5 Cavum Septum Pellucidum
5.1 Case Presentation
5.1.1 History and Physical Examination
An 18-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents with an episode of seizure-like activity.
On physical examination, the patient is alert and oriented with no focal neurologic deficit.
5.1.2 Imaging Findings and Impression
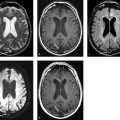
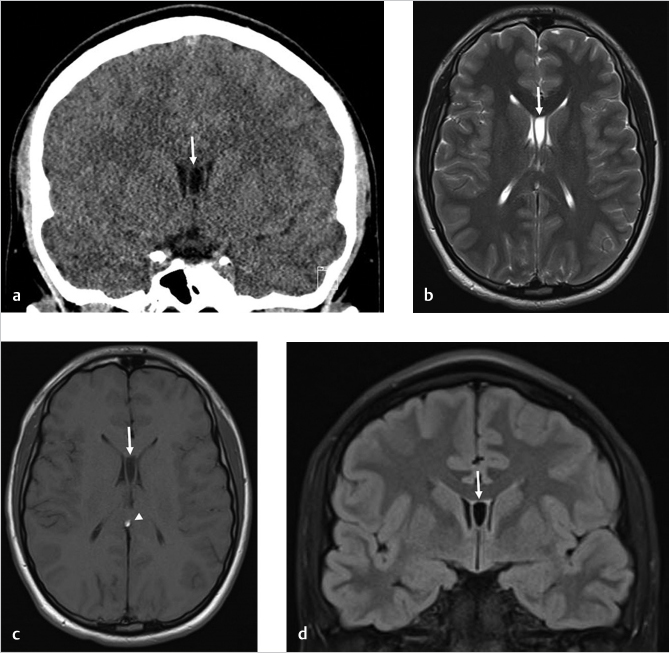
Coronal CT scan of the head without contrast (▶ Fig. 5.1a) and brain MR images without contrast including axial T2-weighted (▶ Fig. 5.1b), axial T1-weighted (▶ Fig. 5.1c), and coronal fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR; ▶ Fig. 5.1d) images show persistence of a fluid-filled cavity (white arrows) in between leaflets of the septum pellucidum extending posteriorly to the foramina of Monro, consistent with a cavum septum pellucidum. There is an incidental curvilinear pericallosal lipoma (white arrowhead) along the splenium.
5.2 Differential Diagnosis
Cavum septum pellucidum (CSP):
It is a fluid-filled cavity within the leaflets of septum pellucidum, which follows the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) signal intensity on all sequences located anterior to columns of fornix.
Cavum septum vergae (CSV):
Posterior extension of CSP beyond the columns of the fornix and foramen of Monro.
CSV is located posterior to the CSP and posterior and superior to the columns of fornix. 1
It is hypodense with CSF density on head CT scans without contrast. It follows CSF signal intensity on MR images of the brain and will be suppressed on FLAIR sequences.
Although the CSP and CSV are believed to represent anatomic variations, investigators have shown an increased prevalence of them in traumatic brain injury patients. 2 , 3
A large CSP in patients with schizophrenia can also be associated with more severe symptoms. 4
Cavum velum interpositum:
It is an enlarged potential space in between infolded layers of the velum interpositum.
Anatomically, it is triangle shaped and lies between the internal cerebral veins.
It is located below the column of the fornix and the splenium of corpus callosum and posterior to the foramen of Monro.
It has CSF-like density on head CT scans with a triangular configuration pointing forward and not extending anterior to the foramen of Monro. 5
Isointense to CSF on all MR sequences with a hypointense membrane surrounding it.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree