Case 7
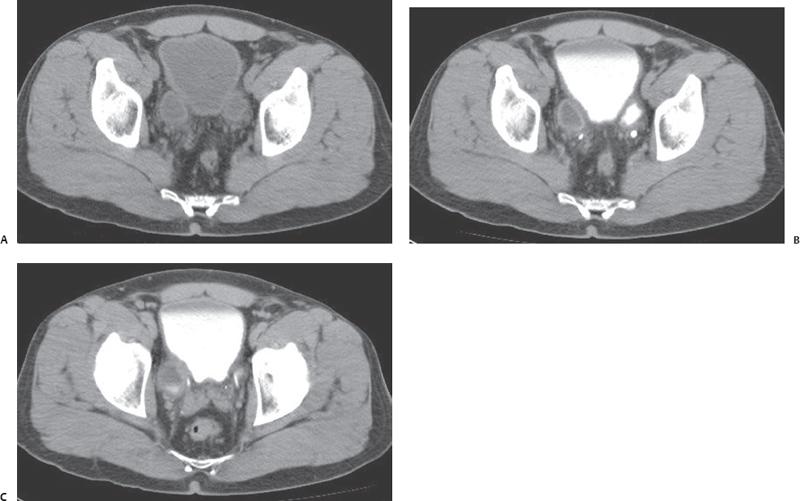
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
A 31-year-old man with recurrent urinary tract infection.
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
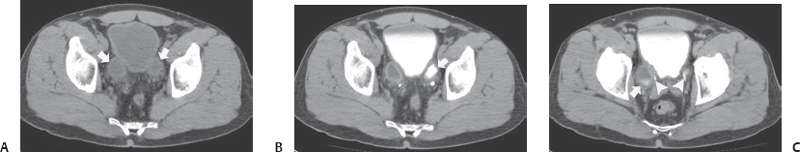
(A) Precontrast axial computed tomography (CT) image at the level of the urinary bladder shows two thick-walled, fluid-filled structures lying posterior to the urinary bladder (arrows). No calcifications are seen within their lumina. No fat stranding is seen in the pelvis. (B) Postcontrast axial CT image obtained in the excretory phase at the same level as Figure A shows excreted contrast in the left fluid-filled structure (arrow), thus demonstrating communication with the urinary tract. No filling defect is seen. (C) Postcontrast axial CT image obtained in the excretory phase at a level below that of Figures A and B shows excreted contrast in the right fluid-filled structure (arrow). The lower ends of the ureters (arrowheads) are seen to be intimately related to the abnormalities close to where they insert into the urinary bladder.
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
• Hutch diverticula: These are congenital outpouchings arising from the urinary bladder. The existence of communication can be deduced indirectly from the presence of excreted contrast on contrast-enhanced excretory phase images. A location adjacent to the ureterovesical junction is characteristic.
• Acquired bladder diverticula:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


