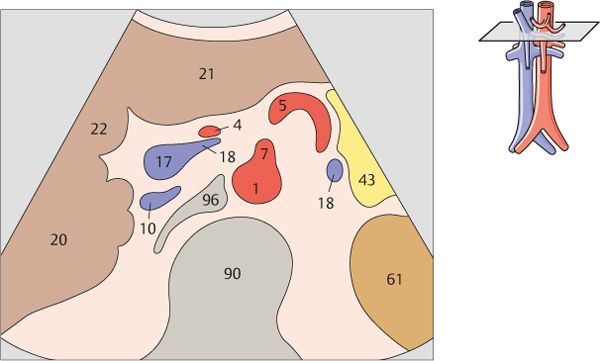
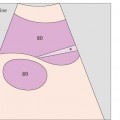
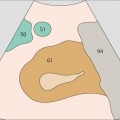
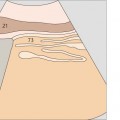
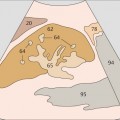
1 Passage of aorta and vena cava through diaphragm
2 Left gastric artery
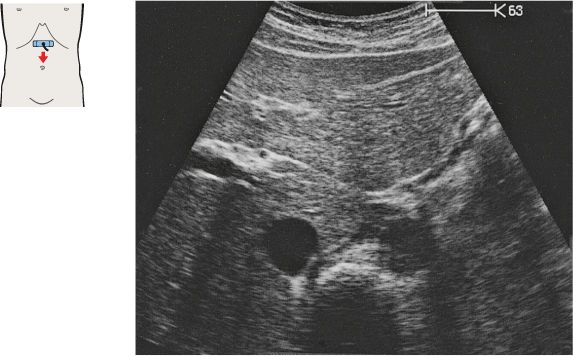
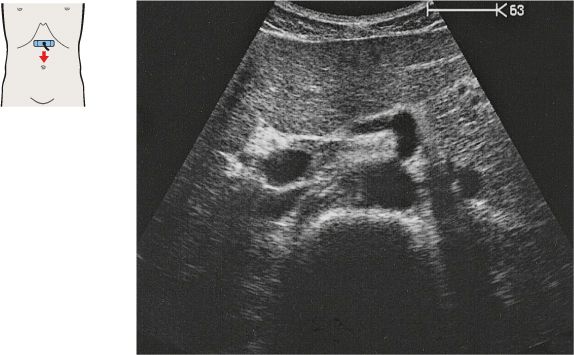
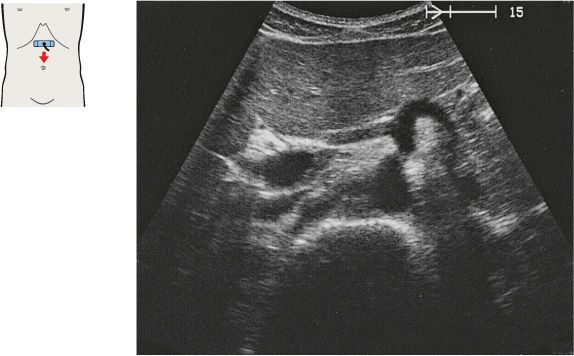
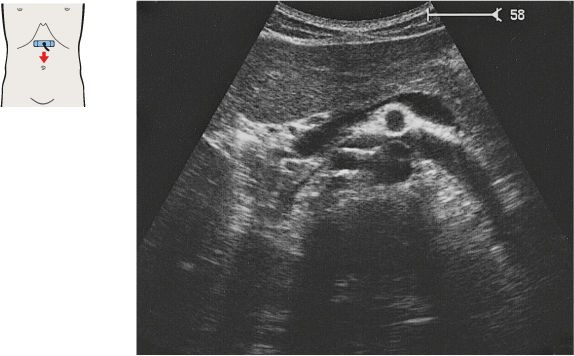
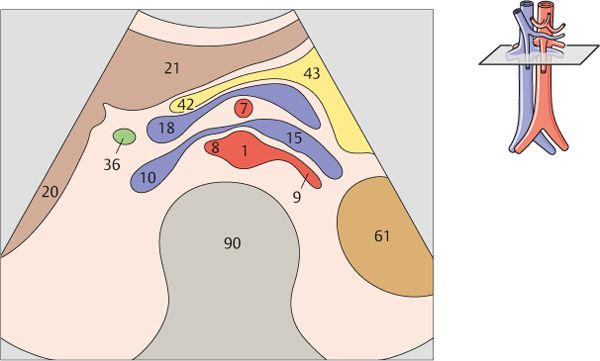
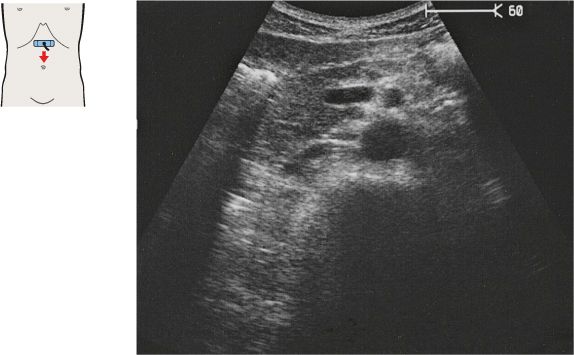
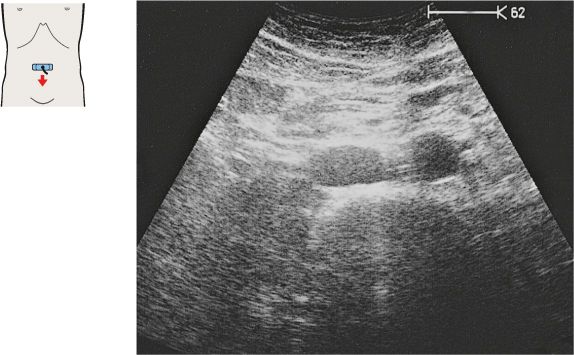
Just below the diaphragm, the vena cava is surrounded by liver tissue. The aorta lies directly behind the gastroesophageal junction, often making the vessel more difficult to scan.
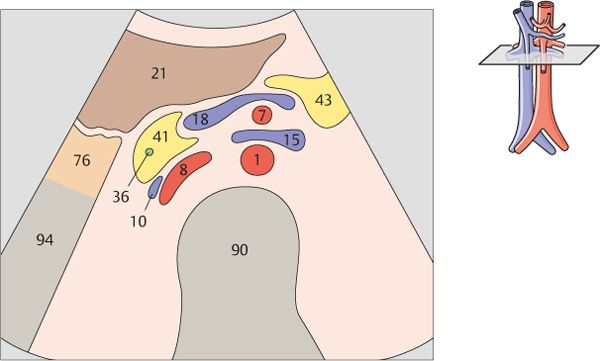
The left gastric artery is identified as a small-caliber vessel cranial to the celiac trunk.
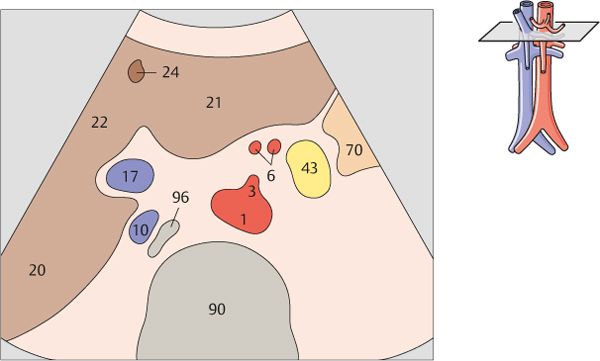
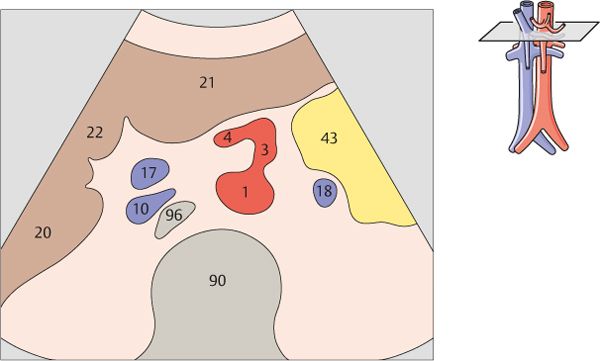
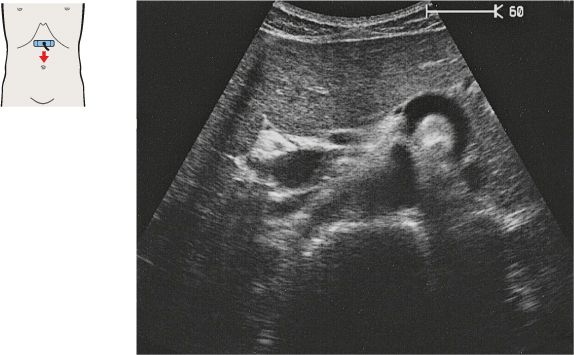
3 Celiac trunk
4 Celiac trunk
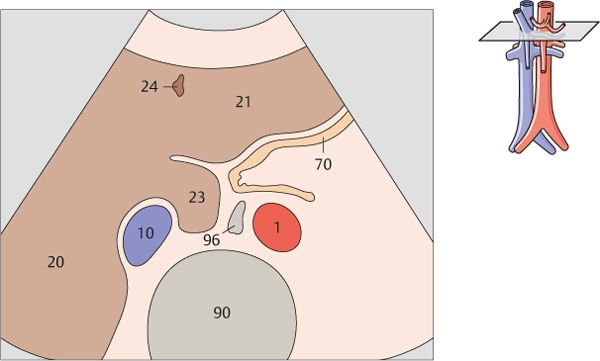
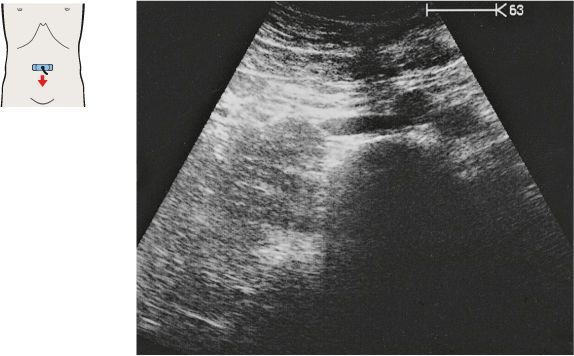
After arising from the aorta, the celiac trunk runs a short distance to the left.
The proximal part of the celiac trunk also turns slightly downward in most cases.
5 Hepatic artery
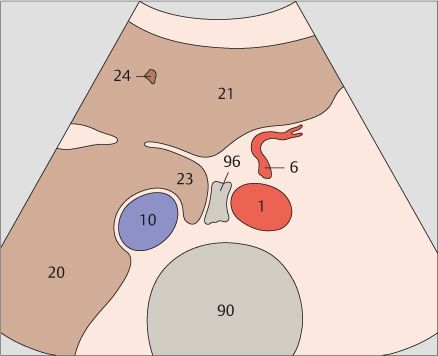
6 Splenic artery
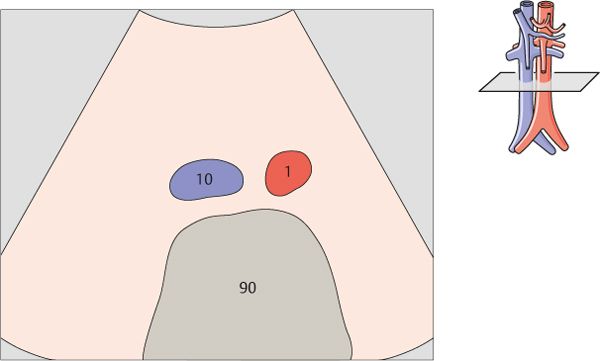
The celiac trunk runs slightly to the right, giving rise to the hepatic artery.
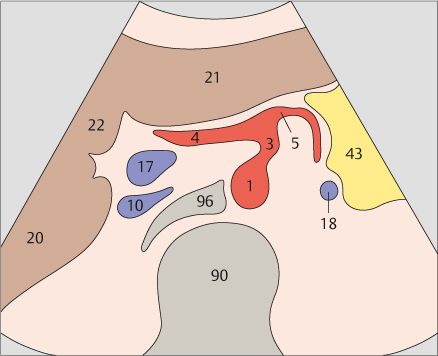
The splenic artery branches from the celiac trunk at a right angle.
7 Superior mesenteric artery
8 Superior mesenteric artery
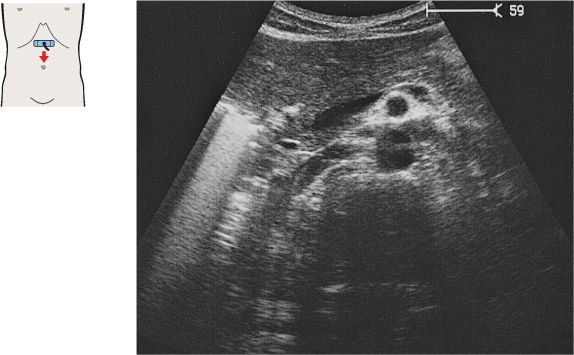
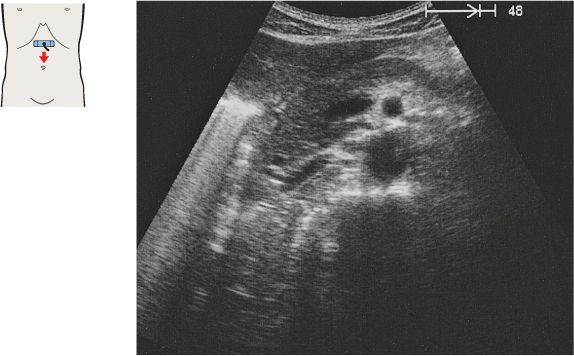
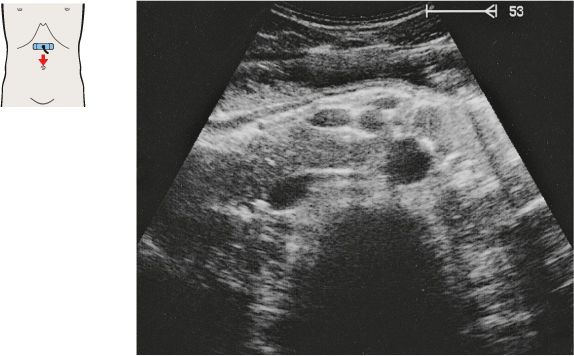
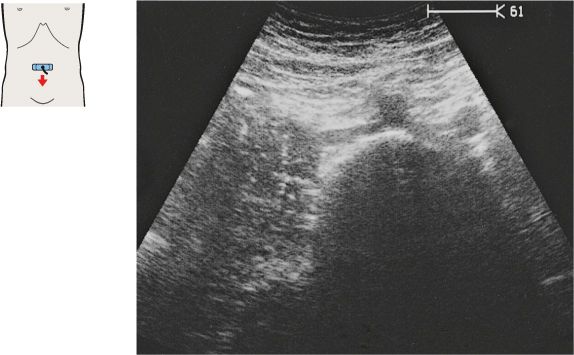
The superior mesenteric artery arises just below the celiac trunk and runs parallel to the aorta.
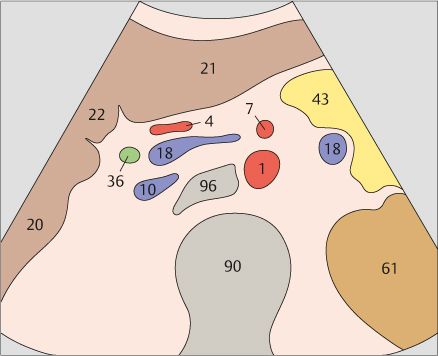
The root of the superior mesenteric artery is usually surrounded by an echodense fat pad.
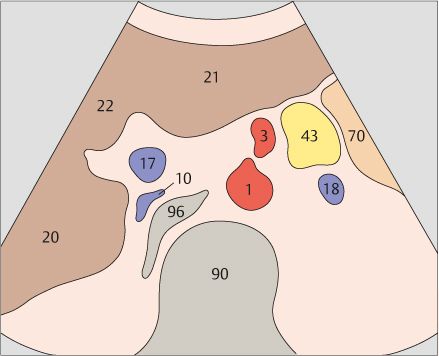
9 Superior mesenteric artery and splenic vein
10 Left renal vein and right renal artery
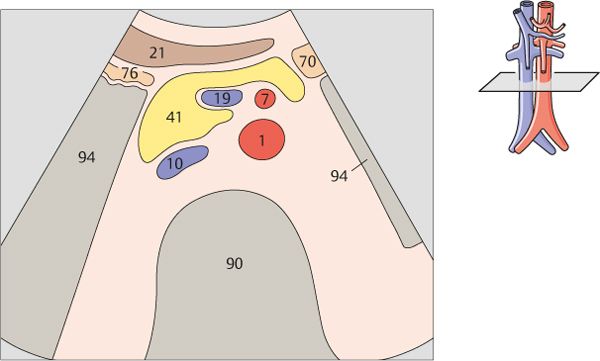
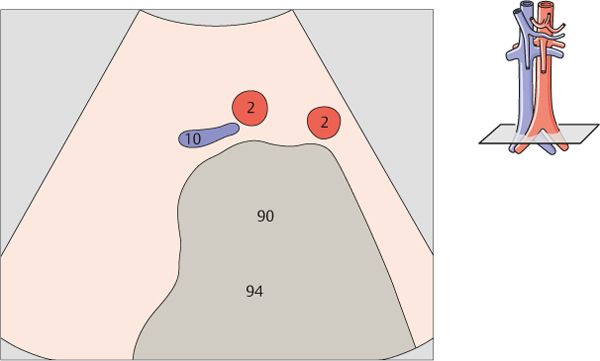
The aorta, the superior mesenteric artery, and the splenic vein crossing over the superior mesenteric artery provide landmarks for identifying the head of the pancreas.
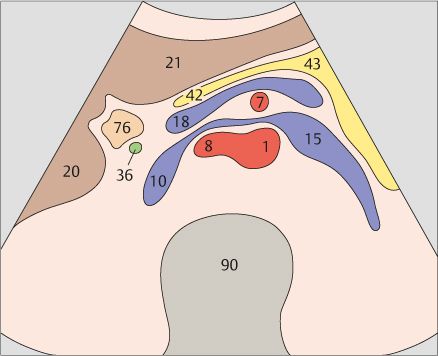
The left renal vein is physiologically compressed between the aorta and the superior mesenteric artery. It is slightly congested proximal to the compression site.
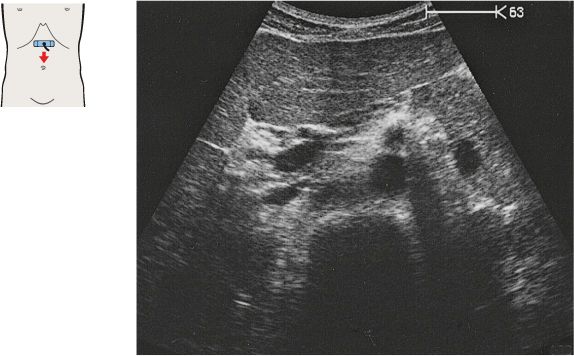
11 Infrarenal aorta and vena cava
12 Infrarenal aorta and vena cava
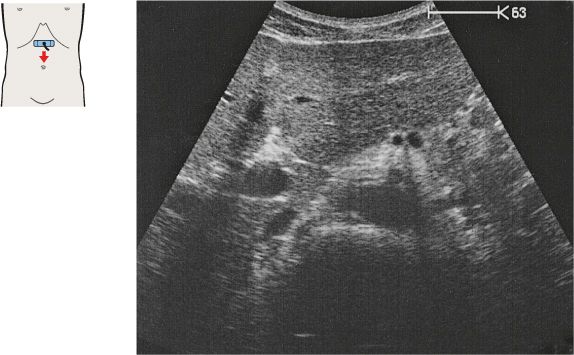
The vena cava is easily compressible with the transducer, and it bears impressions from adjacent organs.
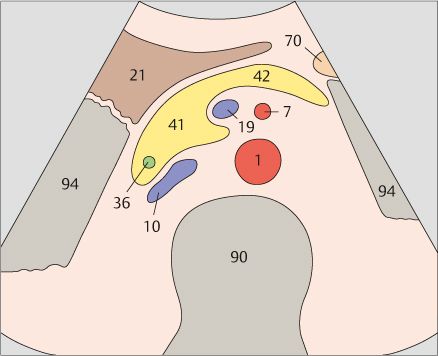
The aorta has a circular cross section, whereas the vena cava is somewhat flattened.
13 Infrarenal aorta and vena cava
14 Infrarenal aorta, vena cava, and superior mesenteric artery and vein
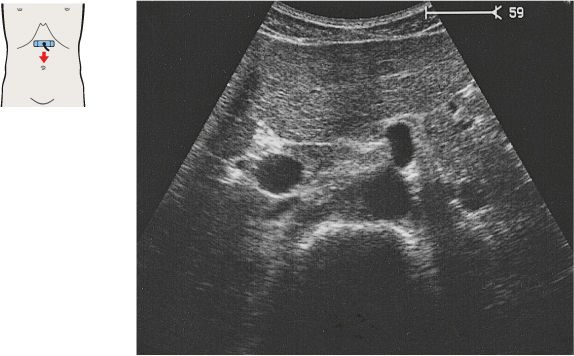
The caliber of the vena cava varies with the pulse and respirations. The diameter of the aorta measures 2.5 cm in its cranial portion, 2.0 cm in its caudal portion.
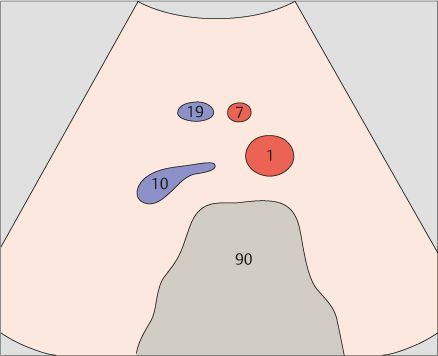
Together with the aorta and vena cava, the superior mesenteric artery and vein form a typical four-vessel pattern in a low transverse scan through the upper abdomen.
15 Infrarenal aorta and vena cava
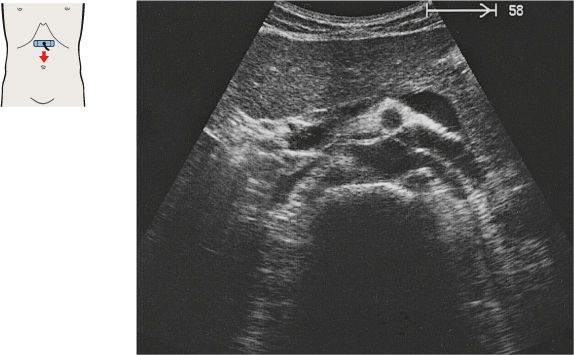
16 Aortic bifurcation
While the aorta and vena cava are relatively far apart in the upper abdomen, they converge at the level of the promontory, coming very close together.
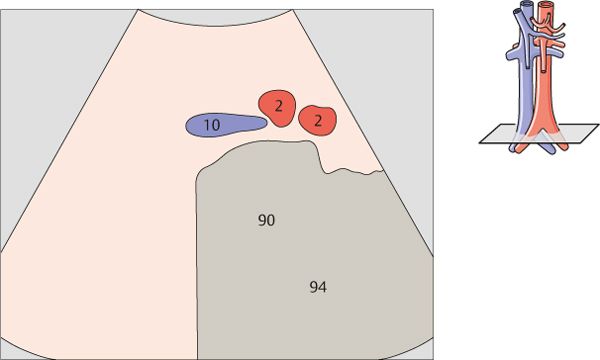
The aorta divides into the common iliac arteries at the level of the L4 vertebral body, above the promontory.
17 Iliac arteries
18 Confluence of iliac veins
The aortic bifurcation is located slightly above the confluence of the iliac veins.
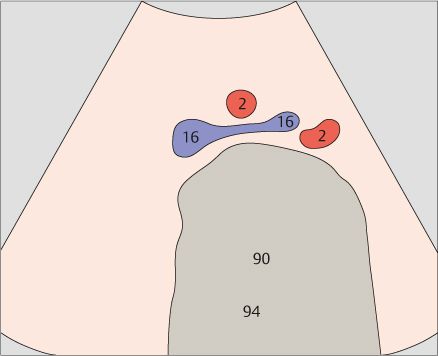
The confluence of the iliac veins lies approximately at the level of the umbilicus.
19 Iliac vessels
20 Iliac vessels
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree