KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Presence of 2 separate pelvicalyceal collecting systems draining 1 kidney, which may join above bladder (partial), drain into bladder separately (complete), or beyond bladder
Imaging
- •
Asymmetric renal enlargement, 20% are bilateral
- •
2 central echogenic renal sinuses with intervening bridging renal parenchyma
- •
2 distinct renal pelves or 2 exiting ureters in single kidney
- •
Weigert-Meyer rule: Upper moiety ureter inserts inferior and medial to lower moiety ureter
- ○
Upper pole tends to obstruct
- ○
Lower pole tends to have vesicoureteral reflux
- ○
- •
Look for ureterocele (cystic structure) in bladder
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Column of Bertin
- •
Segmental multicystic dysplastic kidney
- •
Hydrosalpinx (dilated ureter in pelvis)
Pathology
- •
Abnormal bifurcation of ureteral bud
- •
Increased incidence of ureteropelvic obstruction; genital anomalies found in 50% of affected females
Clinical Issues
- •
Symptoms include infection from reflux/stasis, hematuria, abdominal/flank pain from obstruction or calculi
- •
Most often diagnosed on antenatal ultrasound or as incidental postnatal finding
- •
Longstanding obstruction, reflux and infection can lead to secondary hypertension and renal insufficiency/failure
- •
Ectopic insertion in females: Incontinence due to insertion below bladder sphincter
- •
Ectopic insertion in males: Prostatitis, epididymitis
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Young females with recurrent urinary tract infections
- •
US, IVP or CT/MR urography are imaging modalities of choice
- •
VCUG to exclude reflux
Scanning Tips
- •
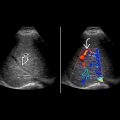
Color Doppler can be useful to distinguish collecting system from vessel in renal pelvis
- •
Ureteral jets can be helpful to identify vesicoureteral junction of both upper and lower moieties
 with hydroureter draining into a ureterocele
with hydroureter draining into a ureterocele  . Note the upper moiety ureter inserts inferior and medial to lower moiety ureter
. Note the upper moiety ureter inserts inferior and medial to lower moiety ureter  .
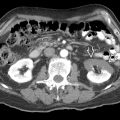
.
 , separated by intervening bridging renal tissue.
, separated by intervening bridging renal tissue.
 , reflecting a dilated upper moiety of a duplex kidney. The lower pole
, reflecting a dilated upper moiety of a duplex kidney. The lower pole  was normal.
was normal.
 with dilatation of the lower moiety
with dilatation of the lower moiety  , secondary to reflux.
, secondary to reflux.
 compatible with duplication. The upper moiety is hydronephrotic
compatible with duplication. The upper moiety is hydronephrotic  and the lower moiety is also mildly dilated
and the lower moiety is also mildly dilated  , secondary to vesicoureteral reflux.
, secondary to vesicoureteral reflux.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree