KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Monochorionic (MC) twin complication caused by intrauterine transfusion of blood from donor twin to recipient twin via arteriovenous placental anastomoses
Imaging
- •
Hallmark finding is oligohydramnios in 1 sac + polyhydramnios in other of diamniotic pair (difficult diagnosis in monoamniotic twins)
- •
Donor has oligohydramnios defined as maximum vertical pocket (MVP) ≤ 2 cm
- ○
“Stuck twin” describes severe oligohydramnios with donor twin “shrink-wrapped” to uterine wall
- ○
Cocooning describes severe oligohydramnios where donor twin, in tight cocoon of membranes, is suspended within pool of fluid from recipient twin
- ○
- •
Recipient has polyhydramnios defined as MVP ≥ 8 cm at < 20 weeks, > 10 cm at > 20 weeks
- •
Discordant twin growth not mandatory feature
Scanning Tips
- •
Establish chorionicity and amnionicity in all multiple gestations in 1st trimester
- •
All MC twins need growth monthly with fluid/bladder check every 2 weeks from 16 weeks gestation
- •
Check movement of any twin near uterine wall
- ○
“Stuck” or cocooned twin cannot extend extremities or change position
- ○
Change maternal position
- ○
Use high-resolution transducer to identify thin membrane reflected off head or between extremities
- ○
- •
Stage twin-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) when seen
- ○
Stage 1: Oligohydramnios/polyhydramnios
- ○
Stage 2: + absent bladder in donor
- ○
Stage 3: + abnormal umbilical artery Doppler with either absent (AEDF) or reversed end diastolic flow (REDF)
- ○
Stage 4: + hydrops
- ○
Stage 5: + demise of 1 twin
- ○
 of deoxygenated blood from the oligemic, poorly grown donor
of deoxygenated blood from the oligemic, poorly grown donor  with oligohydramnios to the hypervolemic recipient
with oligohydramnios to the hypervolemic recipient  with polyhydramnios.
with polyhydramnios.
 . A difference of > 4 cm between maximum vertical pockets is concerning for developing TTTS. The combination of oligohydramnios (< 2 cm) and polyhydramnios (> 8 cm) is diagnostic.
. A difference of > 4 cm between maximum vertical pockets is concerning for developing TTTS. The combination of oligohydramnios (< 2 cm) and polyhydramnios (> 8 cm) is diagnostic.
 . The membrane is no longer visible because it is “shrink-wrapped” around the donor twin
. The membrane is no longer visible because it is “shrink-wrapped” around the donor twin  , which was unable to move at all while the recipient twin was very active.
, which was unable to move at all while the recipient twin was very active.
 and confirmed development of oligohydramnios (red x) and polyhydramnios (white x). The patient was referred for laser therapy. Unfortunately, her membranes ruptured a week after treatment.
and confirmed development of oligohydramnios (red x) and polyhydramnios (white x). The patient was referred for laser therapy. Unfortunately, her membranes ruptured a week after treatment.
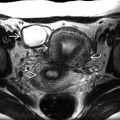
 (recipient twin not included in image) and the “antigravity” appearance of the donor twin
(recipient twin not included in image) and the “antigravity” appearance of the donor twin  stuck to the anterior uterus. Use a high-resolution linear transducer to look for the membrane in this situation.
stuck to the anterior uterus. Use a high-resolution linear transducer to look for the membrane in this situation.
 are visible wrapped in a membrane sling
are visible wrapped in a membrane sling  that reflects back to the uterine wall
that reflects back to the uterine wall  . The donor, suspended by and cocooned in the sling, floats in the large pool of the recipient’s fluid.
. The donor, suspended by and cocooned in the sling, floats in the large pool of the recipient’s fluid.
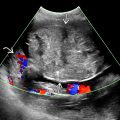
 or reversed
or reversed  end diastolic flow and pulsatile umbilical vein flow
end diastolic flow and pulsatile umbilical vein flow  . The recipient (B) has normal cord flow. This is stage 3 TTTS.
. The recipient (B) has normal cord flow. This is stage 3 TTTS.