 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
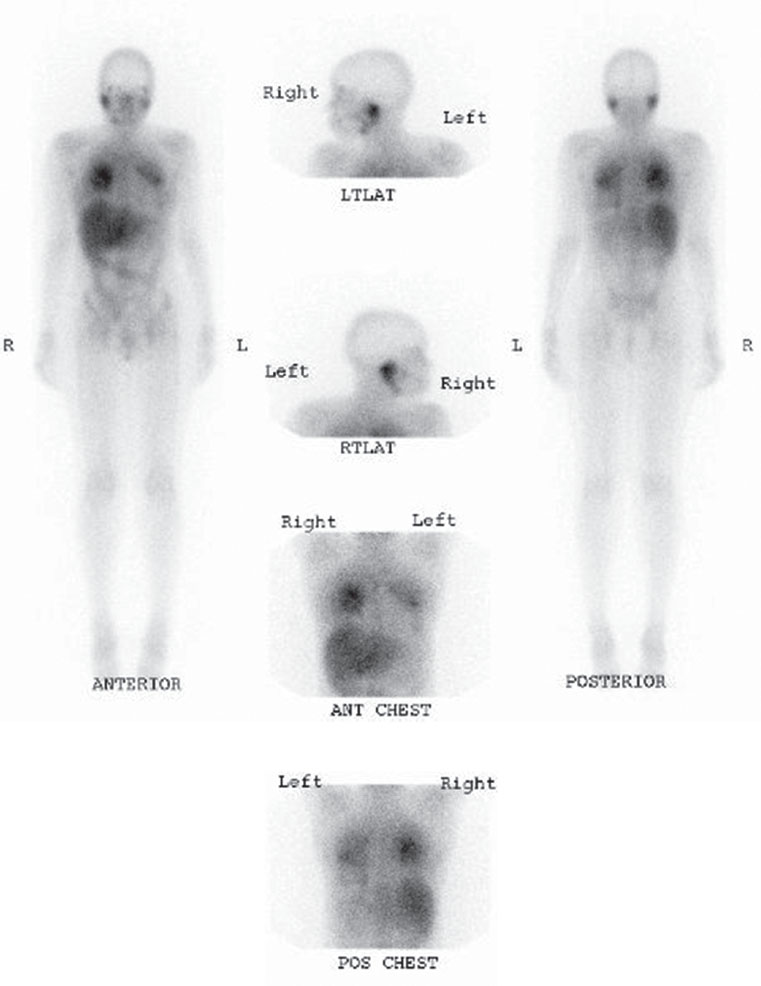
A 42-year-old woman with human immunodeficiency virus and shortness of breath. A chest radiograph was normal. Images were acquired at 48 hours after injection of radiotracer.
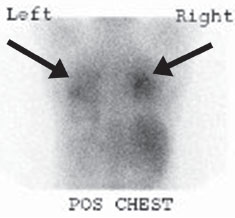
Forty-eight–hour delayed whole-body planar images as well as spot views of the chest demonstrate physiologic uptake in the liver, bowel, and lacrimal and salivary glands. Diffuse, intense uptake (greater than liver) is seen throughout both lungs, most notably in the upper lobes (arrows).
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
• Gallium scan demonstrating Pneumocystis carinii/ jiroveci pneumonia (PCP): The physiologic distribution makes Ga67 the correct radiopharmaceutical. Diffuse, intense pulmonary parenchymal uptake is most likely PCP (or other atypical infection), given the history.
• Sarcoid: This is typically associated with paratracheal and bilateral hilar lymph node uptake on Ga67, often with increased salivary and lacrimal involvement (“panda” sign). It can also, however, present with diffuse pulmonary parenchymal uptake alone.
• Tumor: Several malignancies, including lung cancer, lymphoma, melanoma, and sarcoma (except Kaposi), are Ga67-avid. These are typically more focal, however.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree