and Bruce J. Barron2
(1)
Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Illinois, USA
(2)
School of Medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, USA
1 FDG
1.1 F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG): Positron Emission Tomography (PET/CT)
Clinical Use
Oncology, cardiac viability, brain imaging.
18-F
Cyclotron produced. t phys 109.8 min. Decays positron emission to O-18. 511 KeV photons are emitted (annihilation radiation).
18-FDG Mechanism
Glucose metabolism agent. FDG [conversion by hexokinase/glucokinase FDG-6p] → trapped in cell (missing 2’ OH groups which are needed for metabolism). After full decay from F-18 to O-18 (heavy oxygen), it will combine with H+ ion to create 2’ OH groups and will be metabolized by glycolysis.
Brain: Scan will demonstrate change in cerebral glucose metabolism associated with foci of epileptic seizures/tumors (please refer to “Flash Facts-Brain Scan”).
Cardiac: Normal cells utilize fatty acids as main source of energy; ischemic cells utilize glucose (for more images, please refer to “Flash Fact Cardiac Scans”).
Pre-exam sugar load: Increases insulin secretion and decreases protein breakdown to AA → decrease amino acid plasma level → increase glucose uptake by the ischemic myocardial cells.
Oncology: Hexokinase concentration is higher in cancer cells followed by inflammatory cells.
Percentage of Uptake in Myocardium
1–4 %.
Image Protocol
Cardiac viability: (1) Rb-82 rest perfusion protocol. (2) Glucose/insulin load followed by 10 mCi F-18 FDG. (3) 30 min post-FDG injection CT and PET (wait for 60 min for diabetic patients). Nowadays, glucose load is optional.
Oncology/brain: Fasting for 6–8 h (oncology) and 4 h (brain). (1) FDG injection IV. (2) “Cooking” time for 45 min to 1 h to obtain high target to background. (3) CT and PET images.
Imaging
PET/CT.
Dose
10–15 mCi.
Critical Organ
Bladder.
Distribution
Brain > > kidneys, ureters, and bladder> > liver. Variable: heart, GI, salivary glands, uterus, ovaries, and testes.
Clearance
Kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
Distribution and Clearance
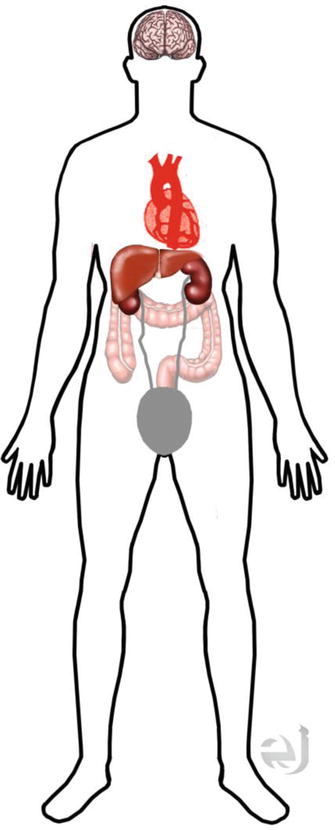
Distribution Brain > > kidneys, ureters, and bladder> > liver. Variable – heart, GI, salivary glands, uterus, ovaries, and testes.
Clearance Kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
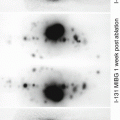
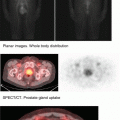
PET/CT Viability Study

PET/CT Oncology Abnormal Patterþns
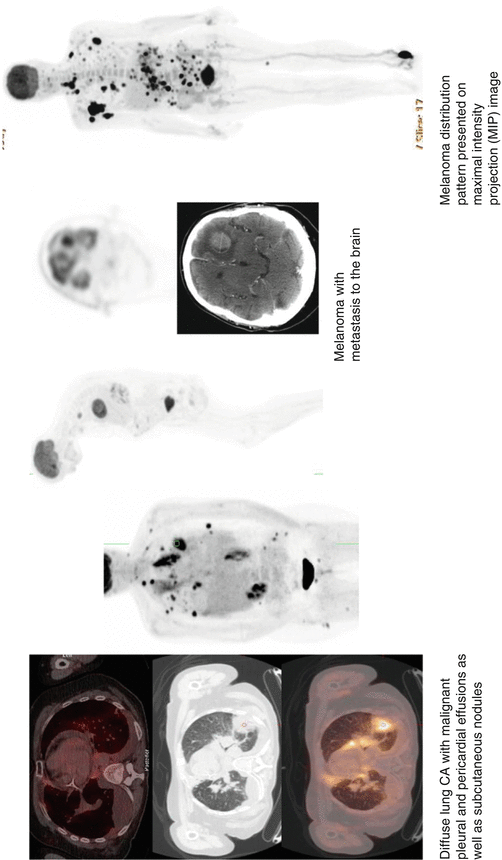
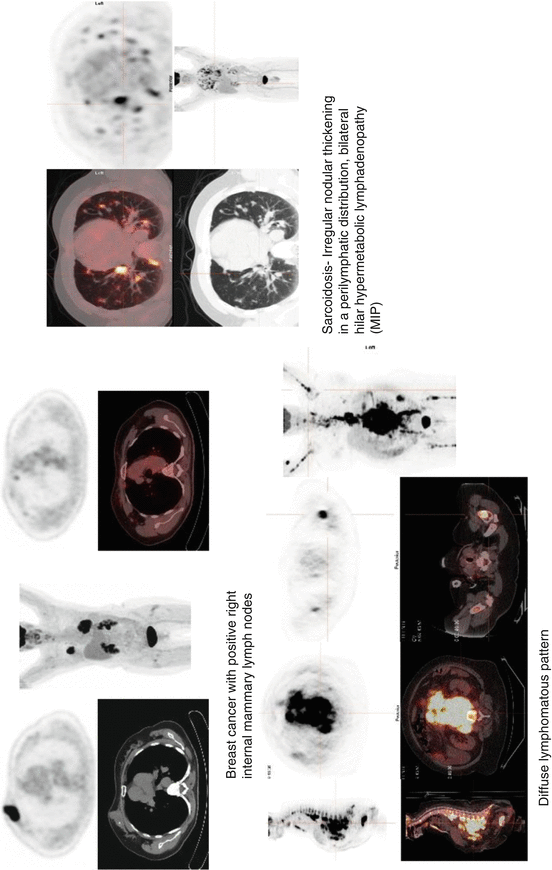
1.2 Flash Facts: FDG PET/CT Findings Which Upstage Cancers
FDG PET/CT is an essential modality for the accurate staging of some cancers in which progression is suspected. FDG PET/CT utility is based on NCCN recommendation. A few key facts are important to remember when reading FDG PET/CT. The presence of these findings may affect patients’ treatment and survival rate.
Lung (NSLC)
Mediastinal lymph nodes (LN), ipsilateral or contralateral → N2 → stage IIIA → inoperable.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree