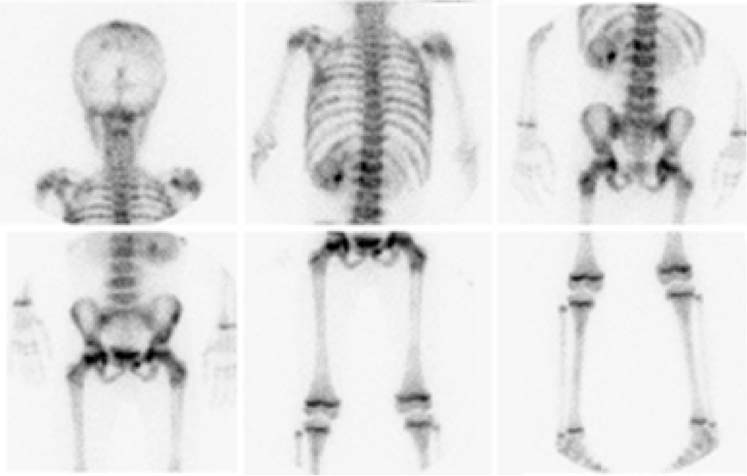
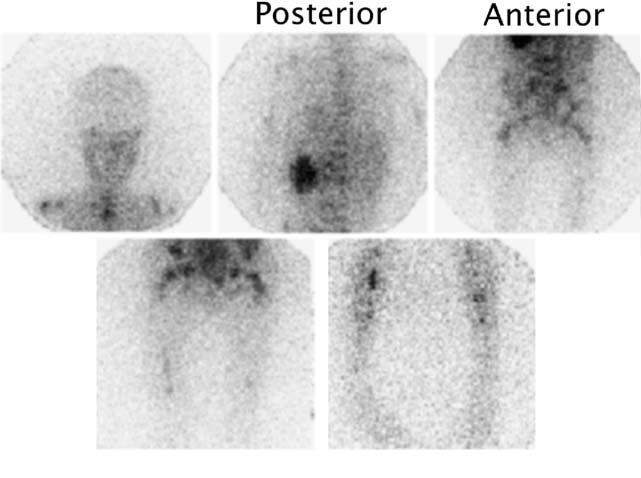
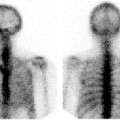
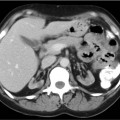
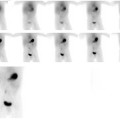
CASE 163 A 10-year-old boy presents with persistent vague abdominal pain, fever, decreased appetite, and diarrhea. Abdominal ultrasonography and CT reveal a left suprarenal mass. Fig. 163.1 Fig. 163.2 • 99mTc-MDP at 0.2 mCi/kg of body weight is given intravenously. The minimum dose is 1 mCi; the maximum dose is 20 mCi. • Use a high- or ultra-high-resolution, low-energy, parallel-hole collimator. Supplemental pinhole magnification images may be obtained for improved detail. SPECT is performed for better three-dimensional localization. • Planar whole-body or spot views of the entire skeleton are obtained 4 hours after tracer injection. • 123I-MIBG at a dose of 0.2 mCi/kg is given intravenously. The minimum dose is 1 mCi, and the maximum dose is 10 mCi. • Use a high- or ultra-high-resolution, low-energy, parallel-hole collimator. • Energy window is 20% centered at 159 keV. • Whole-body images and SPECT are obtained as needed 24 hours after injection. • Thyroid uptake can be blocked by the administration of saturated solution of potassium iodide, one drop three times a day, beginning 1 day before imaging and continuing for 3 days. The workup for metastatic disease includes 99mTc-MDP bone scan (Fig. 163.1) and 123I-MIBG scintigraphy (Fig. 163.2). Scintigraphy with 99mTc-MDP shows areas of abnormal tracer uptake in the calvarium, spine, pelvis, ribs, femora, and tibiae. In addition, tracer is concentrated in the left adrenal mass. Scintigraphy with 123I-MIBG demonstrates an intense focus of radiotracer uptake in the left upper abdomen and diffuse involvement of the skeleton. (MIBG uptake) • Neuroblastoma • Pheochromocytoma • Paraganglioma • Gastrinoma
Clinical Presentation
Technique
99mTc-MDP Bone Scan
123I-MIBG Scintigraphy
Image Interpretation
Differential Diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree