U
ulcer an erosion or loss of continuity of the skin or mucous membrane.
ulcerative associated with or of the nature of an ulcer.
ulcerative colitis superficial inflammatory condition affecting the colon. It always involves the rectum and spreads continuously for a variable distance. Long-standing disease predisposes to colorectal cancer.
ulna the inner bone of the forearm.
ulnar associated with the ulna as in artery, vein and nerve.
ultrasonic relating to mechanical vibrations of very high frequency.
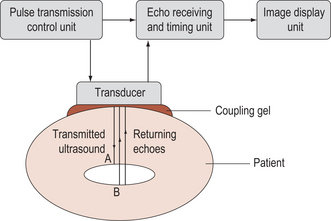
ultrasonography formation of a visible image from the use of ultrasound. A controlled beam of sound is directed into the relevant part of the body. The reflected ultrasound is used to build up an electronic image of the various structures of the body. Routinely offered during pregnancy to monitor progress and detect fetal and placental abnormalities. See also ultrasound, diagnostic ultrasonography, real-time ultrasonography.
ultrasound sound waves with a frequency of over 20000 Hertz, not audible to the human ear.
ultraviolet rays (UV) short wavelength electromagnetic rays outside the visible spectrum.
umbilical cord the cord connecting the fetus to the placenta. It contains a vein and two arteries.
umbilical hernia (omphalocele) protrusion of a portion of intestine through the area of the umbilical scar.
umbilicus (navel) the abdominal scar left by the separation of the umbilical cord after birth.
unconscious incapable of responding to sensory stimuli. That part of mental activity concealed from the consciousness by the psychological sensor.
undescended testis the testis remains within the bony pelvis or inguinal canal. See also cryptorchism.
uniaxial joint a joint with movement round one axis only, for example, flexion and extension.
unicellular consisting of only one cell.
uniformity the variations in count rate detected by a gamma camera when it is exposed to a regular source of gamma rays emitted from a radionuclide.
unilateral relating to or on one side only.
unit cost an average cost for a specific activity, for example, a surgical procedure, or a home visit. It is calculated by dividing the total cost of the service by the number of outputs.
univariate statistics descriptive statistics that analyse one variable, such as frequency distributions.
unrelated the whole groups of data are roughly matched but the individual samples are not.
unsharpness blurring on a radiograph (photographic unsharpness) which can be caused by movement unsharpness, screen unsharpness and/or geometric unsharpness.
upgrade an improvement to a computer system which allows the most recent information to be added to a programme.
upper motor neuron the cell is in the motor cortex and the axon terminates in the anterior horn of the spinal cord.
upper respiratory tract infection (URTI)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree