KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Occlusion of transplant renal artery secondary to thrombus
Imaging
- •
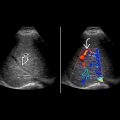
Edematous hypoechoic kidney if total thrombosis
- •
Absence of blood flow in main renal artery
- •
Diffuse absence of parenchymal perfusion on color or power Doppler
- •
Blunted low-resistance waveforms in ischemic areas from collateral flow
- •
If involving accessory renal artery
- ○
Segmental wedge-shaped peripheral area of decreased color flow and altered echogenicity
- ○
- •
Color, power, spectral Doppler US 1st-line imaging modality for complications of renal transplantation
- •
Optimize color and spectral Doppler settings for slow flow
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Transplant renal vein thrombosis
- •
Acute rejection/acute on chronic rejection
- •
Hyperacute rejection
Clinical Issues
- •
Rare (< 1%)
- •
Abrupt onset of oliguria, decreased function, pain and swelling of allograft
- •
Poor prognosis; graft loss typical when single main artery thrombosed
- ○
Transplant nephrectomy
- ○
Thrombectomy or thrombolysis rarely successful unless diagnosis made early
- ○
- •
Accessory or segmental arterial thrombosis → ischemia and subsequent atrophy
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Severe acute rejection or tubular necrosis may cause propagating small vessel thrombosis resulting in infarction and mimicking transplant renal artery thrombosis
- •
Urgent finding requiring prompt communication