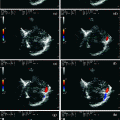
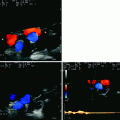
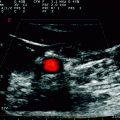
Fig. 6.1
Power-mode TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane (mesencephalic plane). The ipsilateral basal vein of Rosenthal is sampled in the pre-peduncular segment, with flow direction toward the probe
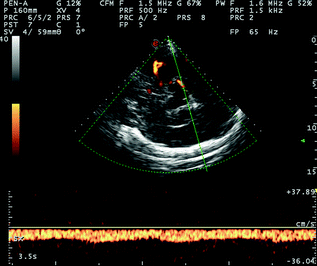
Fig. 6.2
TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane (diencephalic plane) in power mode. The ipsilateral BVR is sampled in the post-peduncular segment, with flow direction away from the probe, like the P3 PCA segment which was co-sampled
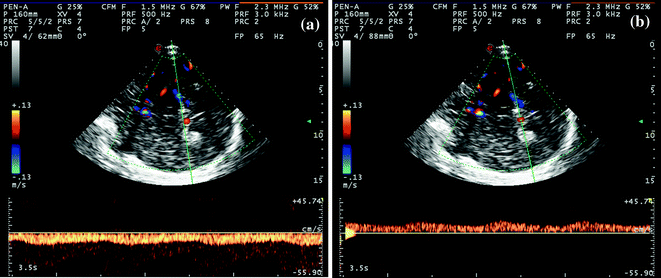
Fig. 6.3
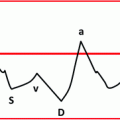
a, b TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane (diencephalic plane) in color mode. In picture (a), the ipsilateral BVR is sampled in the post-peduncular segment, with flow direction away from the probe, like the P3 PCA segment, co-sampled. In picture (b), the contralateral post-peduncular BVR is sampled, with flow direction toward the probe as expected. The flow waveform shows an evident pulsatility; the systolic to diastolic range is lower compared to arterial waveform
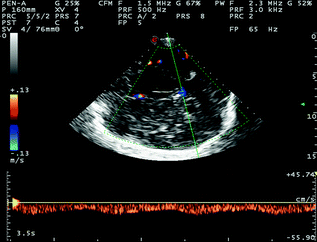
Fig. 6.4
TCCS from temporal widow in axial scanning plane (diencephalic plane) in color mode. Behind the hyperechoic image of the pineal gland, the GV is sampled, with flow direction away from the probe and a Doppler waveform similar to the previous one observed on the BVR
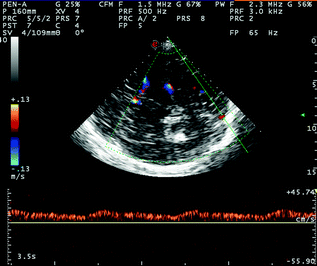
Fig. 6.5
TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane (low diencephalic plane) in color mode. The post-peduncular BVR (yellow asterisk) and the posterior segment of the SSS (green asterisk) are imaged. The SSS has a flow direction toward the probe and a Doppler waveform similar to the previous one of the BVR
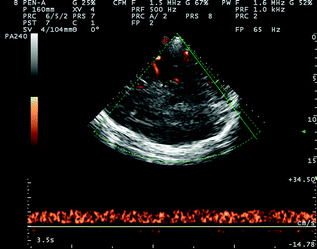
Fig. 6.6
TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane in power mode. The post-peduncular BVR (yellow asterisk) and the posterior segment of the SSS (green asterisk) are imaged. The SSS has a flow direction toward the probe and a Doppler waveform similar to the previous one of the BVR
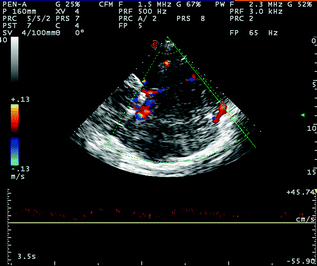
Fig. 6.7
TCCS from temporal widow in axial scanning plane in color mode; posterior cranial fossa approach for the insonation of the proximal segment of the ipsilateral TS, sampled near the confluens of sinuses. See the following detailed image for the parenchymal landmarks
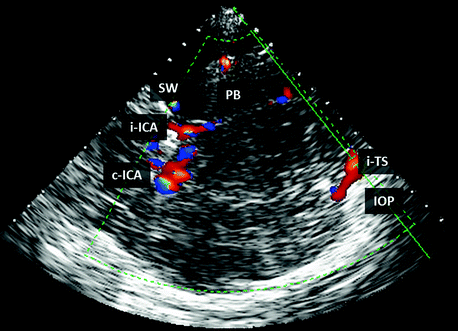
Fig. 6.8
TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane in color mode; posterior cranial fossa approach for the insonation of the proximal segment of the ipsilateral TS. The following structures are imaged: i-ICA ipsilateral internal carotid artery. C-ICA contralateral internal carotid artery. IOP internal occipital protuberance. PB edge of the ipsilateral petrous bone. SW edge of the ipsilateral sphenoid wing. i-TS ipsilateral transverse sinus
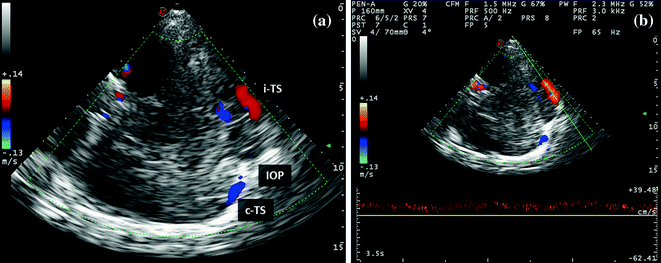
Fig. 6.9
a, b TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane in color mode. This is an extreme approach for insonating the middle segment of the ipsilateral TS (red arrow) (picture a), whose Doppler waveform is imaged in picture (b)
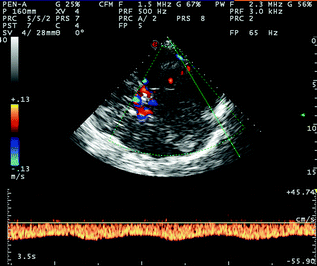
Fig. 6.10
TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane in color mode; posterior cranial fossa approach for the insonation of the distal segment of the ipsilateral TS, sampled near the confluence of the superior petrous sinus (SPS). The insonation plane is slightly more angled than the plane used for the insonation of the proximal segment of the ipsilateral TS, and the approach is in an oblique pontine plane. See the following detailed image for the parenchymal landmarks
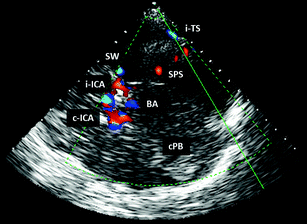
Fig. 6.11
TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane in color mode; posterior cranial fossa approach for the insonation of the distal segment of the ipsilateral TS. The following structures are imaged: i-ICA Ipsilateral internal carotid artery. C-ICA contralateral internal carotid artery. BA basilar artery. cPB edge of the contralateral petrous bone. SW edge of the ipsilateral sphenoid wing. SPS superior petrous sinus. i-TS ipsilateral transverse sinus
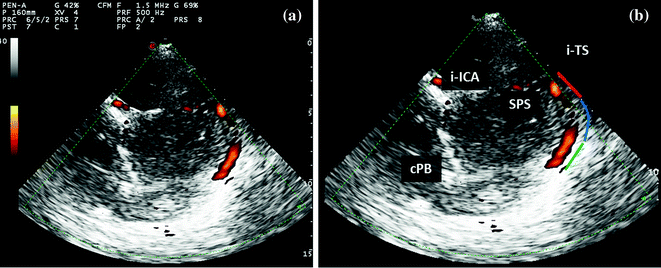
Fig. 6.12
TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane in power mode; extreme posterior cranial fossa approach for the insonation of the ipsilateral TS. The following structures are imaged: i-ICA Ipsilateral internal carotid artery. cPB edge of the contralateral petrous bone. SPS superior petrous sinus. i-TS ipsilateral transverse sinus. The ipsilateral transverse sinus is imaged along its entire course, allowing to distinguish: (1) proximal segment, (2) middle segment, (3) distal segment
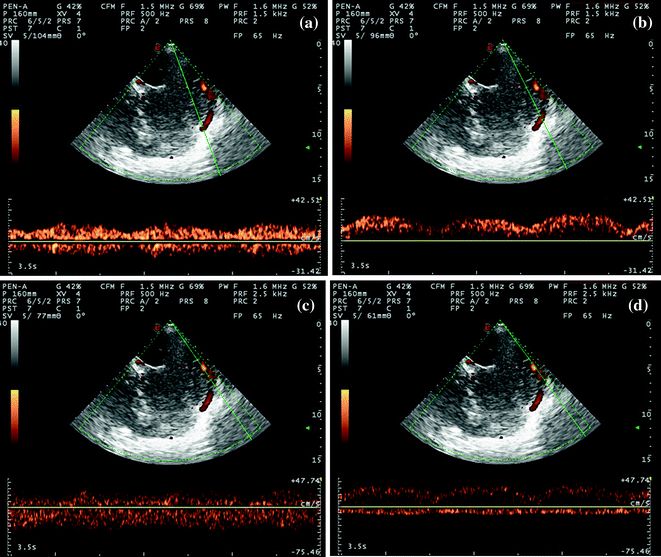
Fig. 6.13
TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane in power mode; extreme posterior cranial fossa approach for the insonation of the ipsilateral TS. From top to bottom, the following segments are sampled with Doppler signal. a Confluens of sinuses with bidirectional flow. b Proximal segment of TS, with a flow directed toward the probe. c A middle segment with a bidirectional flow and a curved course. d A distal segment with a clearer flow directed away from the probe
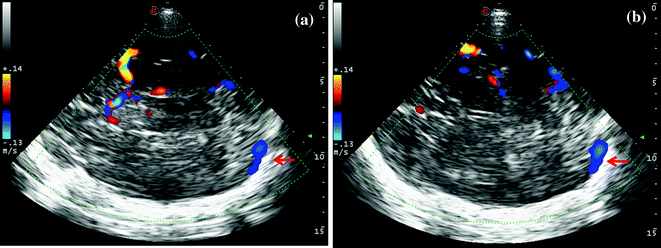
Fig. 6.14




a, b TCCS from temporal window in axial scanning plane in color mode. The picture illustrates the most used approach for insonating the contralateral TS, starting from a mesencephalic plane with the anterior visualization of M1 MCA course up to the M1–M2 passage and the posterior appearance of the color-coded signal of the contralateral TS along the skull (picture a). The posterior persistence of the contralateral TS (picture b) can be displayed by means of a slight tilting of the probe to the diencephalic approach in order to visualize M2 MCA anteriorly. The TS is indicated by the red arrow. In the following figures, parenchymal landmarks are more detailed
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree