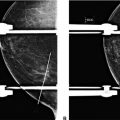
A. Radial fold
B. Capsular contracture
C. Intracapsular rupture
D. Extracapsular rupture
2 What is the most common location for an intramammary lymph node?
A. Upper outer quadrant
B. Upper inner quadrant
C. Lower outer quadrant
D. Lower inner quadrant
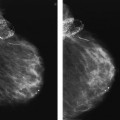
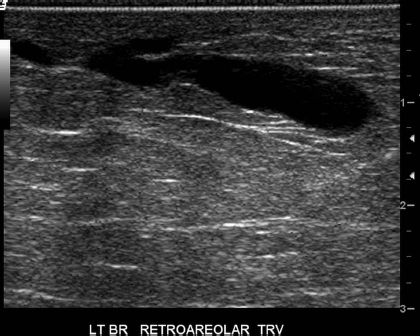
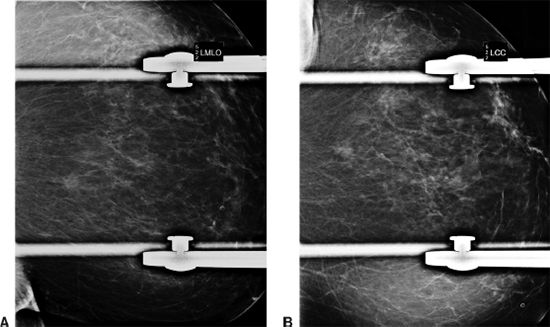
3a Based on the following images, the dominant finding is
A. Subareolar region nonmass-like enhancement
B. Enhancement of the pectoralis muscle
C. Unilateral skin thickening
D. Architectural distortion in the superior right breast
3b What would be an appropriate differential diagnosis for the previous finding?
A. Related to phase of menstrual cycle
B. Mastitis
C. Hormone therapy
D. Renal failure
4a A 16-year-old female presents with a palpable finding in her right breast. What is the most appropriate imaging test?
A. Unilateral right mammogram
B. Bilateral mammogram
C. Unilateral right ultrasound
D. Bilateral ultrasound
E. Unilateral right mammogram and ultrasound
4b Which of the following statements regarding fibroadenomas is correct?
A. Giant fibroadenomas are more common in the Asian population.
B. Most fibroadenomas in teenagers are adult type.
C. Fibroadenomas are more common in postmenopausal women.
D. Fibroadenomas can be found equally in males and females.
4c Based on the following image, what would be the most likely diagnosis?
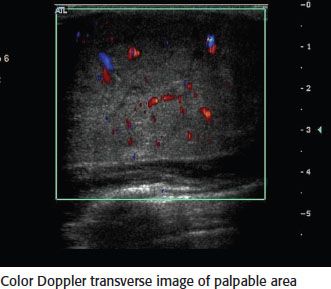
A. Fat necrosis
B. Lymph node
C. Hematoma
D. Juvenile fibroadenoma
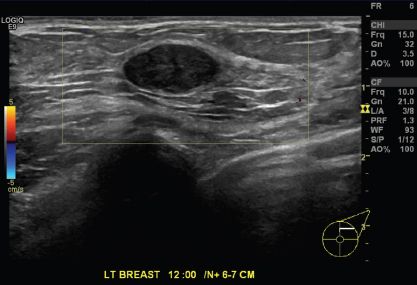
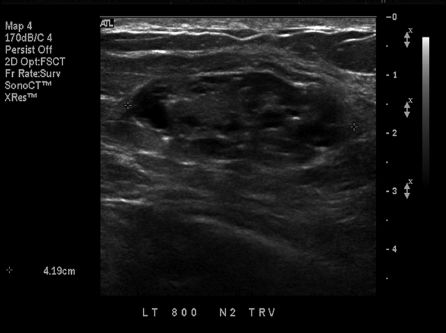
5 A 49-year-old female with no history of prior breast concerns or a family history of breast cancer presents with new onset right bloody nipple discharge. Based on the ultrasound images below, what is the most likely diagnosis?
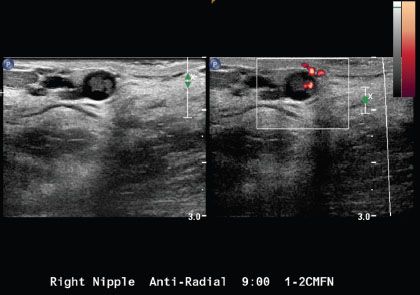
A. Intraductal carcinoma
B. Duct ectasia with debris
C. Fibrocystic change
D. Intraductal papilloma
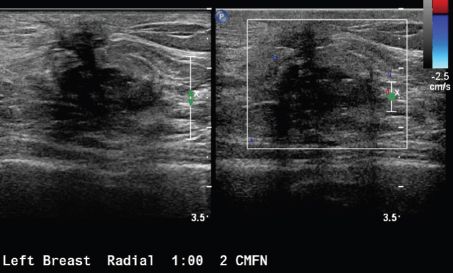
6a Based on the following images, what would be the appropriate BI-RADS category?
A. BI-RADS 2
B. BI-RADS 3
C. BI-RADS 4
D. BI-RADS 5
6b What is the appropriate recommendation?
A. Annual screening mammography
B. Short-term follow-up in 6 months
C. Core needle biopsy
D. Surgical excisional biopsy
7 A 45-year-old female presents with a palpable abnormality in the right breast. Based on the ultrasound image below, what is the most appropriate BI-RADS assessment?
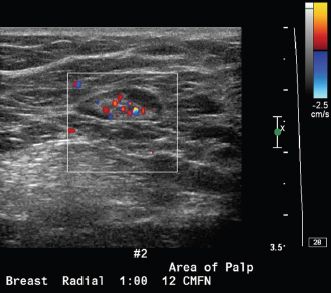
A. BI-RADS 2
B. BI-RADS 3
C. BI-RADS 4
D. BI-RADS 5
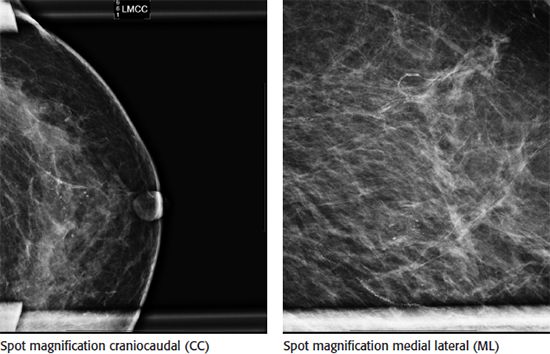
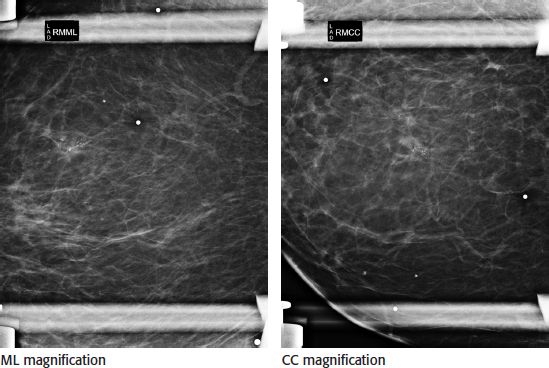
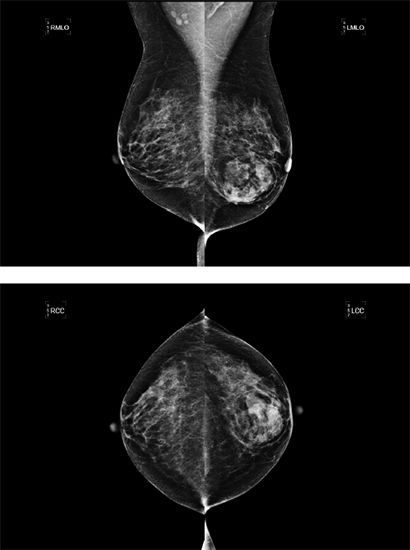
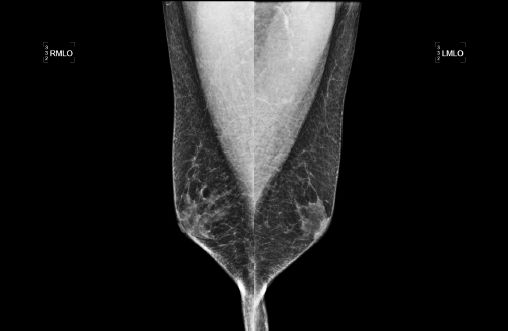
8 A 35-year-old female with a history of a left lumpectomy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy at age 29 presents for her annual diagnostic mammogram. Based on the magnification images of the lumpectomy site, what is the most appropriate next step?
A. 6-month follow-up
B. MRI
C. Stereotactic core biopsy
D. Annual screening mammogram
E. Annual diagnostic mammogram
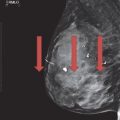
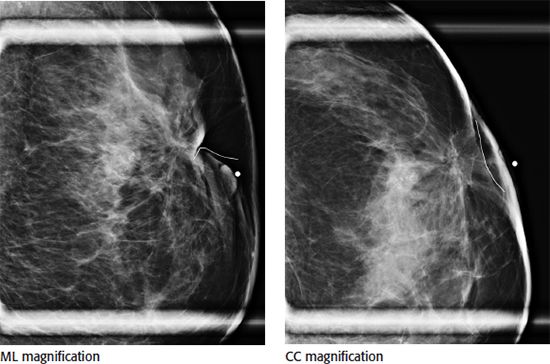
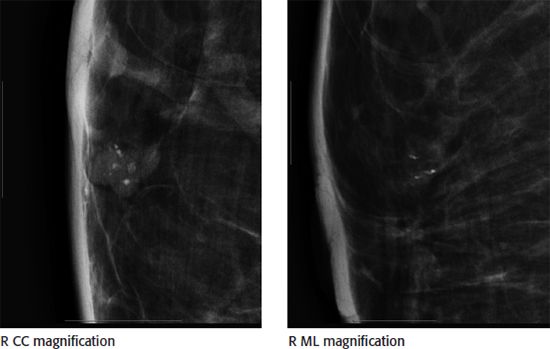
9 A 40-year-old female was recalled from screening for calcifications in the right breast. Based on the magnification views, what is the most appropriate BI-RADS lexicon description for the calcifications?
A. Coarse heterogeneous
B. Secretory
C. Punctate
D. Pleomorphic
10a A 50-year-old female was recalled from screening for a mass within the left breast. Based on images A and B, what is the best description of the mass shape and margins using the BI-RADS lexicon?
A. Round, obscured
B. Irregular, microlobulated
C. Irregular, spiculated
D. Round, speculated
10b An ultrasound of mass was performed. Based on images A and B, what is the best BI-RADS lexicon description of the shape and margins of the mass?
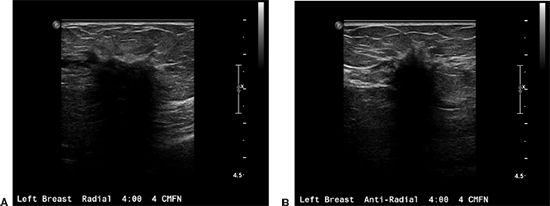
A. Oval, spiculated
B. Oval, angular
C. Irregular, angular
D. Irregular, speculated
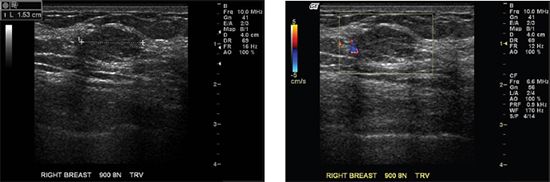
10c The mass was also examined by elastography. Given the image below, which statement is correct?
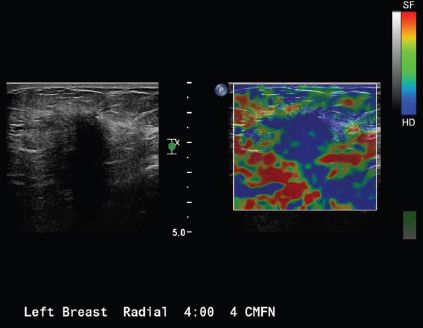
A. The mass measures cystic or soft by elastography.
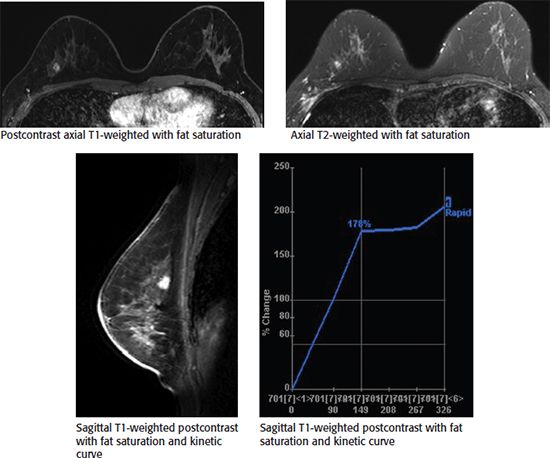
B. The mass measures hard or stiff by elastography.
C. The mass is indeterminate for stiffness by elastography.
D. The mass stiffness suggests malignancy by elastography.
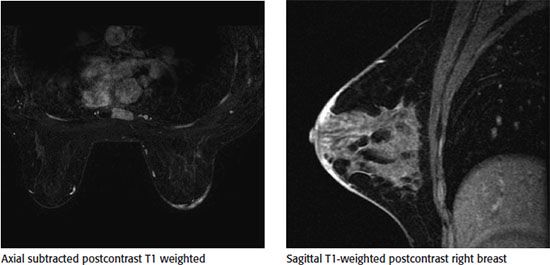
11a A 65-year-old female with a history of right mastectomy, contralateral prophylactic mastectomy, and bilateral TRAM flap reconstruction for right breast–invasive ductal carcinoma and DCIS presents for surveillance breast MRI. Axial T1-weighted and axial postcontrast subtraction images are provided. What is the most likely diagnosis?
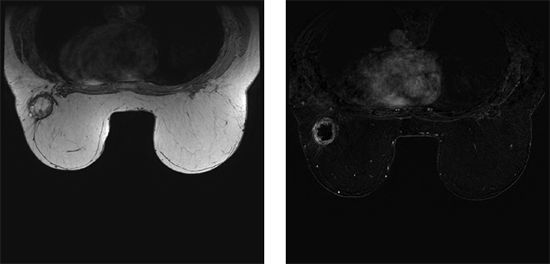
A. Recurrent invasive ductal carcinoma
B. Fat necrosis
C. Breast abscess
D. Postsurgical seroma
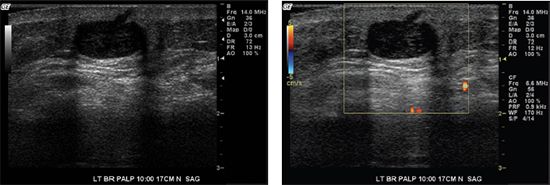
11b The patient’s left mammogram is also shown. No prior mammogram is available for comparison at this time. What is the most appropriate BI-RADS classification?
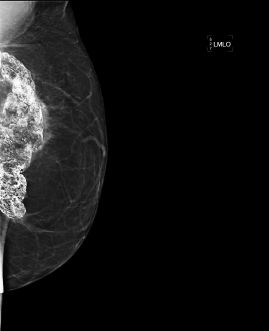
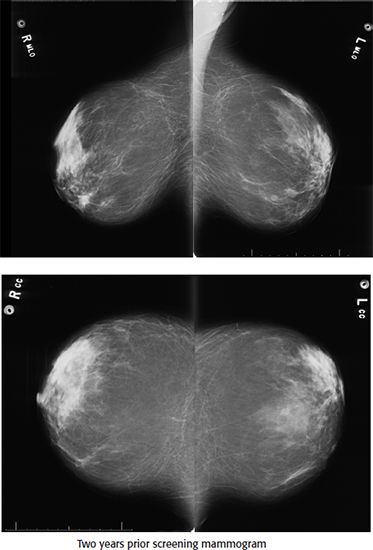
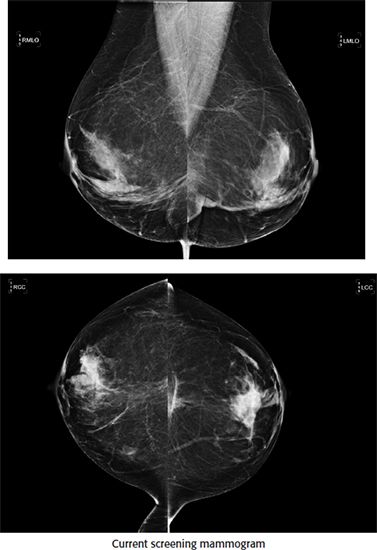
A. BI-RADS 2, benign
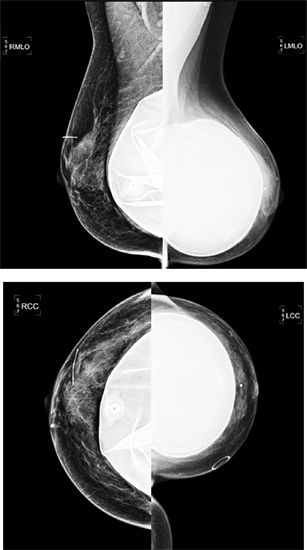
B. BI-RADS 3, probably benign
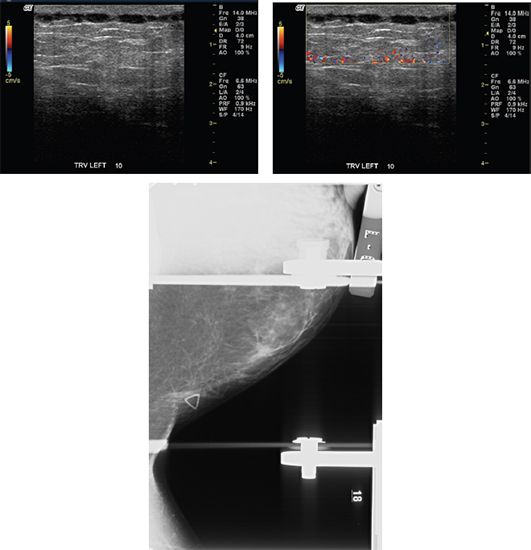
C. BI-RADS 4, suspicious
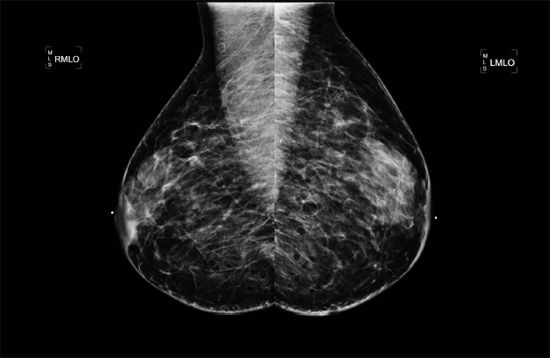
D. BI-RADS 6, known malignancy
12 A 29-year-old female, who is 35 weeks pregnant, presents with a palpable lump in the right breast with associated pain. She denies any fevers. No skin erythema is seen on physical examination. Ultrasound images of the palpable lump are provided. No mammogram was performed due to patient’s age and pregnancy. What is the most appropriate next step?
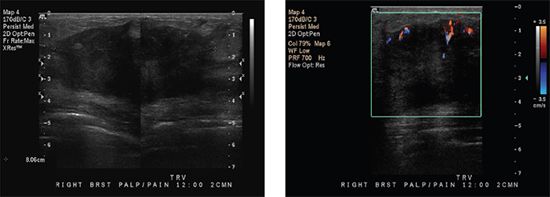
A. Probable abscess, treat with antibiotics and short interval follow-up ultrasound.
B. Probable abscess, recommend drainage/aspiration.
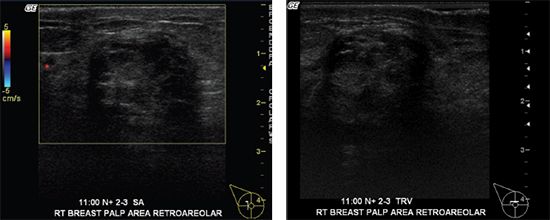
C. Probably benign, lactating adenoma, or fibroadenoma, recommend short interval follow-up ultrasound in 6 months.
D. Suspicious mass, recommend ultrasound-guided core biopsy.
13 A 51-year-old female presents for a diagnostic mammogram, no prior studies are available for comparison. Based on images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
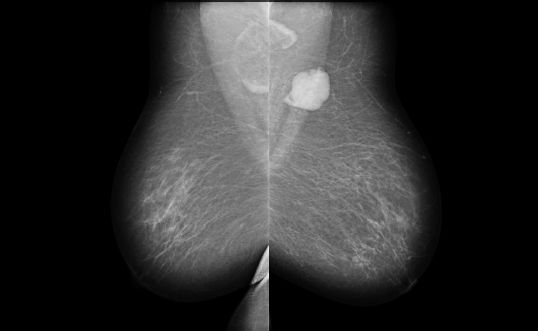
A. HIV
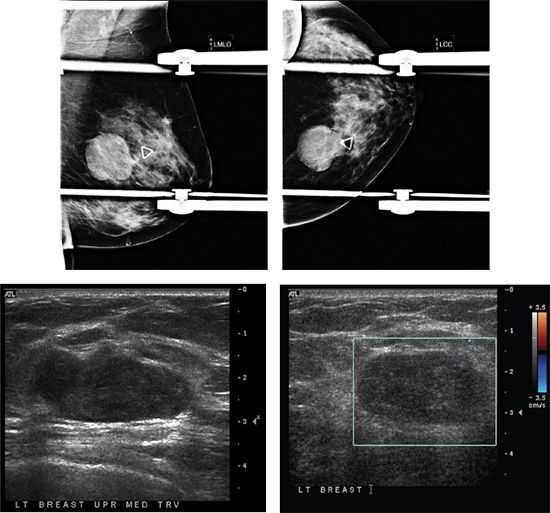
B. Tuberculosis
C. Metastases
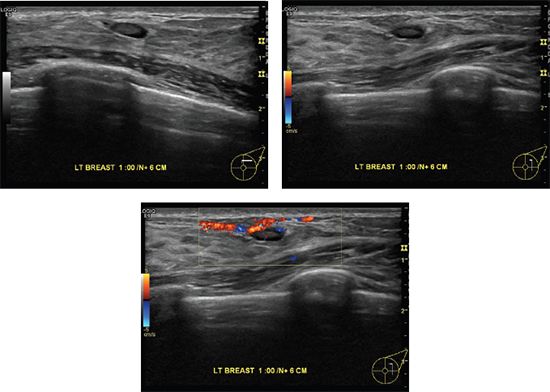
D. Sarcoidosis
E. Rheumatoid arthritis
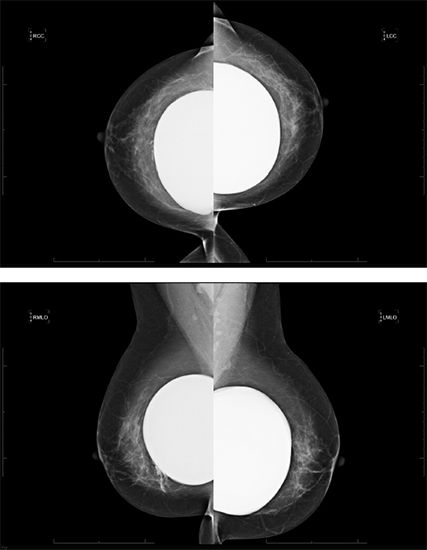
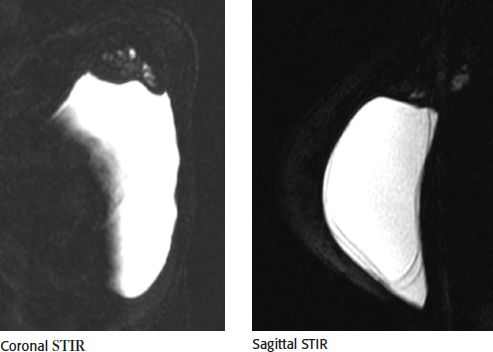
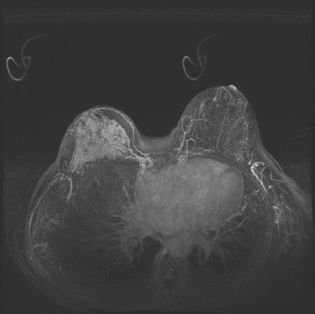
14a A 70-year-old female presents for breast MRI to assess for possible implant rupture. Bilateral axial T1-weighted and left breast axial T2-weighted STIR water saturation images are provided. What type of implant is present?
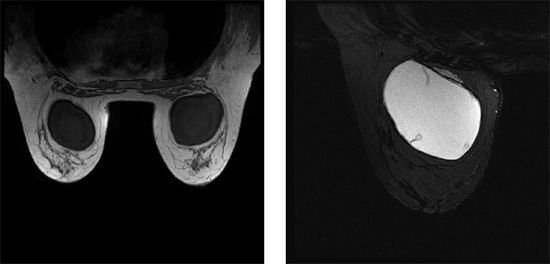
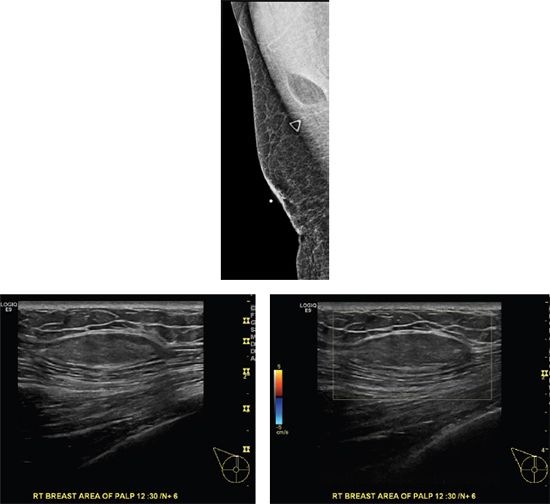
A. Saline, prepectoral
B. Saline, retropectoral
C. Silicone, prepectoral
D. Silicone, retropectoral
14b Which statement best describes the finding seen in the axial T2W STIR water-saturated image of the left implant?
A. Intact implant with normal radial folds
B. Intracapsular rupture only
C. Intact implant with capsular contracture
D. Intracapsular and extracapsular rupture
15 A 65-year-old male is diagnosed with breast cancer. Regarding breast cancer in males, which statement is correct?
A. Breast cancer in males in general has a better prognosis than in females due to the malignancy typically being in an earlier stage at the time of diagnosis.
B. Approximately 20% have axillary adenopathy at the time of diagnosis.
C. Approximately 15% have DCIS associated with their malignancy.
D. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma is less common in men than women.
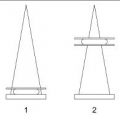
16 What is the protocol for performing rolled craniocaudal (CC) views?
A. Always roll superior half of the breast medial and lateral.
B. Always roll inferior half of the breast medial and lateral.
C. Always roll medial half of the breast superior and inferior.
D. Always roll lateral half of the breast superior and inferior.
17 A 50-year-old female presents with a right breast palpable abnormality at 9 o’clock. Based on the ultrasound image below, what is the most likely diagnosis?
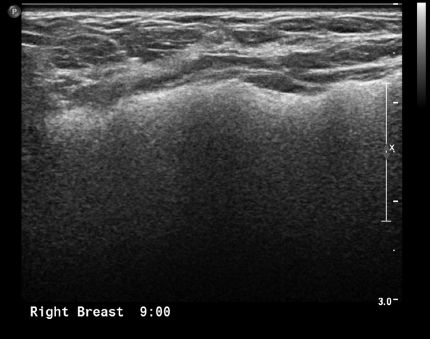
A. Extracapsular silicone implant rupture
B. Intact silicone implant with a focal bulge
C. Intact saline implant with a focal bulge
D. Intracapsular silicone implant rupture
E. Saline implant rupture
18 A cluster of calcifications are seen in the medial breast on the CC view but not seen on the MLO view. What additional mammographic view would be helpful to localize the calcifications?
A. Medial lateral (ML) view
B. Lateral medial (LM) view
C. Spot compression view
D. Cleavage view
E. Exaggerate craniocaudal outer view
19 Mondor’s disease of the breast is typified by which of the following statements?
A. Easily differentiated from inflammatory breast cancer
B. Common disorder characterized by thrombophlebitis of the subcutaneous veins of the anterolateral chest wall
C. Presents as a tender palpable cord corresponding to a superficial tubular density on mammography and a subcutaneous vessel on ultrasound without Doppler vascular flow
D. Rare malignant breast condition that requires biopsy or excision
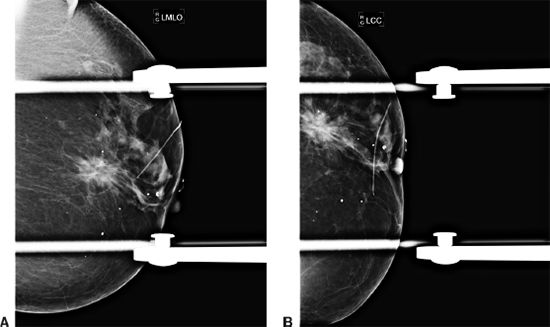
20 A 56-year-old woman presents for a screening mammogram. Based on the two standard mammographic views A and B, what is the most likely diagnosis?
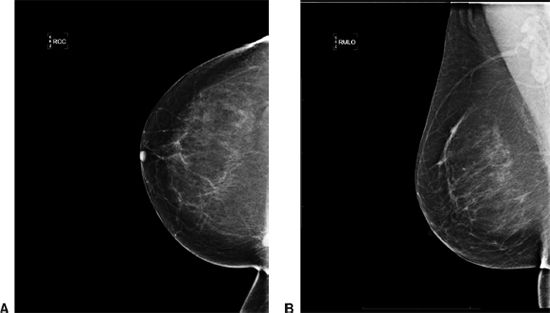
A. Lymph node
B. Invasive ductal carcinoma
C. Radial scar
D. Inframammary fold
E. Sternalis muscle
21 You are shown a standard screening mammogram. What is the MOST appropriate NEXT step?
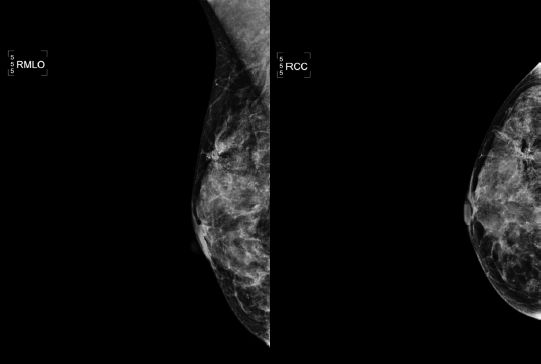
A. 1 year follow-up
B. 6-month follow-up
C. Spot-magnification views
D. MRI
22 A 76-year-old male presents with a painless palpable breast lump. Based on the mammograms A and B, what is the most likely diagnosis?
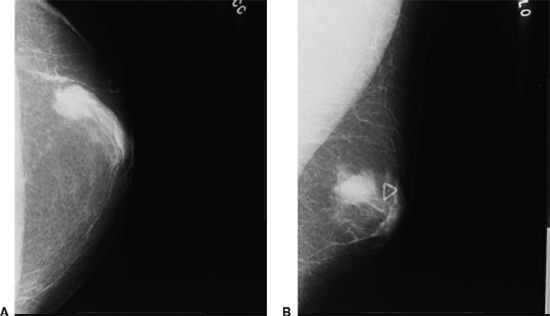
A. Abscess
B. Hematoma
C. Mastitis
D. Breast carcinoma
E. Gynecomastia
23 Diabetic fibrous mastopathy (DFM) is classically associated with which type of diabetes mellitus?
A. Type I
B. Type II
C. Type III
D. Type IV
24 Amongst the choices given below, what is the most common malignancy to metastasize to the breast?
A. Lung
B. Ovarian
C. Melanoma
D. Pancreatic
E. Stomach
25 You are shown standard CC and MLO views of a screening mammogram. Which of the following is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis?
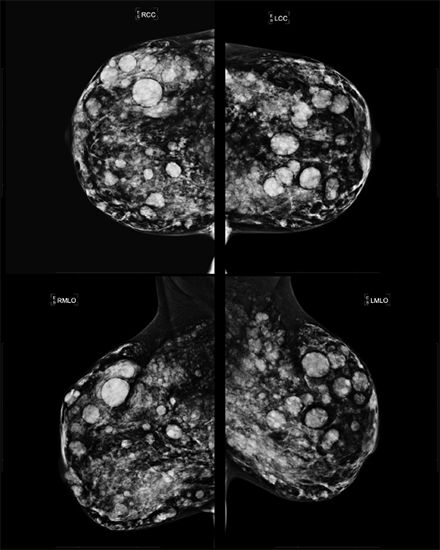
A. Steatocystoma multiplex
B. Metastasis
C. Neurofibromatosis Type I
D. Silicone injection granulomata
26 A 65-year-old male with history of coronary artery bypass surgery, thyroid disease, and depression presents with painful, tender subareolar masses. What is the best next step, based on the provided mammographic images?
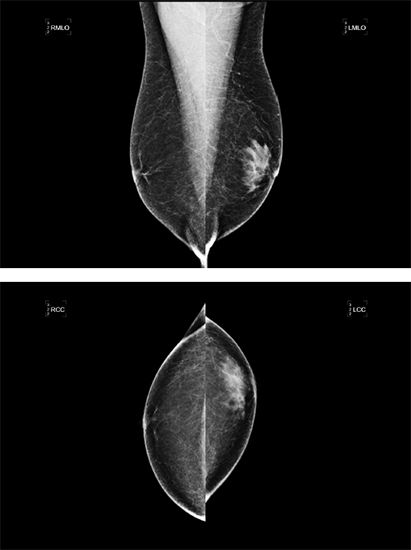
A. Ultrasound
B. Breast MRI
C. Obtaining careful drug history
D. Spot compression views
E. Biopsy and cytological analysis
27 Patient was diagnosed with right breast cancer and elected to undergo bilateral mastectomies with DIEP (deep inferior epigastric perforator) reconstructions. She now presents to her surgeon with persistent right breast skin thickening and heaviness. A bilateral breast MRI with contrast was ordered. Selected images from that examination are shown.
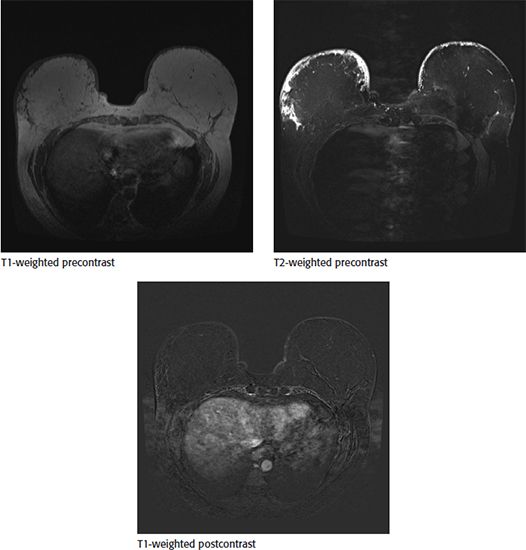
What is the most likely explanation for the patient’s symptoms?
A. Postoperative seroma
B. Fat necrosis
C. Recurrent tumor
D. Flap edema
28a A 31-year-old female presents with a palpable lump in the upper left breast. Her mother was diagnosed with breast cancer at age 46. Targeted ultrasound of the area of palpable abnormality was performed. What is the MOST LIKELY diagnosis based on the ultrasound finding?
A. Complicated cyst
B. Fibroadenoma
C. Invasive ductal carcinoma
D. Phyllodes tumor
E. Simple cyst
28b What are the typical MRI features of this mass, if this patient had a breast MRI done?
A. Enhancing mass with nonenhancing internal septations
B. Low T1-weighted and high T2-weighted signal intensity with no enhancement
C. Multiple small fluid intensity components within a heterogeneous mass
D. Type 3 enhancement kinetic curve
E. Signal loss on fat-saturated sequences
29 Which benign lesion is most likely to demonstrate a classically malignant characteristic on MRI?
A. Fibroadenoma
B. Fat necrosis
C. Simple cyst
D. Hamartoma
30a A 28 year-old, 38-week G2P1 female presents with a painful, erythematous mass in the right breast. Which imaging modality is most appropriate for evaluating this patient?
A. Mammogram
B. Ultrasound
C. MRI
D. Chest radiograph
30b An image from a targeted ultrasound is shown.
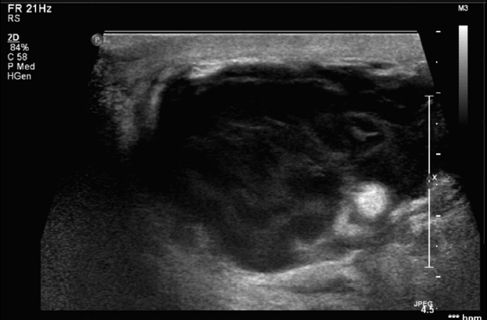
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Enlarged duct
B. Abscess
C. Malignancy
D. Hematoma
31 Which of the following would you expect to present as a spiculated mass on mammogram?
A. Medullary carcinoma
B. Papillary carcinoma
C. Phyllodes tumor
D. Tubular carcinoma
32 A 62-year-old female presents for additional views for a mammographic finding. What is the diagnosis?
A. Skin calcifications
B. Oil cyst
C. Milk of calcium
D. Vascular calcifications
33 Approximately what percentage of all breast cancers occurs in MEN?
A. 1%
B. 5%
C. 10%
D. 15%
34 Calcifications are seen on a poststereotactic biopsy radiograph of the specimen. However, the pathologist states no calcifications are seen in the specimen provided. What is the next BEST step?
A. Accept the pathology results.
B. Recommend 6-month follow-up mammogram.
C. Analyze specimen using polarized light microscopy.
D. Recommend rebiopsy.
35 You are shown a screening mammogram and CC and MLO projection magnification views. What is the MOST appropriate BI-RADS designation?
A. Category 0
B. Category 2
C. Category 3
D. Category 5
36a A 50-year-old female presents for a screening mammogram.
What is the salient finding?
A. Intracapsular rupture
B. Capsular calcification
C. Distortion of the implant contour
D. Free silicone with intracapsular and extracapsular rupture of the implant
36b What is the BI-RADS assessment?
A. 0
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
37 Which of the following is a high-risk lesion?
A. Peripheral duct papilloma
B. Intraductal papilloma
C. Intracystic papilloma
D. Papillary carcinoma in situ
38a A 20-year-old female presenting with a new palpable abnormality in her right breast. Sonographic evaluation of the palpable area was performed.
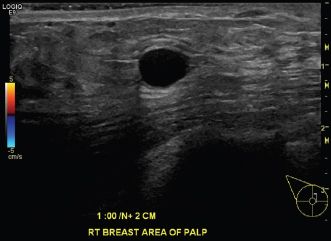
Which of the following is the best description of the sonographic finding?
A. Hypoechoic mass, smooth thin wall, sharp posterior border, posterior acoustic enhancement
B. Anechoic mass, smooth thin wall, sharp posterior border, posterior acoustic enhancement
C. Hypoechoic mass, smooth thin wall, sharp posterior border, increased through transmission
D. Anechoic mass, smooth thin wall, sharp posterior border, posterior acoustic shadowing
38b What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Solid mass
B. Complicated cyst
C. Complex cyst
D. Simple cyst
39 What is the most likely diagnosis for an encapsulated mass with “breast-within-a-breast” appearance on mammogram?
A. Fat necrosis
B. Fibroadenoma
C. Fibroadenolipoma
D. Galactocele
E. Lipoma
40 A 57-year-old female presents with a new palpable left breast mass that she states has grown rapidly over a period of <4 months. Her last screening mammogram was 6 months ago and interpreted as negative. Images from her most recent left breast diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound are shown.
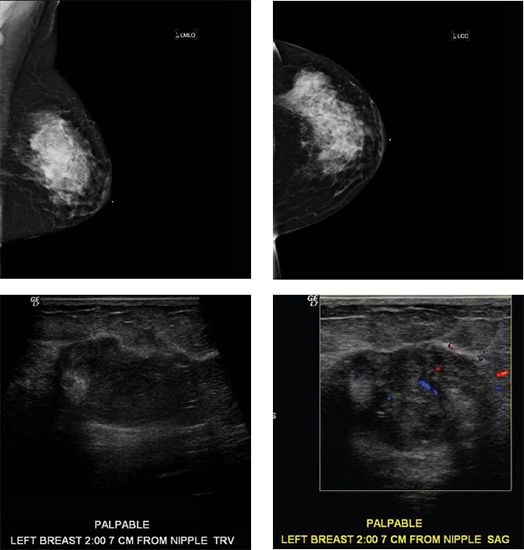
The most likely diagnosis is
A. Fibroadenoma
B. Hamartoma
C. Metaplastic carcinoma
D. Tubular adenoma
41 A 45-year-old female with a history type I diabetes presents with multiple palpable right breast masses that are firm on exam. Diagnostic imaging of the right breast was performed. Mammogram and ultrasound are shown.
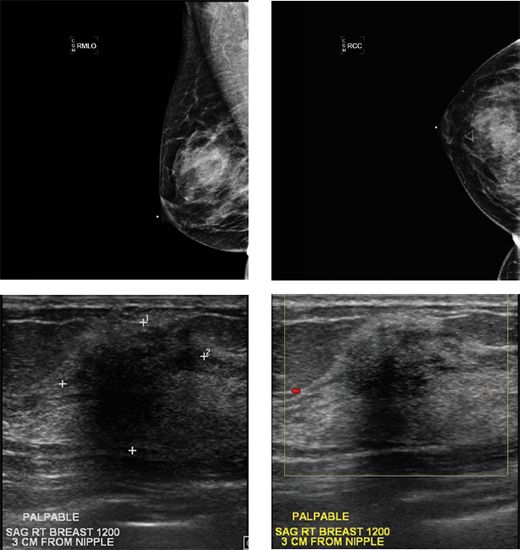
All of the masses were similar in appearance sonographically so a single mass was selected to sample under ultrasound guidance. Pathology demonstrates fibrous stromal proliferation and perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate consistent with diabetic mastopathy. The correct radiologic/pathologic correlation is
A. Concordant; excision recommended
B. Concordant; clinical follow-up recommended
C. Discordant; excision recommended
D. Discordant; repeat biopsy recommended
42 Shown below is a targeted ultrasound image of a 48-year-old female with clinical presentation of spontaneous left nipple yellow colored discharge. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Duct ectasia
B. Ductal carcinoma in situ
C. Papilloma
D. Papillary carcinoma
E. Paget disease of the nipple
43 Screening and diagnostic mammograms of a 52-year-old female demonstrate a spiculated mass with a central lucent area. Core biopsy of the mass proved it to be a radial scar. Subsequently, surgical excision was performed. What specific type of breast cancer may coexist with radial scar?
A. Ductal carcinoma in situ
B. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma
C. Inflammatory carcinoma
D. Medullary carcinoma
E. Tubular carcinoma
44 Approximately what percentage of all invasive breast malignancies are invasive lobular cancer?
A. <1%
B. 10%
C. 50%
D. 90%
45 A 44-year-old female presents for additional views of an abnormality seen on screening mammography. Spot compression CC and MLO views are shown in images A and B. Prior comparison mammogram was negative in this location. Focused ultrasound was performed and demonstrates no sonographic abnormality. What is the most appropriate BI-RADS category given that the finding is not seen on ultrasound?
A. 0, incomplete, breast MRI recommended
B. 2, benign, return to screening in 1 year
C. 3, probably benign, 6-month follow-up mammogram recommended
D. 4, suspicious, biopsy is recommended
46 Which postconservation therapy change on MRI is considered a BI-RADS 4 finding and warrants tissue sampling to exclude recurrence?
A. Architectural distortion
B. Edema
C. Mass-like enhancement
D. Signal void or signal flare
E. Skin thickening
47 A 29-year-old female presents with a palpable mass in the right breast. The patient has ultrasound of the palpable lump. Findings are considered suspicious for malignancy. What is the recommended next step in evaluation of the suspicious mass?
A. MRI breast without and with contrast
B. Fine needle aspiration
C. Core biopsy
D. Diagnostic mammography
E. Stereotactic biopsy
48 A 77-year-old female with the following imaging finding.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Fibroadenoma
B. Tubular carcinoma
C. Complex cyst
D. Mucinous carcinoma
E. Lobular carcinoma
49 What is the diagnosis based on the following images?
A. Intracapsular implant rupture
B. Intact implant with radial folds
C. Extracapsular implant rupture
D. Silicone gel bleed
E. Intra- and extracapsular rupture
50a A 55-year-old high-risk patient presents for screening breast MRI. No comparison available. The following contrast-enhanced breast MR images are available:
The appropriate BI-RADS category is
A. 0
B. 1
C. 2
D. 3
E. 4
50b What is the next most appropriate step?
A. 6-month follow-up breast MRI
B. Focused ultrasound/mammography
C. Annual screening breast MRI
D. MRI-guided breast biopsy
E. Repeat breast MRI
Based on the images, what is the appropriate BI-RADS assessment?
A. BI-RADS 2
B. BI-RADS 3
C. BI-RADS 4
D. BI-RADS 6
51b Based on the images, what is the most common diagnosis?
A. Intraductal papillary carcinoma
B. Intraductal papilloma
C. Ductal carcinoma in situ
D. Invasive ductal carcinoma
52 A 56-year-old female arrives to the mammography department and tells the technologist that she feels a lump in the right upper outer breast. Upon diagnostic workup, several bilateral masses were visualized. The masses were oval in shape, similar in size, and >80% of the margins were visualized. Upon review of prior studies, similar findings were seen 3 years prior. What is the appropriate BI-RADS category?
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
E. BI-RADS 6
53 A 45-year-old female had a biopsy of a hypoechoic mass-like area in the right breast, and the pathology result was radial scar. Which of the following statements about radial scar is correct?
A. There is skin retraction and thickening associated
B. Incidence is 0.1 to 2 per 1,000 screening mammograms
C. Related to prior surgery or trauma
D. No association with cancer
54 A 56-year-old female presents with a palpable finding in the right breast. Patient states she takes Coumadin. Mammogram images A and B and ultrasound image C are given.
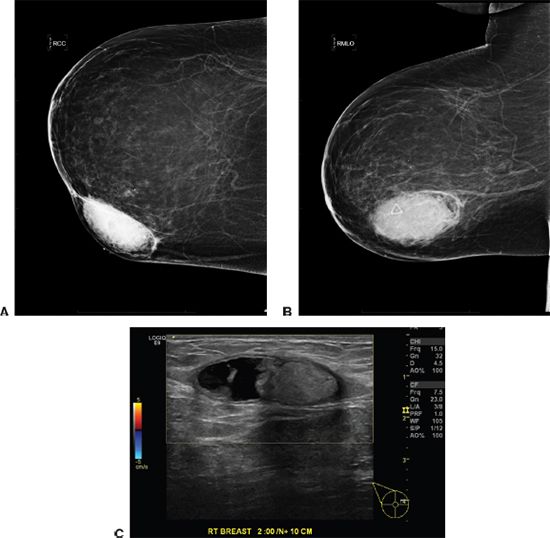
What is the BI-RADS assessment?
A. BI-RADS 1
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
E. BI-RADS 0
55 A 52-year-old woman had a stereotactic core biopsy of the following calcifications results were atypical ductal hyperplasia. What is the next appropriate step in the management?
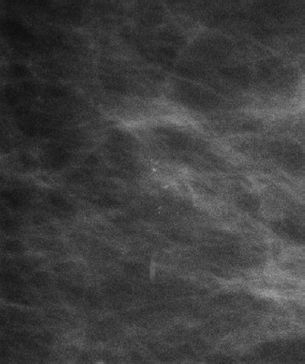
A. No further intervention is required.
B. Follow-up in 6 months
C. Follow-up in 12 months
D. Surgical excision
56 Regarding fibrocystic changes, which of the following is a correct statement?
A. More common in patients younger than 30 years of age
B. Enhances homogenously on T1-weighted sequence of breast MRI
C. Thick peripheral enhancement suggests simple cyst
D. Cysts originate from terminal lobules
E. Size of the cysts gets bigger with time
57 What is the most common pleural presentation of breast cancer?
A. Pleural effusion
B. Pleural-based soft tissue nodules
C. Round atelectasis
D. Pleural and pulmonary metastatic nodules
E. Interstitial reticulonodular changes extending to the pleura
58 A stereotactic breast biopsy shows radial scar. What is the most appropriate treatment?
A. 6-month follow-up
B. Resume yearly routine screening mammogram
C. Surgical excision
D. Second-look ultrasound
E. Rebiopsy
59 In breast MRI, which one of the following is a feature of malignant finding?
A. Lobulated border of a lesion
B. Dark internal septations without significant enhancement
C. Thick rim enhancement
D. A lesion parallels Cooper ligament
E. Microcysts
60 Regarding phyllodes tumor, which one of the following is a correct statement?
A. The pathology is usually very different from fibroadenoma.
B. It is considered a benign neoplasm, although the size at presentation is usually large and is rapidly growing.
C. Complete surgical excision often curative, but chemotherapy and radiation therapy are usually needed at the same time.
D. It is a biphasic neoplasm with double-layered epithelial component surrounded by overgrowing stroma.
E. It will not affect the skin as breast cancer does, such as skin ulceration or dimpling.
61 Regarding male breast cancer, which one of the followings is correct?
A. It is not associated with Klinefelter syndrome.
B. The most common location is upper inner breast.
C. Most patients do not have BRCA gene mutations.
D. It is associated with gynecomastia.
E. Majority of the carcinoma is ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS).
62a A patient is called back for additional views for a one-view finding on screening mammography in the central breast on the craniocaudal (CC) view. The asymmetry persists on spot compression views but is not seen on either the mediolateral oblique (MLO) or the true lateral projection, what is the next best step?
A. Perform ultrasound of the 12:00 and 6:00 positions, as well as the retroareolar plane.
B. Request the patient to return for a short interval follow-up in 6 months.
C. Recommend a breast MRI.
D. Perform rolled views.
62b Rolled views were performed. On the CC rolled lateral (CC RL) view, the lesion moves laterally, this indicates that
A. The lesion is in the superior breast.
B. The lesion is in the inferior breast.
C. The lesion is in the central breast.
D. The lesion location cannot be determined based on the information provided.
63 A 72-year-old female presents with two new groups of suspicious calcifications in the right breast on screening mammogram. A two-site stereotactic core biopsy was performed. Pathology results of the core biopsy of both sites demonstrate atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH). What is the next best step for management of this patient?
A. Return to annual screening.
B. Recommend 6-month follow-up mammogram of the right breast.
C. Recommend surgical excision of both sites.
D. Recommend MRI to evaluate for underlying malignancy.
E. Recommend surgical excision of one site.
64 A 40-year-old female with a palpable lump presents for diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound for an abnormality seen on screening mammogram. Mammogram demonstrated a circumscribed oval mass (not shown). Ultrasound image is shown. The lesion was biopsied, and pathology results were pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH). Regarding PASH, which is the most accurate statement?
A. Usually presents as a spiculated mass.
B. Usually presents with calcifications.
C. Can present as a circumscribed mass but is often incidentally found on biopsy.
D. Is only an incidental finding and cannot present as a mass lesion.
65 An ultrasound was performed for a persistent focal asymmetry with associated pleomorphic calcifications. Based on the ultrasound image below, what is the next appropriate step in management?
A. Ultrasound-guided core biopsy
B. Stereotactic core biopsy
C. MRI
D. 6-month follow-up
E. Annual diagnostic mammogram
66 A 60-year-old female presents for a diagnostic mammogram to workup calcifications in the lower inner quadrant of the left breast seen on recent screening mammogram. Skin calcifications are suspected. What is the most appropriate next step in determining the true nature of the calcifications?
A. Spot compression CC
B. True ML
C. Tangential view
D. Repeat MLO
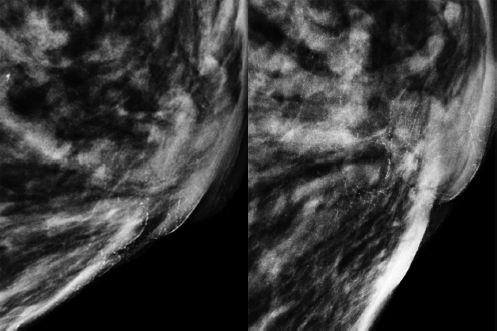
67 Breast edema as the result of lymphatic obstruction and the presence of elongated, serpentine, nonductal calcifications on mammography most likely are due to:
A. Staphylococcus aureus infection
B. Streptococcus species infection
C. lymphoma
D. filariasis
E. congestive heart failure
68 A 65-year-old male with a strong family history of breast cancer presents for a diagnostic mammogram for palpable abnormalities in both breasts. Based on the images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Gynecomastia
B. Fibrocystic change
C. Normal fibroglandular tissue
D. Breast cancer
69 A 50-year-old female presented for a screening mammogram, the MLO views of which are shown. What is the diagnosis?
A. Neurofibromatosis
B. Steatocystoma multiplex
C. Malignancy
D. Silicone granulomas
70 Which of the following is correct about invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC)?
A. Higher false-negative rates are reported with ILC, than with any other forms of cancer.
B. ILC most commonly presents as calcifications.
C. MR imaging usually does not affect management of patients with ILC.
D. ILC has a lesser rate of multiplicity and bilaterality than invasive ductal carcinoma.
71 Which of the following statements is correct about inflammatory carcinoma of the breast?
A. It is considered a stage T1 lesion.
B. Most common presentation is skin erythema.
C. Majority of patients have axillary nodal involvement at presentation.
D. Inflammatory carcinoma accounts for 10% of breast cancers.
72 Regarding pregnancy-associated breast cancer, which of the following statements is correct?
A. It represents <1% of the breast cancers.
B. Breast cancer is the most common cancer during pregnancy.
C. At the time of diagnosis, pregnant women have larger and more advanced
cancers than nonpregnant women of the same age.
D. The average age of diagnosis is 40 to 45 years.
73 An MRI is shown from a patient with a palpable abnormality in the right breast. Based on these images, what is the most likely pathologic diagnosis?
A. Invasive ductal carcinoma
B. Invasive lobular carcinoma
C. Fibroadenoma
D. Phyllodes tumor
74 In patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy, which is the best at assessing response to therapy?
A. Clinical exam
B. Mammography
C. Ultrasound
D. MRI
75 An MRI was performed in a patient with biopsy-proven breast cancer along the chest wall to evaluate for invasion of the pectoralis muscle. Which of the following criteria is most predictive of chest wall invasion?
A. Enhancement of the pectoralis muscle
B. No intervening fat plane between the mass and muscle
C. There is no predictive criteria.
D. Vessels extending from the mass into muscle
76 Which of the following statements is correct about recurrent breast cancer?
A. Local recurrence rate after breast conservation therapy is 10% to 20%.
B. Most cases of recurrence occur within the first 2 years of treatment.
C. MRI offers an advantage over other modalities in assessing recurrence.
D. On MRI, physiologic enhancement at the surgical site is seen up to 2 months after surgery.
77 A 39-year-old female with a strong family history of breast cancer presents for diagnostic mammogram for left breast pain. Based on the images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
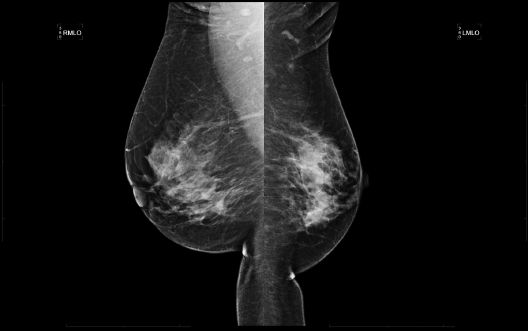
A. Transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap reconstruction
B. Poland syndrome
C. Mastectomy
D. Reduction mammoplasty
78 The following images from a contrast-enhanced breast MRI are provided. In the central right breast, there is clumped nonmass enhancement. Kinetic assessment of the nonmass enhancement using CAD (computer-aided detection) processing software demonstrates which type of curve?
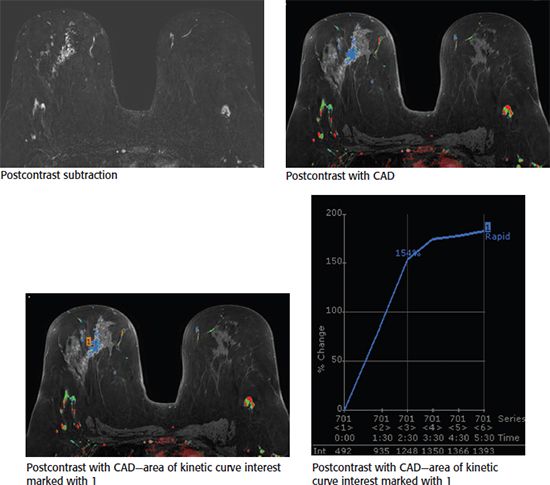
A. Initial slow, delayed washout
B. Initial rapid, delayed persistent
C. Initial rapid, delayed plateau
D. Initial rapid, delayed washout
E. Initial slow, delayed plateau
79 The most common malignant breast mass in a pregnant and postpartum patient is:
A. invasive medullary carcinoma
B. invasive lobular carcinoma
C. invasive ductal carcinoma
D. invasive mucinous carcinoma
E. invasive tubular carcinoma
80 A 55-year-old female was recently diagnosed with an invasive ductal carcinoma of two masses in the left breast. Mass A is 3.1 cm in greatest diameter and is located in the left upper outer quadrant at posterior depth. Mass B is 4 cm in greatest diameter and located in the left lower inner quadrant at middle depth. Which statement is correct?
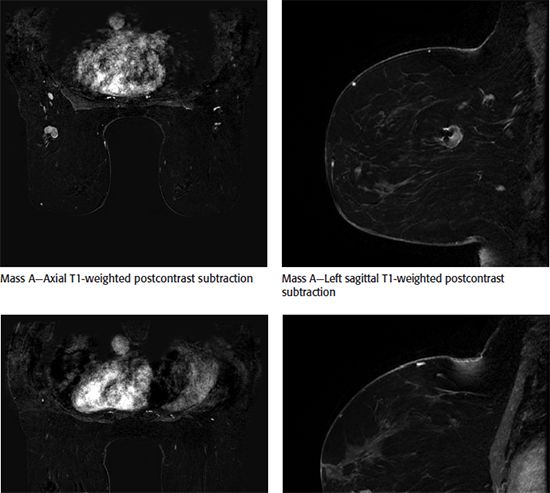
A. The patient is a candidate for whole-breast radiation therapy.
B. The patient is a candidate for breast conserving surgery.
C. The findings are suspicious for multifocal invasive breast cancer on MRI.
D. The findings are suspicious for multicentric invasive breast cancer on MRI.
81
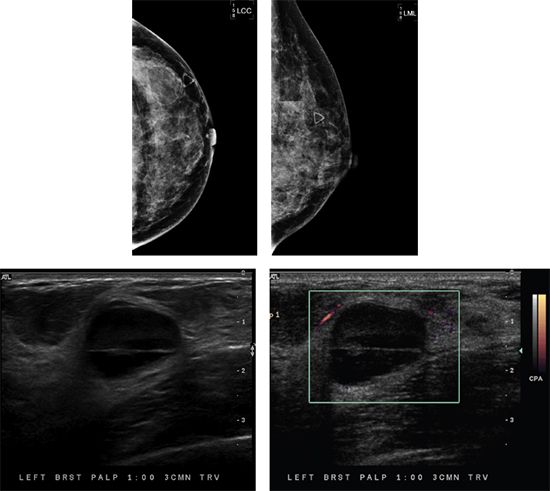
81a A 34-year-old female presents with a palpable lump in her left breast. Based on the mammogram and ultrasound images, which one of the following is the most appropriate BI-RADS category assessment?
A. BI-RADS 1
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
81b Based on the ultrasound images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Hamartoma
B. Galactocele
C. Intramammary lymph node
D. Lipoma
E. Fat necrosis
82 A 41-year-old female presents with a palpable lump in her left breast. Based on the images, what is the most appropriate management?
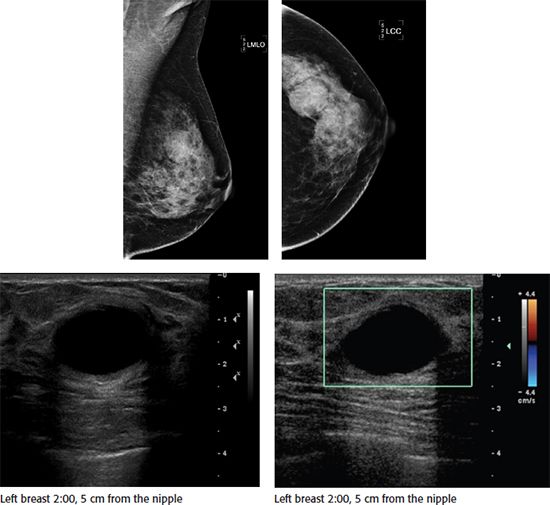
A. No further evaluation
B. Cyst aspiration for diagnosis
C. Core needle biopsy
D. Antibiotic therapy
83 The most common mammographic finding of pregnancy associated breast cancer is:
A. microcalcifications
B. edema
C. architectural distortion
D. mass
E. axillary adenopathy
84 Shown is a spot magnification view of axillary lymph nodes along with ultrasound images taken of the left axillary region. These lymph nodes were seen on ultrasound as well. If this is a new finding in a patient that has a history of ipsilateral breast cancer, what is the BI-RADS category assessment?
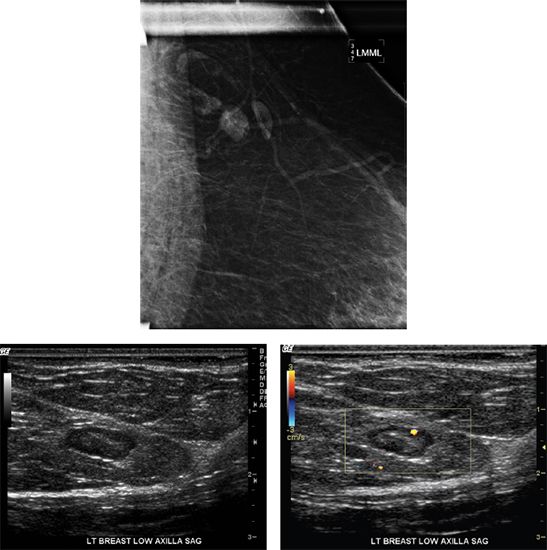
A. BI-RADS 2
B. BI-RADS 3
C. BI-RADS 4
D. BI-RADS 6
85 Shown is a breast MRI image demonstrating a mass in the right breast at 7 o’clock at a middle depth. The time–intensity kinetic curve showed a type I curve. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
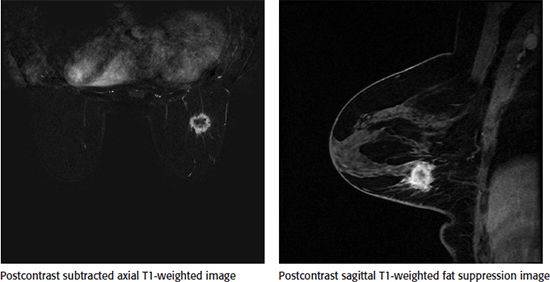
A. Recommend a follow-up 6-month breast MRI to document stability.
B. The mass should be categorized as BI-RADS 2, and continued risk-appropriate screening should be recommended.
C. Biopsy should be performed despite benign kinetics.
D. The study is limited due to suboptimal technique and should be repeated.
86 Based on the diagnostic ultrasound images, which one of the following is the most appropriate BI-RADS category assessment?
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
87 A 46-year-old female presents with two sets of bilateral screening mammograms that are 2 years apart. Based on the images, what is the appropriate BI-RADS category assessment?
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
E. BI-RADS 6
88 Based on the images, what is the correct breast finding?
A. Intracapsular rupture of the right breast implant
B. Radial fold of the right breast implant
C. Collapse/rupture of the right breast implant
D. Capsular contracture of the right breast implant
89 A 48-year-old female complains of a palpable cord-like area in her left breast. Based on the diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound images, what is the appropriate clinical management?
A. Refer patient to a breast surgeon for surgical excision and axillary node sampling.
B. Ultrasound-guided core biopsy is recommended.
C. Assure the patient that the condition is self-limited and will resolve.
D. Breast MRI is recommended.
E. Wide local excision should be performed.
90 A 40-year-old female comes for a baseline screening mammogram. Based on the mammogram images, what is the appropriate BI-RADS category assessment?
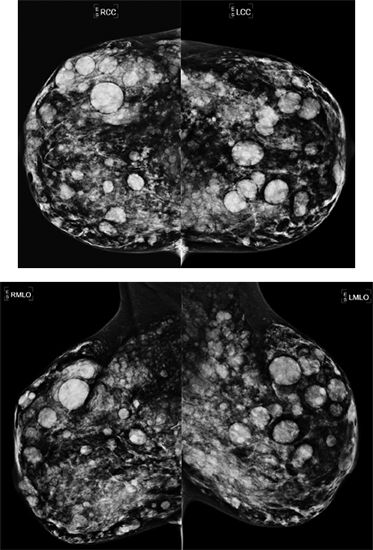
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
91 Poland syndrome can be associated with increased incidence of which of the following cancer?
A. Hodgkin lymphoma
B. Ovarian cancer
C. Thyroid cancer
D. Breast cancer
E. Hepatocellular cancer
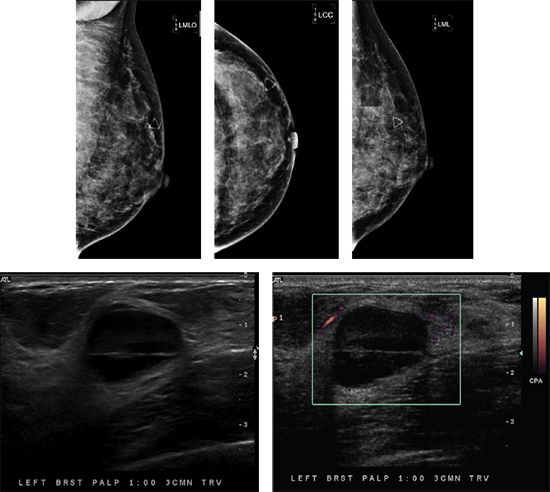
92 A 34-year-old female presents with history of a palpable abnormality in the left breast. Based on the images, what is the most appropriate management?
A. No further evaluation
B. Cyst aspiration for diagnosis
C. Core needle biopsy
D. Antibiotic therapy
93 What is the inheritance pattern of Poland syndrome?
A. Mitochondrial inheritance
B. Autosomal dominant
C. Autosomal recessive
D. X-linked dominant
E. X-linked recessive
94 An 87-year-old female presents with a palpable lump (triangular skin marker). Six years ago she was diagnosed with breast cancer and had a subsequent lumpectomy, followed by radiation therapy. The most likely diagnosis is
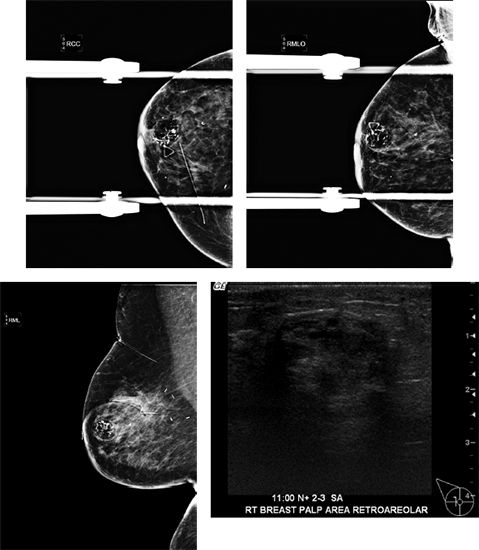
A. Intramammary lymph node
B. Hemangioma
C. Lipoma
D. Fat necrosis
E. Hamartoma
95 A 57-year-old postmenopausal female with a recent breast biopsy diagnosis of focal fibrosis is likely taking which one of the following medications?
A. High-dose aspirin
B. Corticosteroids
C. Thyroid replacement therapy
D. Hormone replacement therapy
E. Insulin
96 Molecular breast imaging in a 45-year-old woman shows bilateral, extensive, patchy uptake of the isotope. The most likely diagnosis is
A. Active fibroglandular breast tissue
B. Simple breast cysts
C. Fibroadenomas
D. Chronic fat necrosis
E. Postoperative scar tissues
97 What is the most common cancer to spread to the breast?
A. Melanoma
B. Breast cancer
C. Lung cancer
D. Medullary thyroid cancer
E. Endometrial cancer
98 Shown are diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound images of a 52-year-old female with history of a palpable lump in the left breast. The patient underwent an ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy. Pathology results came back as phyllodes tumor. Based on imaging finding and pathology results, which of the following statement is most appropriate recommendation?
A. Surgical excisional biopsy
B. Breast-specific gamma imaging (BSGI)
C. Breast MRI
D. Follow-up diagnostic ultrasound in 6 months
99 Which condition most commonly causes bilateral breast edema?
A. Inflammatory breast cancer
B. Superior vena cava syndrome
C. Mastitis
D. Trauma
E. Coumarin necrosis
100 A 28-year-old female presents with a palpable abnormality in the left breast. Based on the images, what is the most appropriate management?
A. No further management
B. Cyst aspiration
C. Core needle biopsy
D. Antibiotic therapy
101 After lumpectomy and radiation therapy the enhancement of the postoperative cavity site begins to subside on postcontrast breast MRI after how many months?
A. 3–5 months
B. 6–7 months
C. 8–9 months
D. 10–18 months
102 The statement “Multiple, bilateral, circumscribed, noncalcified masses” is given a BI-RADS of:
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
103 A 78-year-old male presents with a palpable lump in the right breast. Based on the diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound images, what is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Invasive ductal carcinoma
B. Cyst
C. Lipoma
D. Fibroadenoma
E. Gynecomastia
104 A 2.5 cm in greatest dimension malignant mass with metastasis to a level 2 movable ipsilateral level 1 axillary lymph node and with no clinical or radiographic evidence of distant metastasis has a TNM staging classification of
A. T1a, N2, M0
B. T2, N1, M0
C. T3, N3, M0
D. T2, N2a, M1
E. T4, N3, M0
105 The calcifications seen on the mammogram below are dermal in nature. What is the cause?
A. Calcium carbonate
B. Methyl salicylate
C. Zinc oxide
D. Glycerol
106 Based on the mammographic and sonographic images below, what is the most likely diagnosis?
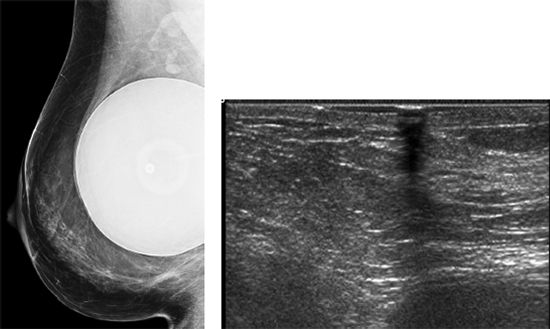
A. Sebaceous cyst
B. Normal breast tissue
C. Scar
D. Invasive lobular carcinoma
107a The first set of mammographic images is from 3 years ago. After this mammogram, asymmetry in the upper outer quadrant was excised demonstrating pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia (PASH). Patient returns for annual screening mammogram. What is the appropriate BI-RADS category assessment?
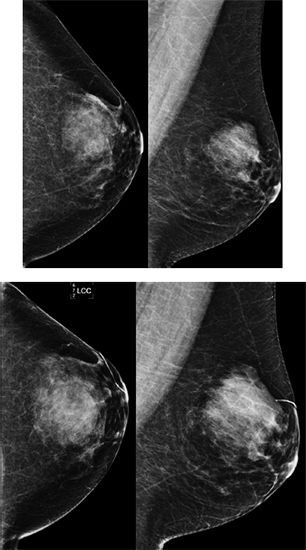
A. 0
B. 1
C. 3
D. 4
107b Additional views and ultrasound images are given below. What is the next step in management?
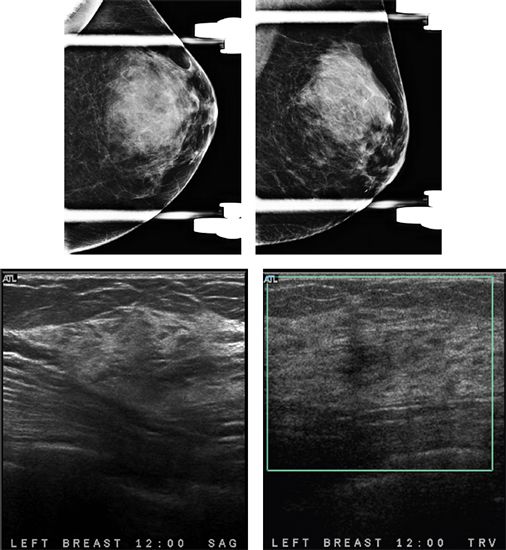
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree