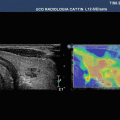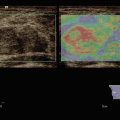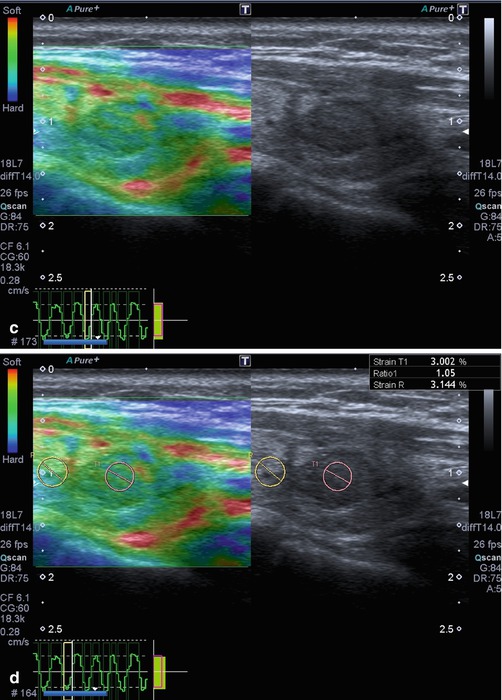
Fig. 7.1
Hyperplastic follicular lesion histologically proven. (a) At baseline ultrasound the lesion appears iso-hypoechoic with peripheral halo sign. (b1, b2) At power Doppler and at Advanced Dynamic Flow™ (ADF), the nodule shows pattern III. (c) Qualitative evaluation with SE shows score 1 by Itoh et al. and Rubaltelli et al. (d) At semiquantitative evaluation, nodule appears benign with a strain ratio of 1.05 under the cutoff value of 2.0

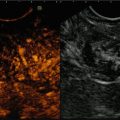
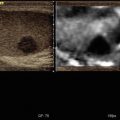
Fig. 7.2
Benign nodule at FNAC. Isoechoic nodule with halo sign which shows score 2 at qualitative evaluation


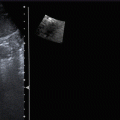
Fig. 7.3
Papillary carcinoma histologically proven. (a1, a2) Hypoechoic nodule with irregular margins and pattern I at color Doppler evaluation. (b) At qualitative evaluation the nodule appears hard

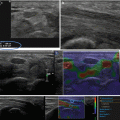
Fig. 7.4
Anaplastic carcinoma (histologically proven). (a) B-mode of the tumor revealed diffuse infiltration with cervical lymphadenopathy. (b) Elastography revealed stiff tissue

Fig. 7.5
Papillary carcinoma histologically proven. (a) Baseline ultrasound shows an isoechoic nodule with a partially continuous halo sign and pattern III at SMI evaluation. (b) At shear wave elastography, the lesion appears hard with high elasticity values. It was a carcinoma histologically proven

Fig. 7.6
Papillary carcinoma histologically proven. (a) Iso-hypoechoic nodule with high peri- and intranodular vascularization (pattern III). (b) At SSI the lesion presents mixed stiffness but high elasticity values expressed in m/s and k/Pa
References
1.
2.
3.
Remonti LR, Kramer CK, Leitao CB, Pinto LC, Gross JL. Thyroid ultrasound features and risk of carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Thyroid. 2015;25:538–50.CrossRefPubMedPubMedCentral
4.
5.
6.
Tramalloni J, Leger A, Correas JM, Monpeyssen H, Szwagier-Uzzan C, Helenon O, Moreau JF. Imaging of thyroid nodules. J Radiol. 1999;80:271–7.PubMed
7.
8.
Haugen BRM, Alexander EK, Bible KC, Doherty G, Mandel SJ, Nikiforov YE, Pacini F, Randolph G, Sawka A, Schlumberger M, Schuff KG, Sherman SI, Sosa JA, Steward D, Tuttle RMM, Wartofsky L. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid. 2015;26(1):1–133.CrossRef
9.
Ferraioli G, Filice C, Castera L, Choi BI, Sporea I, Wilson SR, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF, Amy D, Bamber JC, Barr R, Chou YH, Ding H, Farrokh A, Friedrich-Rust M, Hall TJ, Nakashima K, Nightingale KR, Palmeri ML, Schafer F, Shiina T, Suzuki S, Kudo M. WFUMB guidelines and recommendations for clinical use of ultrasound elastography: Part 3: liver. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2015;41:1161–79.CrossRefPubMed
10.
Tunbridge WM, Evered DC, Hall R, et al. The spectrum of thyroid disease in a community: the Whickham survey. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 1977;7(6):481–93.CrossRef
11.
12.
13.
Iannuccilli JD, Cronan JJ, Monchik JM. Risk for malignancy of thyroid nodules as assessed by sonographic criteria: the need for biopsy. J Ultrasound Med. 2004;23(11):1455–64.PubMed
14.
15.
16.
17.
18.
19.
20.
21.
22.
23.
24.
Ahuja AT. Lupmps and bumps in the head and neck. In: Ahuja AT, Evans R, editors. Practical head and neck ultrasound. London: Greenwich Medical Media Limited; 2000. p. 87–106.CrossRef
25.
Bhatia KS, Rasalkar DD, Lee YP, Wong KT, King AD, Yuen YH, Ahuja AT. Real-time qualitative ultrasound elastography of miscellaneous non-nodal neck masses: applications and limitations. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2010;36:1644–52.CrossRefPubMed
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree