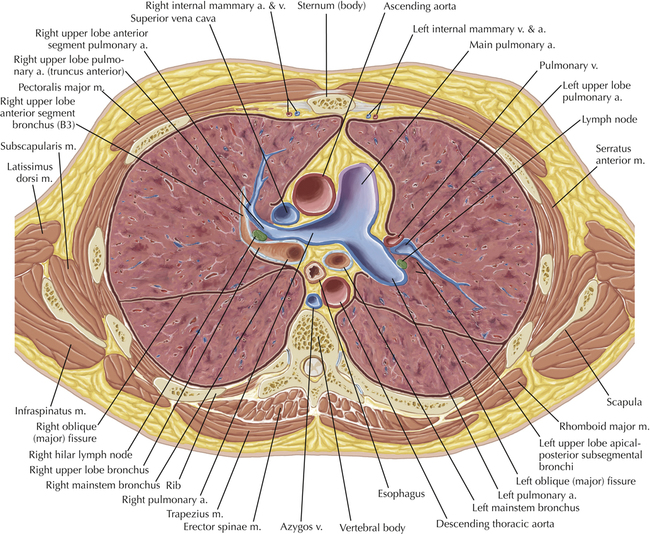
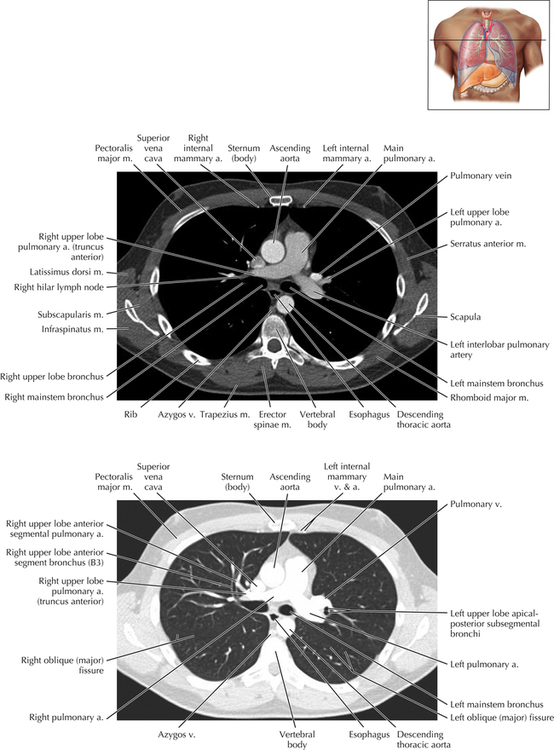
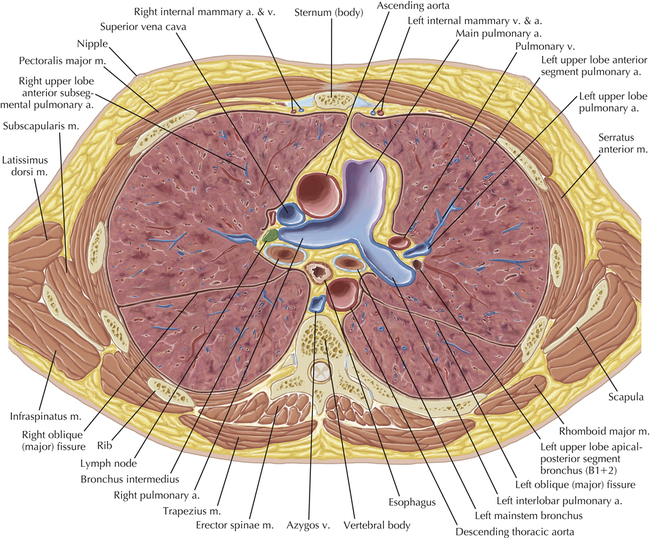
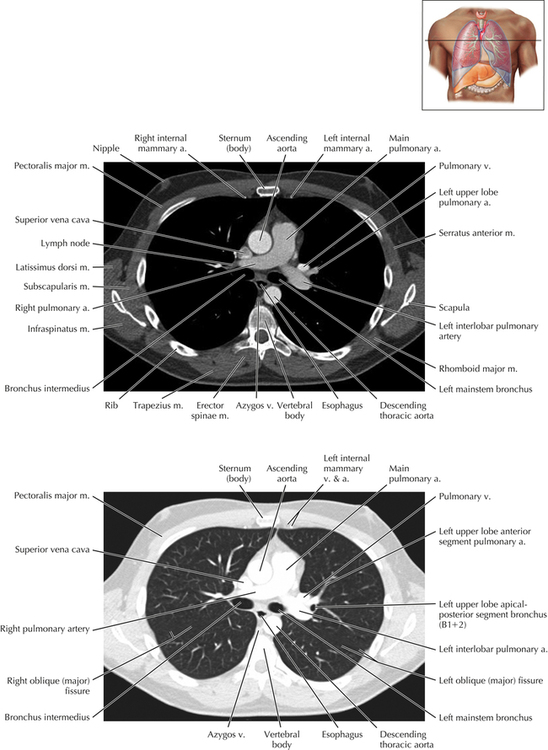
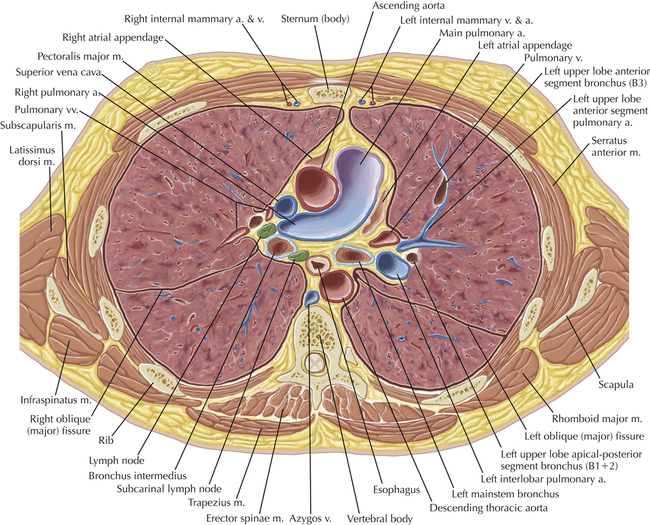
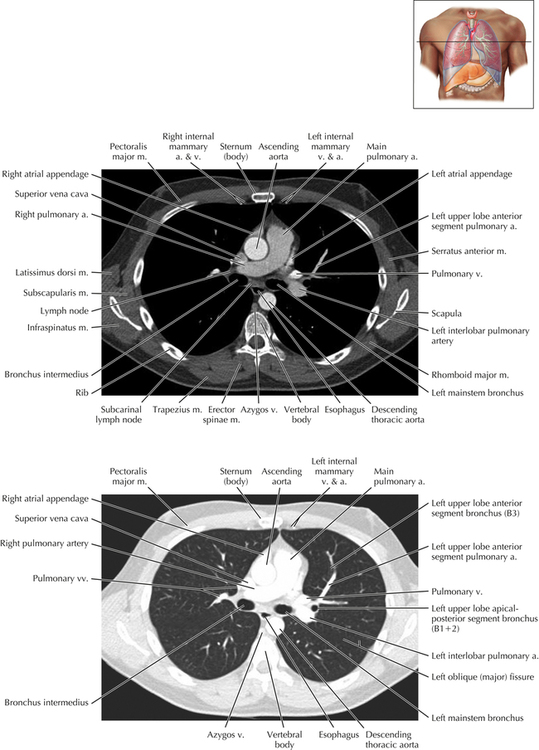
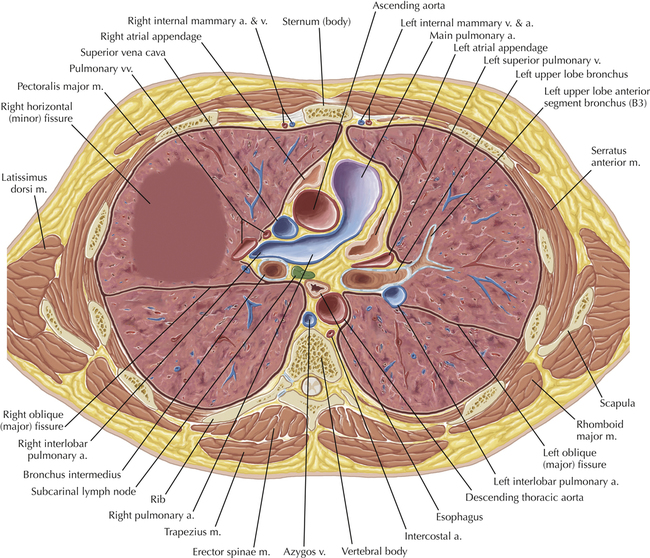
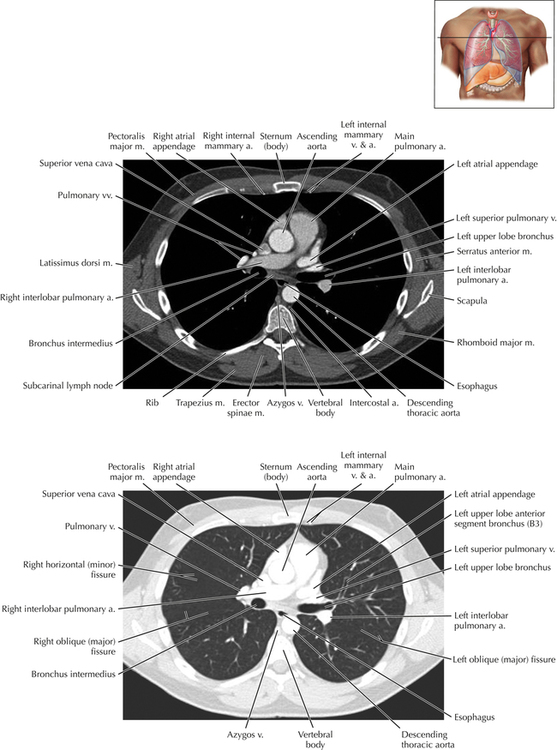
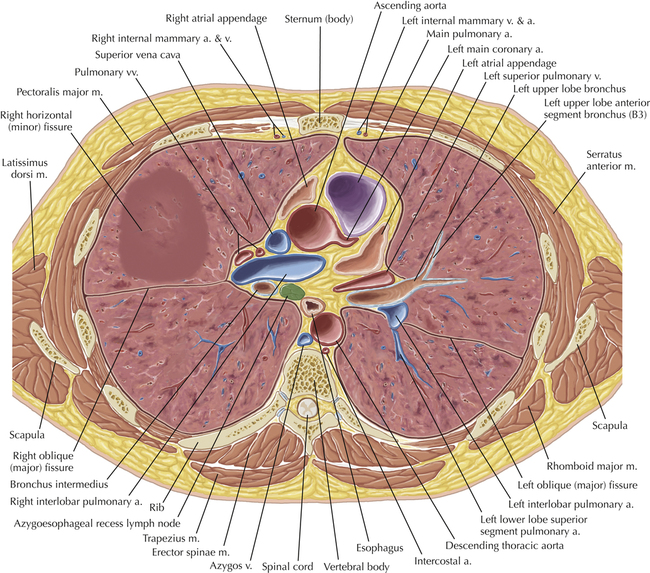
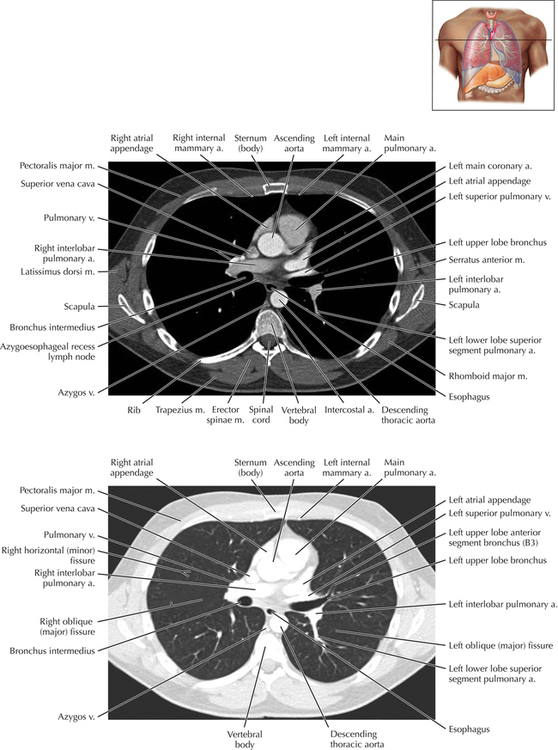
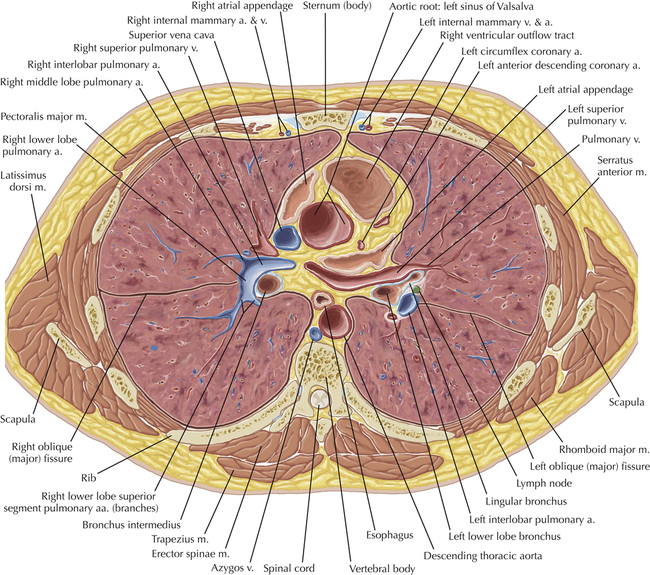
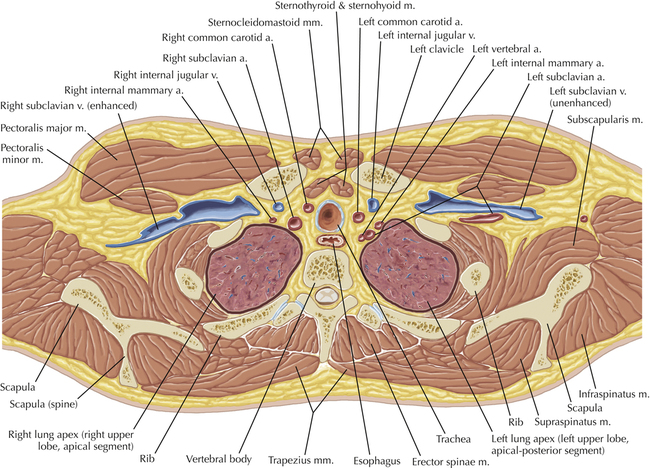
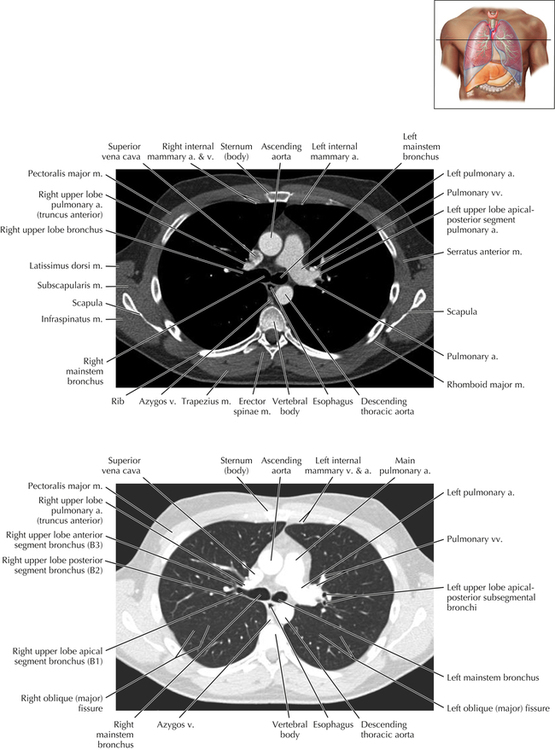
Chapter 2 Thoracic CT scans may be performed with or without the intravenous injection of iodinated contrast. Contrast-enhanced thoracic CT scanning is usually performed following injection into an upper extremity vein, with imaging started at 30 to 40 seconds after the injection is begun, depending on the specific application. In this patient, contrast was injected via the right upper extremity, resulting in dense enhancement of the right subclavian vein (and the right brachiocephalic vein on Axial 5 and subsequent images); the left subclavian vein (and left brachiocephalic vein on Axial 5 and subsequent images) remains unenhanced in this patient because imaging was begun before injected contrast had sufficient time to circulate throughout the body and reach the left subclavian vein. At this level, the segmental bronchi within the right upper lobe are now visible. Segmental bronchi are commonly named for the anatomic segment they supply (e.g., apical segment right upper lobe bronchus). Another nomenclature system for segmental bronchi may occasionally be encountered, as described by the Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology in Terminologia Anatomica. This terminology identifies the segmental bronchi according to numbers (e.g., B1 = apical segment right upper lobe bronchus, B1+2 = apical-posterior segment left upper lobe bronchus; see Axial 19). Both nomenclature systems are illustrated in this text. A number of variations in the branching pattern of the pulmonary arteries are recognized. In particular, variations in the branching pattern of the left upper lobe pulmonary artery are commonly encountered in clinical practice. In the most common pattern, the left upper lobe pulmonary artery gives rise to apical-posterior and anterior segmental branches in a manner analogous to the bronchial branching pattern. Less commonly, as in this patient, a posterior left upper lobe subsegmental artery arises directly from the left pulmonary artery. The left upper lobe pulmonary artery can be seen originating from the left pulmonary artery on Axials 17 and 18.
Thoracic Soft Tissue and Lung
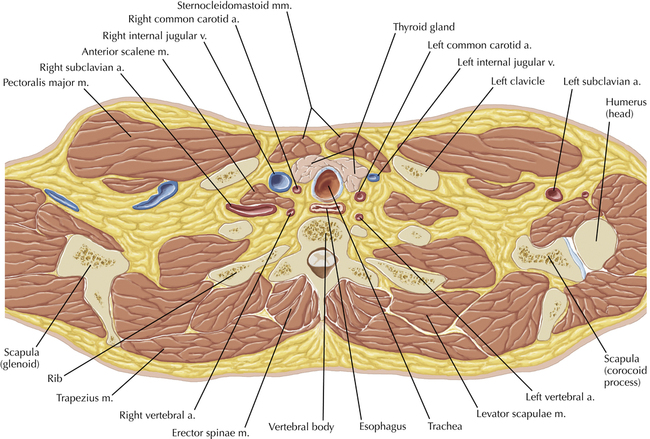
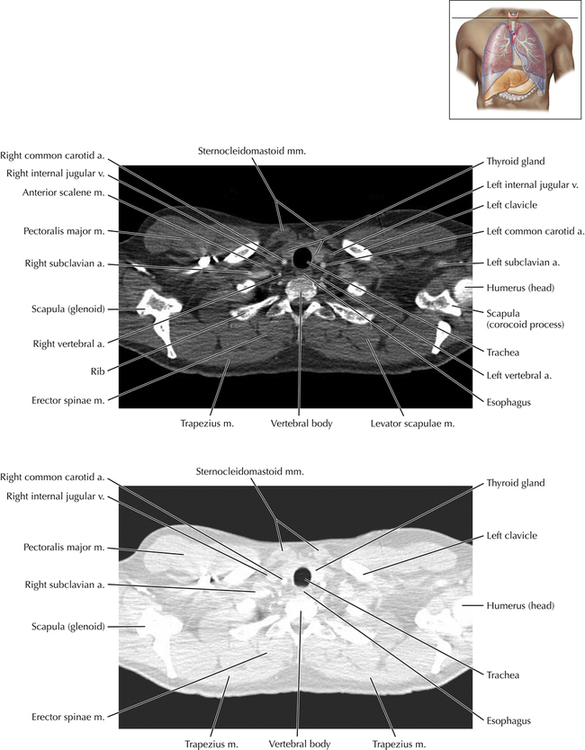
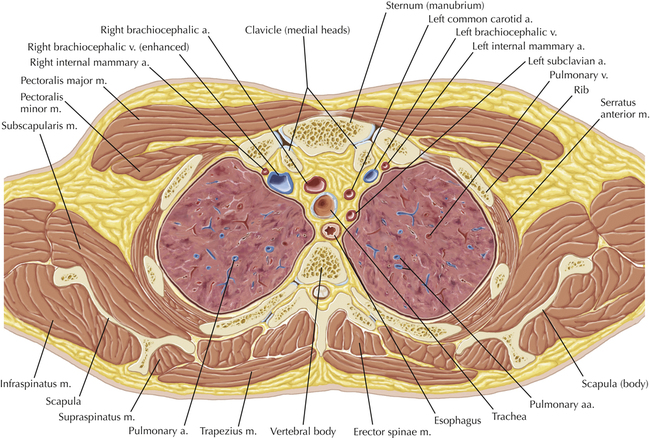
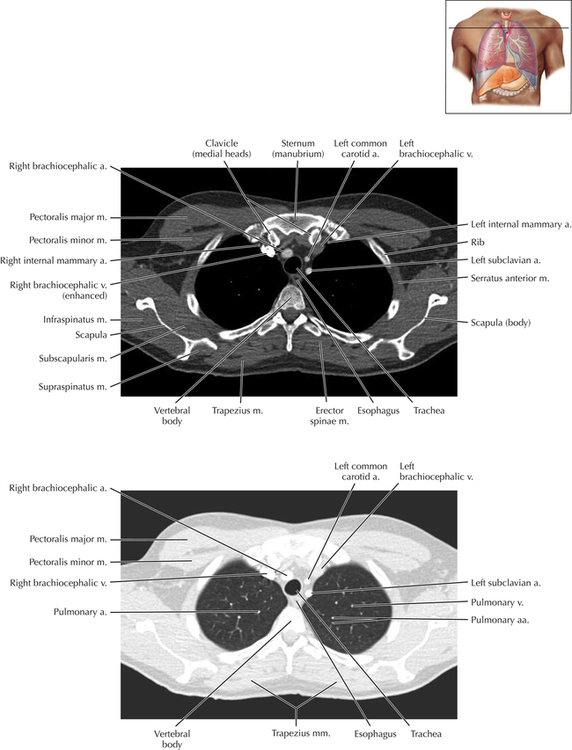
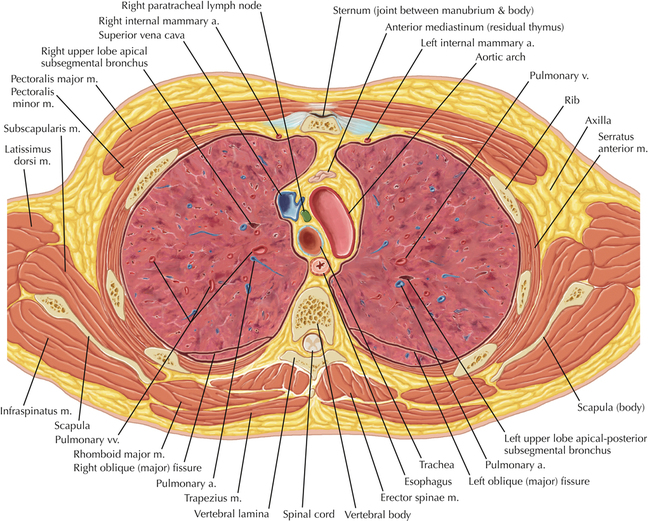
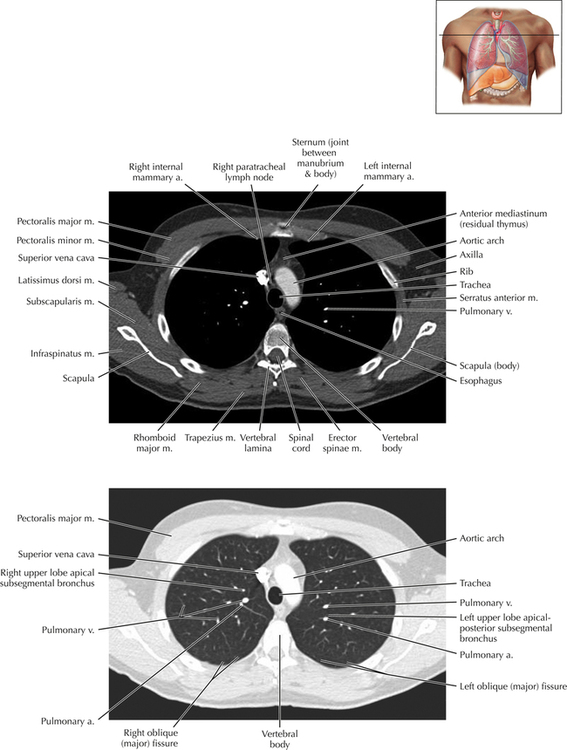
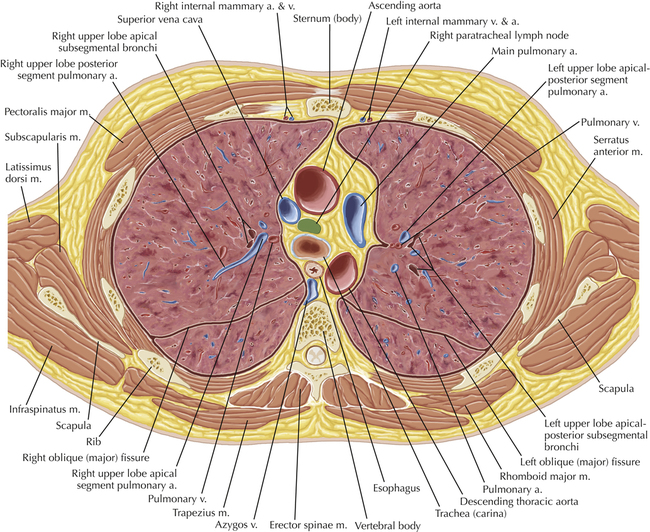
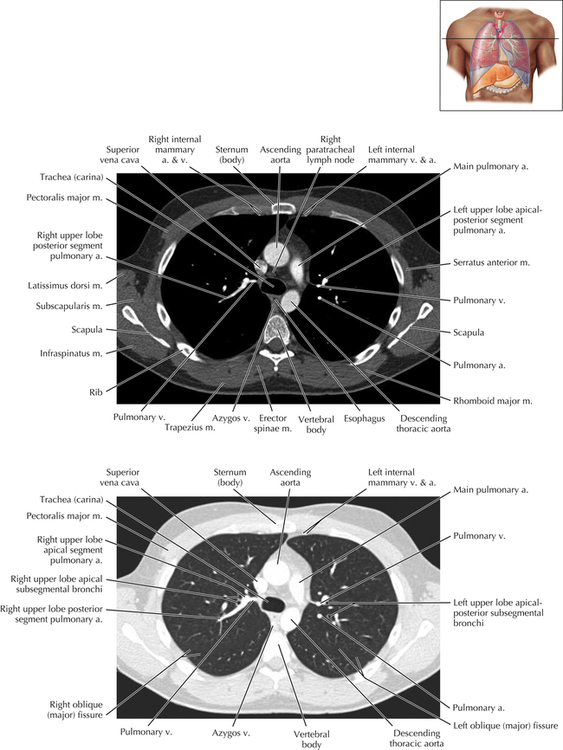
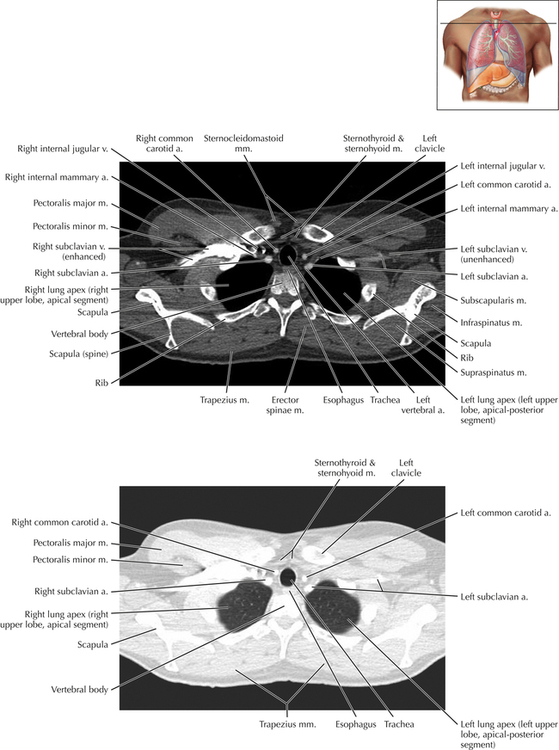
Soft Tissue and Lung Axial 3
Diagnostic Consideration
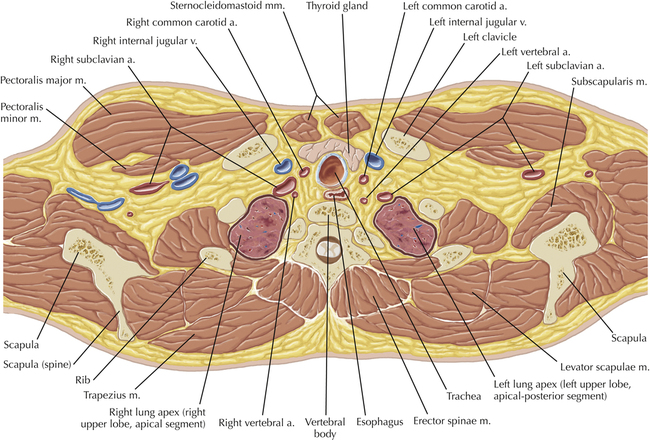
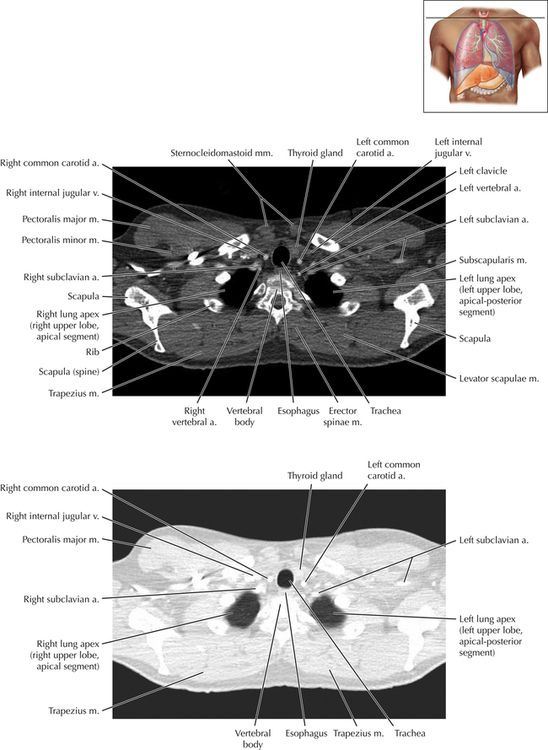
Soft Tissue and Lung Axial 16
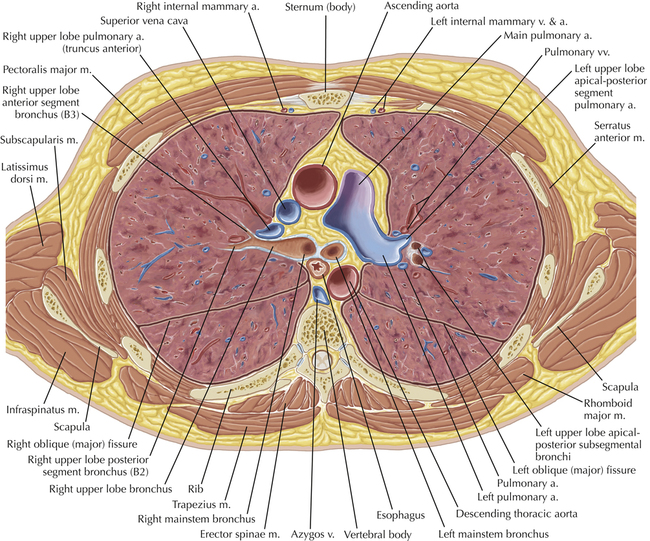
Normal Anatomy
Normal Variant
Thoracic Soft Tissue and Lung