CHAPTER 16 Aberrant (Intratympanic) Internal Carotid Artery
Epidemiology
The incidence of an aberrant course of the internal carotid artery (ICA) is less than 1%. More than 60 to 90% of the cases described in the literature occur in females, with a majority occurring on the right side. No explanation for this preponderance is provided in the literature.
Clinical Features
This is an unusual but important condition that may be detected incidentally or may present with pulsatile tinnitus or conductive hearing loss. The aberrant ICA appears as a vascular-appearing bluish retrotympanic mass that resembles a middle ear paraganglioma clinically. This is rarely seen bilaterally. It is important that the diagnosis be made to prevent the disastrous outcome of an inadvertent biopsy or surgical injury.
Pathology
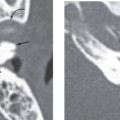
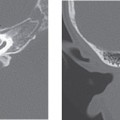
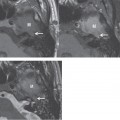
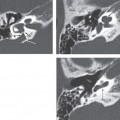
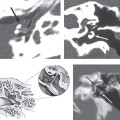
Embryologically, an aberrant ICA appears to occur when there is regression or atresia/agenesis of the cervical segment of the ICA, and it is replaced by an enlarged inferior tympanic branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery, which anastomoses with an enlarged caroticotympanic artery. This usually tiny vessel enters the tympanic cavity through the inferior tympanic calculus along with the Jacobson tymased panic branch of cranial nerve IX. There is then reconstitution of the petrous ICA via the communication through a dehiscence in the carotid canal.
Treatment
There is no treatment for an aberrant ICA, because it is a rare developmental anomaly that provides a critical anastomosis for intracranial blood flow. As stated above, clinical findings can mimic a glomus tympanicum. Correct diagnosis is important to prevent the disastrous outcome of a biopsy or potentially the endaural resection of a presumed small glomus tumor.
For cases of an aberrant ICA associated with pulsatile tinnitus or hemorrhage, treatment has included interposition of synthetic material or sacrifice of the vessel.
Imaging Findings
CT
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree