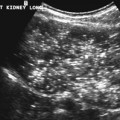
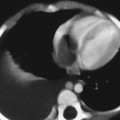
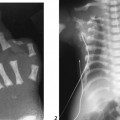
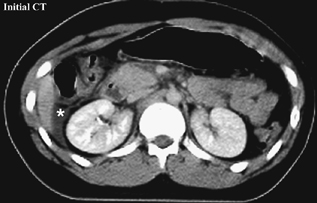
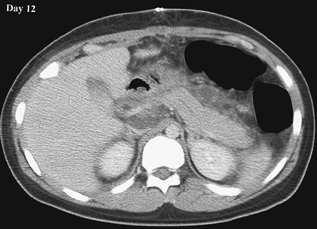
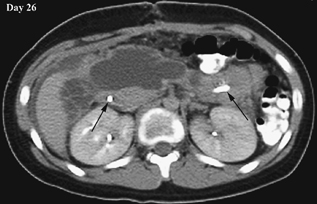
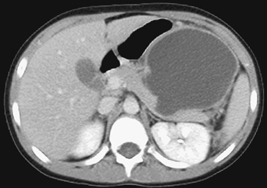
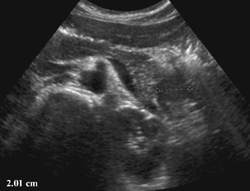
CASE 72 A 14-year-old boy hit in a motor vehicle accident was brought to the emergency department. CT scan was performed with subsequent follow-up studies on days 12 and 26. Figure 72A Figure 72B Figure 72C On the initial abdominal CT, there is free fluid in the subhepatic area and adjacent to the duodenum (Fig. 72A, asterisk). On day 12, the CT demonstrates injury to the anterior aspect of the head of the pancreas and a peripancreatic fluid collection (Fig. 72B). On day 26, a pseudocyst is noted next to the body and head of the pancreas (Fig. 72C), with persistent perihepatic fluid. A nasojejunal tube is present (Fig. 72C, arrows). Figure 72D Traumatic pancreatic pseudocyst following a handlebar injury. CT shows transection of the tail of the pancreas with pseudocyst formation. Figure 72E (Same patient as in Fig. 72D) Follow-up ultrasound 4 months later demonstrates significant reduction of size of pseudocyst, without interventional procedure.) Pancreatic pseudocyst Cystic lesions of pancreas include: A pseudocyst is the most common type of pancreatic cyst in children. Granulation and fibrous tissue line the pseudocyst. They may be solitary or multiple, and of variable size (5–10 cm). Pseudocysts may be present within the pancreas or adjacent to the pancreas, or they can be found in the lesser sac or extending into the chest or pelvis. Infection of pseudocysts may occur with Escherichia coli, Enterococcus, or Staphylococcus.
Clinical Presentation
Radiologic Findings
Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Discussion
Background
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree