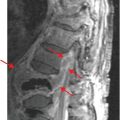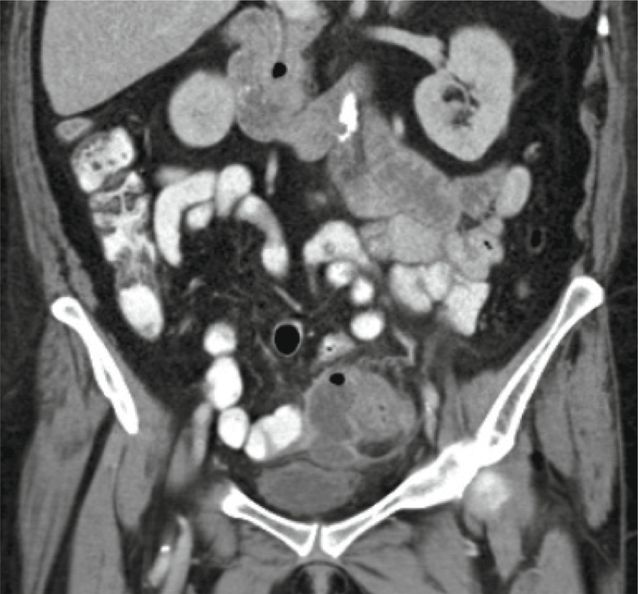
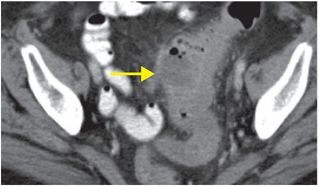
Diagnosis: Diverticulitis with abscess
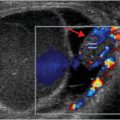
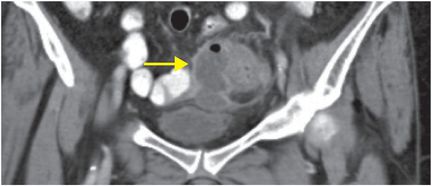
Axial (left image) and coronal (right image) contrast-enhanced CT shows thickening of the sigmoid colon, with pericolonic fat stranding. A focal fluid collection (arrows) containing foci of gas adjacent to the colon is consistent with an abscess.
Discussion
Diverticulitis is the acute inflammation and infection of a colonic diverticulum.
Diverticulosis, the asymptomatic disease of multiple colonic diverticula, is a Western disease thought to be due to low-fiber diet, with increasing prevalence with age.
Nearly all diverticula are located in the left colon, but occasionally the rare right-sided diverticula can become inflamed and mimic other more common causes of right lower quadrant pain.
CT is the primary modality for imaging acute diverticulitis and plays a central role in triage.
In addition to confirming the presence and severity of diverticulitis, CT can evaluate for potential complications.
Diverticulitis can be characterized as uncomplicated or complicated.
Uncomplicated diverticulitis implies that the bowel lumen is intact, and features two primary CT findings:
Colonic wall thickening (greater than 3 mm is abnormal)
Pericolonic fat stranding. Often, a diverticulum will be identified as the epicenter of the inflammation.
Diverticulitis can become complicated when one or more associated findings are present in addition to the colonic wall thickening and pericolonic fat stranding:
Abscess
Extraluminal air, which would signify perforation or microperforation
Bowel obstruction
Fistula, with colovesicular being the most common
Mesenteric vein thrombosis
The difficulty in distinguishing acute diverticulitis from malignancy is a longstanding clinical problem.
After an initial episode of acute diverticulitis, follow up with either colonoscopy or CT colonography is recommended to evaluate the extent of diverticular disease, and to exclude colon cancer.
Clinical synopsis
This patient, a 68-year-old male with diverticulitis and a small intramural abscess, was admitted and treated initially with intravenous ceftriaxone. He was discharged on a 7-day course of oral antibiotics and did well after this episode.
Self-assessment
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree