Amyloidosis, Airways
Melissa L. Rosado-de-Christenson, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Extracellular deposition of abnormal protein
Localized tracheobronchial amyloidosis; rare but most frequent form of 1° pulmonary amyloidosis
Imaging Findings
CT/HRCT
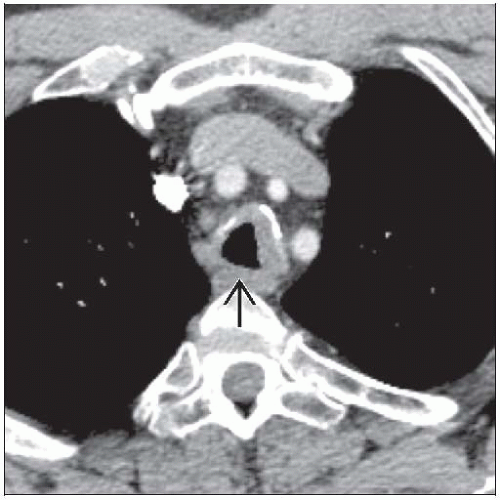
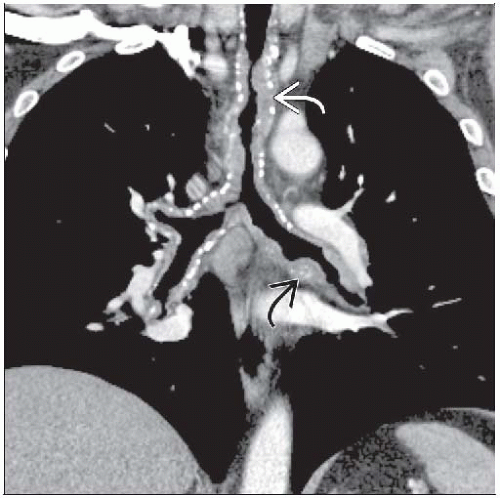
Tracheal &/or bronchial involvement
Focal or diffuse airway wall thickening
Eccentric or circumferential; may involve posterior tracheal wall
May exhibit calcification
May produce tracheobronchial stenosis
MR
Low signal intensity on T2WI
Nuclear medicine
Radionuclide uptake on bone scan
Top Differential Diagnoses
Tracheal Stenosis
Tracheopathia Osteochondroplastica
Wegener Granulomatosis
Relapsing Polychondritis
Neoplasm
Pathology
Abnormal protein in airway wall submucosa
Stains with Congo Red; characteristic apple-green birefringence on polarized microscopy
Clinical Issues
Asymptomatic; cough, dyspnea, wheezing
Diagnostic Checklist
Focal or diffuse, eccentric or circumferential airway wall thickening ± calcification
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Amyloid light (AL) chain: May be associated with multiple myeloma and macroglobulinemia
Amyloid A (AA) chain: Inflammatory conditions (rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease), chronic infection, familial Mediterranean fever
Amyloid transthyretin (ATTR): Genetic mutation responsible for hereditary amyloidosis
Amyloid β-2 microglobulin (Aβ2M): Normal plasma component not cleared by hemodialysis; amyloidosis in patients on dialysis
Definitions
Amyloid
Describes starch-like appearance of substance
Group of molecularly diverse proteins composed of nonbranching fibrils arranged in sheets
Heterogeneity of amyloid related to diversity of fibril precursor peptide units
Amyloidosis = extracellular deposition of abnormal protein; resistant to proteolysis, stains with Congo Red
Biochemical classification based on specific fibrillar protein type
Most respiratory amyloidosis due to AL subtype
Anatomic classification
Systemic amyloidosis: AL proteins, frequent pulmonary involvement, may be asymptomatic
Localized respiratory tract amyloidosis
Less common than systemic amyloidosis
AL proteins produced by lymphocytes and plasma cells
Focal and organ-limited amyloidosis without systemic disease
Large airway involvement typically seen in this form of disease
Systemic amyloidosis: Includes primary, secondary, and familial amyloidosis
Localized amyloidosis: Includes organ-limited and focal amyloidosis
Calcification more common in localized deposits
Primary amyloidosis: No preceding or concurrent disease (except multiple myeloma and Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia)
Secondary amyloidosis: Concurrent infection, inflammation, neoplasia
Thoracic amyloidosis: Tracheobronchial, nodular parenchymal, diffuse alveolar septal, lymphadenopathy, pleural
Tracheobronchial > pulmonary nodular > adenopathy > diffuse alveolar septal
Tracheobronchial amyloidosis: Rare, but most frequent form of primary pulmonary amyloidosis
Amyloid deposits in tracheobronchial submucosa and muscle
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue: Focal or diffuse nodular soft tissue thickening of airway walls ± calcification
Patient position/location: Focal or circumferential airway wall involvement
Size: Variable thickness; may obstruct airway lumen
Morphology: Nodular luminal surface; may exhibit calcification