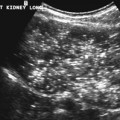
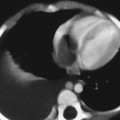
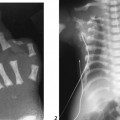
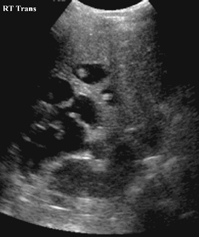
CASE 67 A 2 1/2-year-old boy was followed since prenatal ultrasonographic diagnosis of abdominal abnormalities. Figure 67A Figure 67B Ultrasonographic examination (transverse scan of the liver) shows extensive saccular dilatation of intrahepatic biliary tree with the “dot sign” (7A, arrow). Renal enlargement (14.7 cm long) with hyperechoic parenchyma is noted (Fig. 67B). Figure 67C Differential diagnosis: simple liver cyst on routine ultrasound of an infant. Figure 67D Differential diagnosis: extensive hepatic involvement on ultrasound of a 16-year-old girl with abdominal lymphangioma. Figure 67E Differential diagnosis: CT of amebic abscess of liver dome in a child with cough and febrile illness. Figure 67F Coronal MRI (inversion recovery) demonstrating saccular dilatation with high signal intensity within the liver from Caroli’s disease. There also is bilateral renal enlargement of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. Caroli’s disease Figure 67G Sonogram of a 12-year-old patient with gastrointestinal bleeding, splenomegaly, and congenital cystic renal disease. The dot sign is pathognomonic of Caroli’s disease.
Clinical Presentation
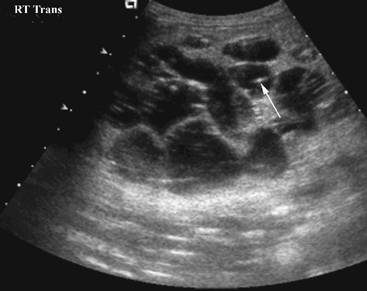

Radiologic Findings




Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree