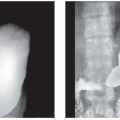
Umbilical Hernia
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Amir A. Borhani, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Protrusion of abdominal contents (omental fat ± bowel) into or through anterior abdominal wall via umbilical ring
Congenital: Diagnosed in infancy
Acquired: Develops in later life
Imaging
Midline; usually in upper 1/2 of umbilicus
Size varies, usually small
CECT best imaging tool
Multiplanar views can offer additional information
Useful to evaluate possible bowel obstruction
Top Differential Diagnoses
Omphalocele
Congenital defect in abdominal wall at umbilicus, evident at birth or in utero
Ventral hernia
Epigastric and hypogastric hernias develop above and below umbilicus, respectively
Incisional hernias: Through prior incision site
Spigelian hernia
Hernia protruding between linea semilunaris and lateral edge of rectus muscle
Pathology
Usually secondary to ↑ intraabdominal pressure: Obesity, multiple pregnancy, ascites, etc.
Cirrhosis with tense ascites is a common cause