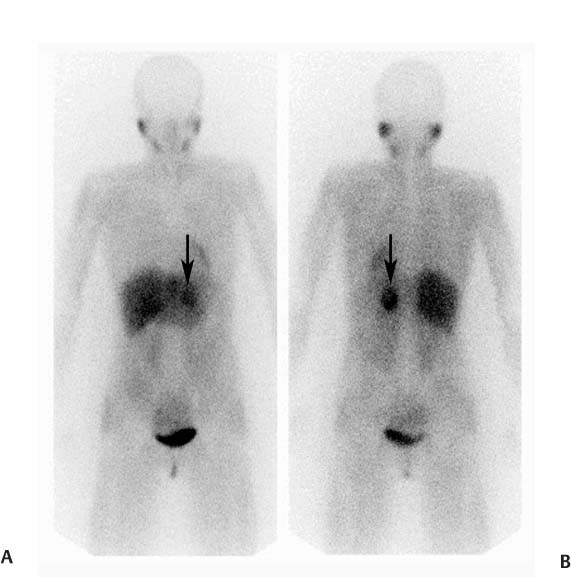
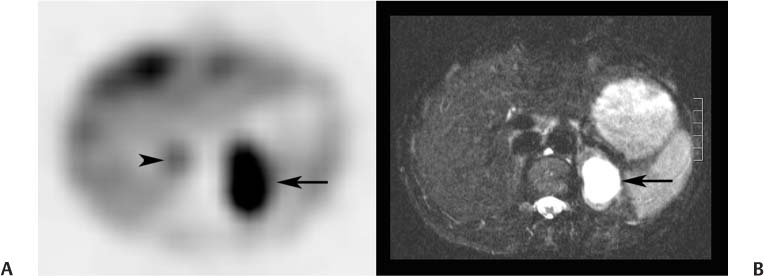
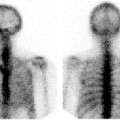
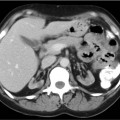
CASE 92 A 41-year-old woman presents with palpitations associated with nausea and severe headaches. At the time of assessment, her blood pressure is normal at 126/78 mm Hg, and her heart rate is normal at 84 beats/min. Laboratory workup demonstrates significantly elevated levels of urinary vanillylmandelic acid, epinephrine, and norepinephrine. Fig. 92.1 Fig. 92.2 • 123I-MIBG • The patient should be well hydrated. • Drugs known or expected to interfere with MIBG uptake should be withheld. These include some β-blockers (in particular, labetalol), catecholamine agonists including oral decongestants, anti-psychotics, tricyclic antidepressants, some calcium channel blockers, and cocaine. A more detailed list, along with the recommended withholding period, is provided in Bombardieri et al. (2003). • Thyroid blockade should be performed with saturated potassium iodide three times daily, three drops each time, beginning on the day before the injection and continuing for a total of 3 days (123IMIBG) or 5 days (131I-MIBG). • 5 mCi • Slow intravenous injection over 5 minutes • Low-energy, high-resolution collimator • 159-keV photopeak, 20% window • Planar: anterior and posterior views from head to pelvis at 4 and 24 hours • SPECT: abdomen and pelvis at 4 hours • SPECT: chest, abdomen, and pelvis at 24 hours Anterior (Fig. 92.1A) and posterior (Fig. 92.1B) planar images from a 123I-MIBG scan demonstrate markedly increased uptake in a structure (arrow) in the left upper abdomen posteriorly. There are no other abnormalities. There is normal physiologic uptake within the liver, heart, salivary glands, and bladder. An axial slice from the 123I-MIBG SPECT acquisition (Fig. 92.2A) confirms intense uptake in a structure (arrow) in the left retroperitoneum. There is very mild uptake in the right retroperitoneum associated with the adrenal gland (arrow-head). The corresponding MRI (Fig. 92.2B) demonstrates intense signal on T2 sequence in the structure in the left retroperitoneum. There is no MRI abnormality in the vicinity of the right adrenal gland. • Pheochromocytoma • Ganglioneuroma • Carcinoid Left adrenal pheochromocytoma. Normal mild uptake in right adrenal gland. The patient underwent left adrenalectomy, including removal of a 3.7-cm pheochromocytoma. She has remained asymptomatic since, and urinary catecholamine levels have repeatedly been normal.
Clinical Presentation
Technique
Image Interpretation
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosis and Clinical Follow-Up
Discussion
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree