KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Localized pus collection in liver due to Entamoeba histolytica with destruction of hepatic parenchyma
Imaging
- •
General feature
- ○
Most often solitary (85%), peripherally located
- ○
- •
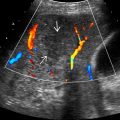
Ultrasound
- ○
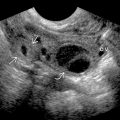
Sharply demarcated, round or ovoid mass
- ○
Hypoechoic with low-level internal echoes
- ○
May see internal septa or wall nodularity
- ○
May see posterior acoustic enhancement
- ○
- •
CECT
- ○
Typically hypoattenuating unilocular lesion
- ○
Peripheral rim or capsule enhancement
- ○
May see hypodense halo due to edema
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Hepatic metastasis (post treatment, cystic, or necrotic)
- •
Hepatic pyogenic abscess
- •
Hepatic hydatid cyst
- •
Biliary cystadenoma/cystadenocarcinoma
- •
Infarcted liver after transplantation
Pathology
- •
Entamoeba histolytica
- •
Primary source of infection: Human carriers passing amebic cysts into stool
Clinical Issues
- •
Right upper quadrant pain, tender hepatomegaly, diarrhea with mucus
- •
Indirect hemagglutination positive in 90% of cases
Scanning Tips
- •
Rule out pyogenic or fungal abscess, cystic lesions
- •
Check for history of transplantation, ablation, or chemotherapy for liver tumor or metastasis, which may simulate amebic abscess on imaging
 and central anchovy paste consistency of contents
and central anchovy paste consistency of contents  .
.
 . The contents are heterogeneous due to floating debris
. The contents are heterogeneous due to floating debris  . Also note the mild posterior acoustic enhancement
. Also note the mild posterior acoustic enhancement  .
.
 .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree