| SKULL BASE REGION | Cerebellopontine angle |
| HISTOPATHOLOGY | Diagnosis based on neuroimaging only |
| PRIOR SURGICAL RESECTION | No |
| PERTINENT LABORATORY FINDINGS | N/A |
Case description
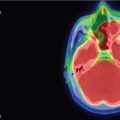
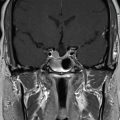
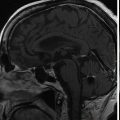
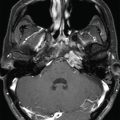
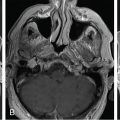
The patient is a 36-year-old patient who presented with a 2-month history of diplopia. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a lesion compatible with a fourth nerve schwannoma. Clinical follow-up demonstrated worsening diplopia, and repeat MRI showed volumetric growth of the lesion ( Figure 7.35.1 ). Upfront Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKR) was performed to prevent tumor growth and stabilize/improve the neurological signs ( Figure 7.35.2 ).
| Radiosurgery Machine | Gamma Knife – Icon |
| Radiosurgery Dose (Gy) | 12, at the 70% isodose line |
| Biologically Effective Dose (Gy) | 67.8 Gy |
| Number of Fractions | 1 |

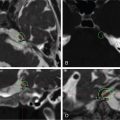
Axial T1-gadolinium injected MRI showing a small lesion compatible with a fourth nerve schwannoma that was clinically symptomatic.

From left to right: Axial T1 injected and T2 CISS/Fiesta MRI fused with bone CT. Dosimetry is colored yellow and corresponds to the 12-Gy marginal dose prescription.
| Critical Structure | Dose Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Brainstem | Marginal dose is 12 Gy, although there is slight contact with the brainstem; the risk of adverse radiation events (AREs) at the brainstem level remains virtually zero. |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree