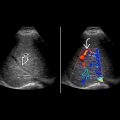
KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Acute inflammation of gallbladder (GB) secondary to calculus obstructing cystic duct
Imaging
- •
US 1st-line imaging test
- •
Distended GB (> 5 cm transverse diameter) with rounded/ballooned shape
- •
Gallstones ± impaction in GB neck or cystic duct
- •
Diffuse GB wall thickening (> 4-5 mm)
- •
Hazy delineation of GB wall with echogenic pericholecystic fat ± pericholecystic fluid
- •
Positive sonographic Murphy sign: Pain and tenderness with transducer pressure directly over GB
- •
Combination of gallstones, wall thickening, and positive Murphy sign increase specificity
- ○
Murphy sign may be negative after opioids or when gangrenous
- ○
- •
Gangrenous cholecystitis : Asymmetric wall thickening, marked wall irregularities, intraluminal membranes
- •
Gallbladder perforation : Defect in GB wall with pericholecystic abscess or extraluminal stones
- •
Emphysematous cholecystitis : Gas in GB wall/lumen
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Secondary GB wall thickening or adjacent inflammatory disease
Clinical Issues
- •
Typically > 25 years; M:F = 1:3
- •
Acute right upper quadrant pain, nausea, anorexia, vomiting, local tenderness to palpation
- •
Increased WBC; mild elevation in liver enzymes
Scanning Tips
- •
Move patient to look for impacted stone in neck/cystic duct, assess Murphy sign and surrounding area
 . Note the thick wall with subserosal edema
. Note the thick wall with subserosal edema  . Murphy sign was positive.
. Murphy sign was positive.
 with a sludge level
with a sludge level  and increased echogenicity of the pericholecystic fat
and increased echogenicity of the pericholecystic fat  .
.
 . Murphy sign was positive. There is sludge
. Murphy sign was positive. There is sludge  , but the wall was not thick. Small stones and acute cholecystitis were found at surgery.
, but the wall was not thick. Small stones and acute cholecystitis were found at surgery.
 and a focal collection at the fundus
and a focal collection at the fundus  . The lumen is less distended once the wall has perforated.
. The lumen is less distended once the wall has perforated.
 and sludge in the fundus
and sludge in the fundus  . This was acute on chronic cholecystitis at surgery.
. This was acute on chronic cholecystitis at surgery.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree