KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Strict definition: Ureter not inserting into bladder trigone
- •
Common usage: Ureter terminating outside bladder
Imaging
- •
70-80% have complete ureteral duplication, 5-17% bilateral
- •
Intravesicular insertion
- ○
Weigert-Meyer rule: Upper moiety ureter inserts inferior and medial to lower moiety ureter, upper renal moiety obstructs
- ○
Lower moiety tends to have vesicoureteral reflux
- ○
Ureterocele may be present if ectopic vesicular insertion
- ○
- •
Orifice commonly stenotic, leading to obstruction of renal moiety
- •
Extravesicular insertion
- ○
Dilated ureter extends beyond bladder
- ○
Males: Prostatic urethra most common insertion site
- ○
Females: Vestibule or urethra most commonly
- ○
- •
Transrectal/transvaginal US may delineate site of insertion
- •
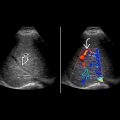
Compare normal position of contralateral ureteral jet at interureteric bar
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Bladder diverticulum, urachal cyst, or diverticulum
- •
Hydrosalpinx
- •
Seminal vesicle, müllerian, ejaculatory duct, utricular cysts
Pathology
- •
Failure of separation of ureteral bud from wolffian duct results in caudal ectopia
- •
Associated anomalies
- ○
Hypoplasia or dysplasia of renal moiety drained by ectopic ureter
- ○
Urethral duplication, hypospadias, cloacal abnormalities
- ○
VACTERL spectrum, including imperforate anus, tracheoesophageal fistula
- ○
Clinical Issues
- •
M:F = 1:6; predominantly duplicated systems in females (80%) vs. single systems in males
- •
Recurrent or chronic urinary tract infections, dribbling urinary incontinence in females, chronic or recurrent epididymitis in males
- •
Females: Continuous dribbling (50%) due to insertion below external sphincter
- •
Females: 80% of ectopic ureters are duplicated systems
- •
Males: Majority associated with single system ectopic ureter
- •
Males: No incontinence due to insertion above external sphincter
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Consider diagnosis in female with continuous dribbling urinary incontinence
Scanning Tips
- •
Trace dilated ureter to its termination below bladder
- •
Ureteral jet can be used to identify ectopic intravesicular insertion

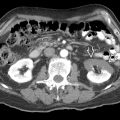
 , which did not insert into the trigone of the bladder. There is mild urothelial thickening
, which did not insert into the trigone of the bladder. There is mild urothelial thickening  .
.