and Bruce J. Barron2
(1)
Loyola University Medical Center, Maywood, Illinois, USA
(2)
School of Medicine, Emory University, Atlanta, USA
1 Thyroid Ablation
1.1 Thyroid Ablation with I-131 Na. Low-Dose Treatment <33 mCi
Indications
Clinical and subclinical hyperthyroidism (low TSH).
I-131
Fission product. t phys 8.1 days Emits gamma photons 364.4 KeV and ß-energy.
Thyroid radiation dose approximately 1 rad/μCi.
I- 123
Cyclotron-produced t phys 13.3 h Emits gamma photons 159 KeV.
Mechanism
Rapid GI absorption of iodine to the extracellular fluid → active uptake in the thyroid follicles by Na/I symport (trapping) → protein bound iodine (organification). All drugs which affect the thyroid hormone synthesis pathway will affect iodine uptake (highly regulated by TSH). Additional uptake (nonprotein-bounded uptake mechanism) by salivary gland, stomach cells (no trapping), and hepatocytes (thyroglobulin metabolism).
Thyroid Uptake Evaluation
Preparation Stop Tapazole (methimazole) and PTU for 3 days; no iodinated contrast study in the last 6 weeks. Stop amiodarone 3–6 m prior to treatment.
Perform pregnancy test (when applicable) using urine or serum test, ideally within 24 h prior treatment.
Diagnostic Dose with I-123 NaI
Day 1 0.2–0.4 mCi of I-123 NaI oral uptake.
Day 2 Thyroid scan and uptake.
Ablation Dose with I-131 NaI
(Written directive is required, signed by an authorized user).
Method 1: Formula based: Dose will be calculated based on % thyroid gland uptake and thyroid mass.
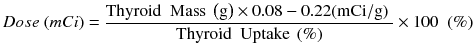
Range is typically 6–30 mCi.Method 2: Empiric dose for Graves’ disease, toxic multinodular goiter, and solitary toxic nodules. 15 (toxic nodule) −30 mCi (multinodular goiter).
Day of treatment: Check for pregnancy test results when applicable. Sign an agreement for therapy consent. Call to order (dose, name of the patient, and date of birth). Give the capsule with one glass of water. Hold food and liquids for 2 h.
Follow up
with endocrinology for TSH level.
1.2 Thyroid Ablation with I-131 NaI. High-Dose Treatment >33 mCi
Preparation
Target TSH level: >30 μU/mL (achieved by Thyrogen IM injections or withdrawal of Synthroid). No iodinated contrast study in the last 6–8 weeks.
Low iodine diet: 10–14 days before administration of therapy. Stop low iodine diet 2 h up to 72 h after treatment (no definitive consensus).
Pregnancy test: (when applicable) using urine or serum test, ideally within 24 h prior treatment.
Ablation Protocols
Surveillance protocol indicated when patient has low thyroglobulin level after prior ablation.
Day 1 Thyrogen 0.9 mg IM.
Day 2 Thyrogen 0.9 mg IM.
Day 2 or 3 4 mCi of I-131 NaI or 2 mCi of I-123 NaI.
Day 4 or 5 Whole body scan at 48 h after the oral uptake of I-131 NaI or at 24 h after the oral uptake of I-123 NaI.
If treatment is indicated, repeat with treatment protocol.
Treatment protocol indicated when patient has high thyroglobulin level after prior ablation or 2–3 months after thyroidectomy.
Thyrogen (recombinant TSH) injection protocol
Day 1 Thyrogen IM.
Day 2 Thyrogen IM + NaI-123 oral uptake.
Day 3 Whole body scan followed by treatment with I-131 NaI as needed (ideally I-131 NaI treatment will be given when TSH peaks at 36 h post 2nd Thyrogen injection).
Withdrawal protocol
Patient preparation: Discontinue thyroid hormone – T4 (thyroxine) for 3–4 weeks, T3 (triiodothyronine) 10–14 days, until TSH > 30 μU/mL.
Day 1 I-123 NaI 2 mCi (may also use I-131 NaI 2–4 mCi).
Day 2 or day 3 Whole body scan at 48 h after the oral uptake of I-131 NaI or at 24 h after the oral uptake of I-123 NaI.
Treatment: As long as patient is off thyroid hormones, treatment can be given on any day. Resume thyroid replacement hormones 72 h posttreatment.
TSH Suppression Posttreatment
High-risk and intermediate-risk thyroid cancer patients: TSH < 0.1 mU/L.
Low risk patients: TSH 0.1–0.5 mU/L.
Dose
Diagnostic Dose with I-123 NaI
0.2–0.4 mCi of I-123 NaI oral uptake.
Ablation dose with I-131 NaI
Will be based on I-123 distribution and pathology report.
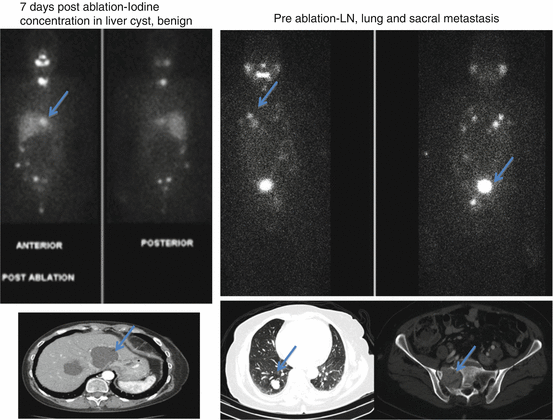
Local disease (thyroid bed): 30–100 mCi I-131 NaI (the higher the uptake in the thyroid surgical bed, the lower the ablation dose).
Positive LNs: 150–200 mCi I-131 NaI.
Metastasis: ≥200 mCi I-131 NaI.
Lung metastasis will be based on dosimetry to prevent long-term pulmonary fibrosis; limit of 80 mCi/2.96 GBq activity retention in the lung (George Sgouros et al., J Nucl Med. 2006;47(12):1977–1984).
Safety
Negative pregnancy test (when applicable).
Critical Organ
Thyroid.
Distribution
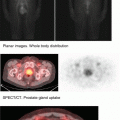
Iodine containing tissue (thyroid tissue, salivary gland, sebaceous glands, and stomach), GI lumen (oral admin), 7 days post therapy scan may demonstrate liver uptake due to circulating thyroglobulin. Thyroglobulin will be metabolized by the hepatocytes.
Clearance
By kidneys, metabolized in the liver.
Suggested Reading
Society of nuclear medicine procedure guideline for therapy of thyroid disease with iodine-131 (sodium iodide) 3.0
Bryan R. Haugen et al; 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer.
Distribution and Clearance
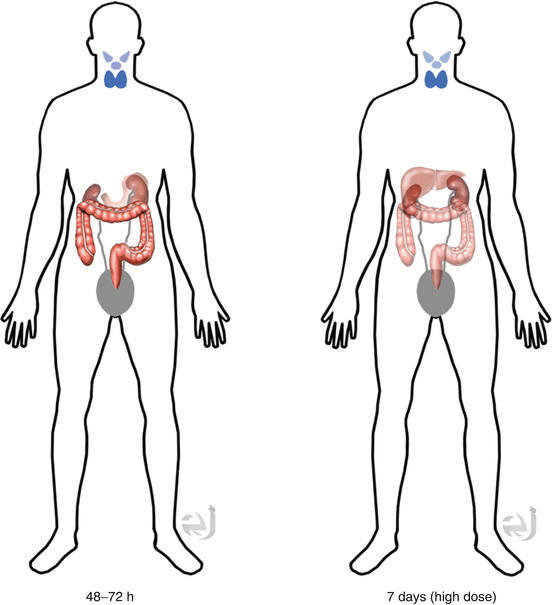
Distribution Iodine containing tissue (thyroid tissue, salivary gland, and stomach) + GI lumen (oral admin), 7 days post scan – liver uptake due to thyroid hormone metabolism.
Clearance By kidneys, metabolized in the liver.
Distribution and Clearance

Distribution Iodine containing tissue (thyroid tissue, salivary gland, and stomach) + GI lumen (oral admin), 7 days post scan – liver uptake due to thyroid hormone metabolism.
Clearance By kidneys, metabolized in the liver.
Abnormal Distribution Patterns
2 Liver Tumor Ablation
2.1 Radioembolization with Yttrium-90 Microspheres
Indication
Ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma and metastatic disease to the liver
Y-90
Pure β-emitter with bremsstrahlung radiation produced and detectable externally. Y-90 production bombardment of Y-89 from nuclear reactor. Decays into stable zirconium. t phys 64.1 h. Emits: ß– with maximum energy of 2.284 MeV. Average penetration: ~ 5 mm in soft tissue (100–200 cells) Images : Y-90 low E Bremsstrahlung X-rays.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree