Anatomy
The vessels supplying the lungs include the pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and bronchial arteries. In this chapter, the predominant branching patterns are illustrated and variants of the pulmonary vasculature are explored. Knowledge of variant anatomy, on occasion mimic disease, is important because it can allow correct planning of any necessary surgical and interventional procedures.
 Pulmonary Arteries
Pulmonary Arteries
 The main pulmonary artery arises from the right ventricle distal to the pulmonary valve and courses cephalad and dorsally; it divides into right and left pulmonary arteries (Figs. 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5).
The main pulmonary artery arises from the right ventricle distal to the pulmonary valve and courses cephalad and dorsally; it divides into right and left pulmonary arteries (Figs. 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5).
 The right pulmonary artery divides into the truncus anterior (superior trunk) and the interlobar pulmonary artery.
The right pulmonary artery divides into the truncus anterior (superior trunk) and the interlobar pulmonary artery.
 The left pulmonary artery supplies the upper lobe, lingula, and lower lobe of the left lung.
The left pulmonary artery supplies the upper lobe, lingula, and lower lobe of the left lung.
 In each lung, the common patterns are lobar and 10 segmental arterial structures.
In each lung, the common patterns are lobar and 10 segmental arterial structures.
 The segmental arteries are adjacent to their accompanying bronchi, situated medial to the bronchi in the upper lobes and laterally in the lingula and middle and lower lobes.
The segmental arteries are adjacent to their accompanying bronchi, situated medial to the bronchi in the upper lobes and laterally in the lingula and middle and lower lobes.
 The subsegmental arteries are identified as dichotomous divisions of the segmental arteries.
The subsegmental arteries are identified as dichotomous divisions of the segmental arteries.
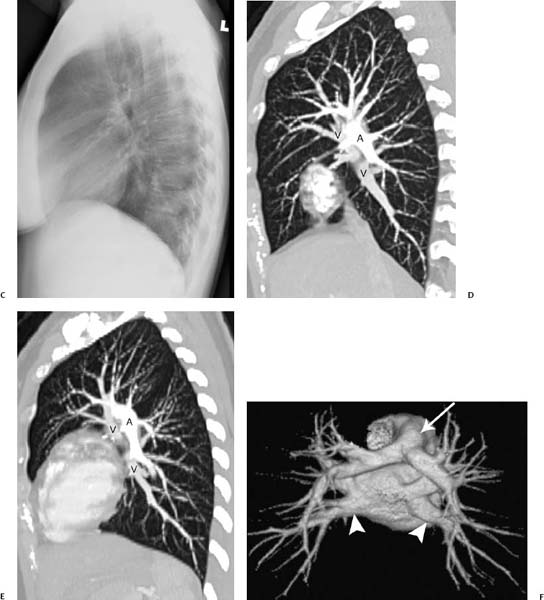
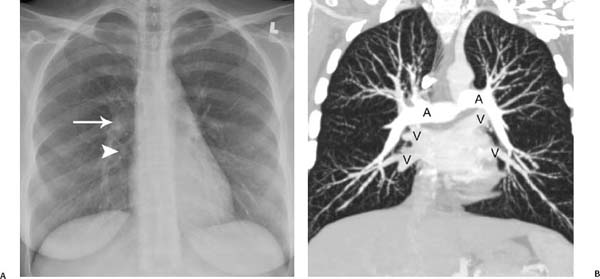
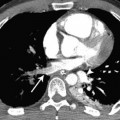
Fig. 1.1 (A–F) Normal chest radiographs and CT images in a 22-year-old woman. (A) Anteroposterior chest radiograph. The normal hila shadows are made up of pulmonary arteries and veins and bronchial walls. The right superior pulmonary vein is overlying the right interlobar artery (arrow). The right inferior pulmonary vein is also identified (arrowhead). (B) Coronal reformatted CT image of the same patient demonstrates the normal hilar relationships of the right and left pulmonary arteries (A) and the right and left superior and inferior pulmonary veins (V). Normal chest radiographs and CT images in a 22-year-old woman. (C) Normal lateral radiograph has both hilar shadows superimposed to form a composite shadow, which can be difficult to interpret. (D) Sagittal reformatted CT image elegantly demonstrates the normal hilar relationships of the right pulmonary artery (A) and the right superior and right inferior pulmonary veins (V). (E) Sagittal reformatted CT image shows the normal hilar relationships of the left pulmonary artery (A) and the left superior and left inferior pulmonary veins (V). (F) Posterior view of a surface-rendered three-dimensional CT image demonstrates the orientation of the pulmonary arteries with respect to the pulmonary veins; the main pulmonary artery (arrow) and inferior pulmonary veins (arrowheads) are indicated.
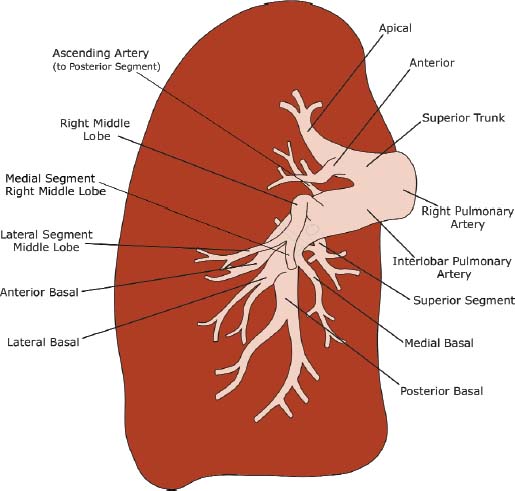
Fig. 1.2 Illustration of right pulmonary artery anatomy.
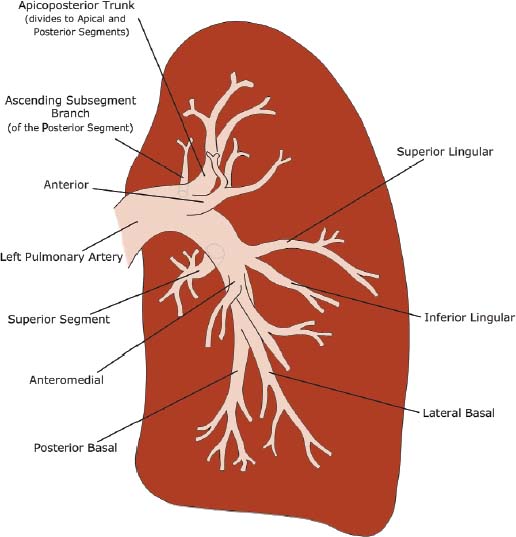
Fig. 1.3 Illustration of left pulmonary artery anatomy.
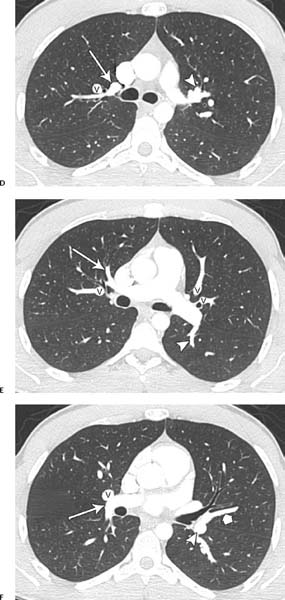
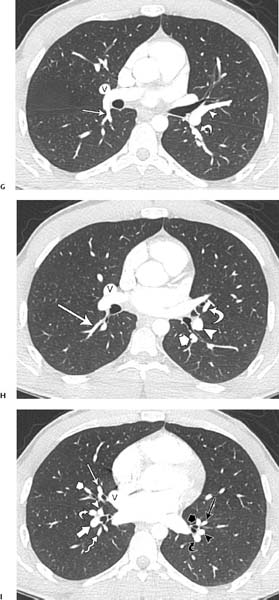
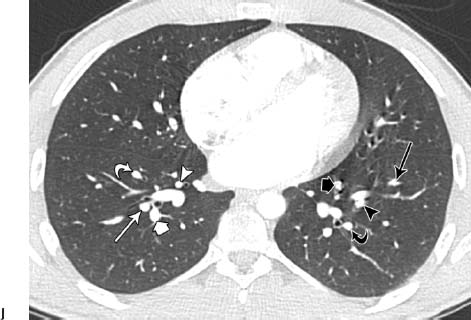
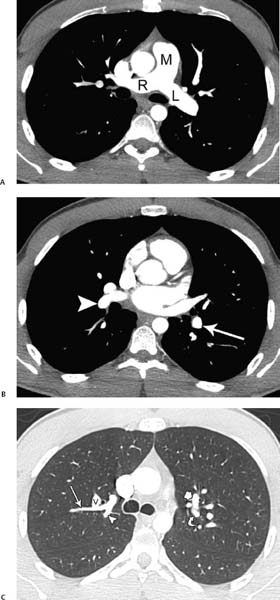
Fig. 1.4 (A–J) Normal axial CT pulmonary angiograms in a 22-year-old woman. (A) Mediastinal window settings demonstrate the normal main (M), right (R), and left (L) pulmonary arteries. (B) Image at the level of the left atrium demonstrates the normal right interlobar pulmonary artery (arrowhead) and left lower lobe artery (arrow). (C) Lung window settings at the level of the carina demonstrate subsegmental branches of the right upper lobe posterior artery (arrow and arrowhead) and a branch of the right superior pulmonary vein (V). On the left side, the apical (short arrow) and posterior (curved arrow) segmental arteries are identified. Normal axial CT pulmonary angiograms in a 22-year-old woman. (D) Image obtained slightly more caudad than the image in C demonstrates the right upper lobe apical segmental artery (arrow) and a branch of the right superior pulmonary vein (V), as well as the left upper lobe anterior segmental artery (arrowhead). (E) Image at the level of the main pulmonary artery demonstrates a branch of the right upper lobe anterior artery (arrow) and a branch of the right superior pulmonary vein (V). On the left side, a branch of the left lower lobe superior segmental artery (arrowhead) and branches of the left superior pulmonary vein (V) are seen. (F) Image at the level of the right ventricle outflow tract shows the right interlobar artery (arrow), right superior pulmonary vein (V), superior lingular segmental artery (short arrow), and left lower lobe artery (arrowhead). Normal axial CT pulmonary angiograms in a 22-year-old woman. (G) Image obtained slightly more caudad than the image in F shows the right lower lobe superior segmental artery (arrow), right superior pulmonary vein (V), lingular artery (arrowhead), and left lower lobe superior segmental artery (curved arrow). Normal axial CT pulmonary angiograms in a 22-year-old woman. (J) Image at the level of the left atrium demonstrates the right medial basal segmental artery (white arrowhead), right anterior basal segmental artery (white curved arrow), lateral basal segmental artery (white arrow), and right posterior basal segmental artery (white thick arrow). On the left side, the left posterior basal segmental artery (black curved arrow) and lateral basal segmental artery (black arrowhead) are seen, and the anteromedial basal segmental artery has branched into subsegmental arteries (black long and short arrows).
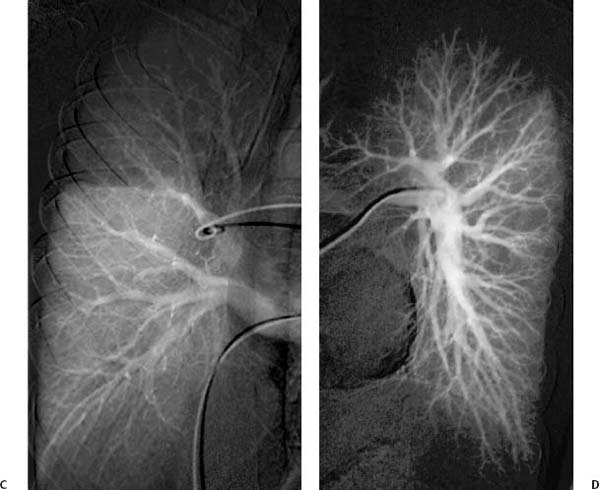
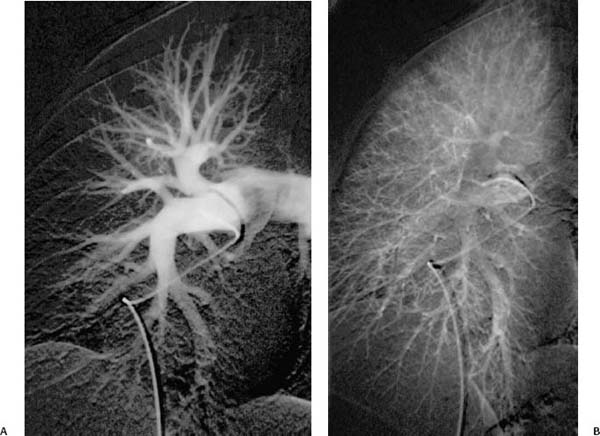
Fig. 1.5 (A–D) Normal pulmonary angiograms in a 36-year-old woman. (A) Right lung in arterial phase. (B) Right lung in capillary phase. Normal pulmonary angiograms in a 36-year-old woman. (C) Right lung in venous phase. (D) Left lung in arterial phase.
Fig. 1.6 Variant middle lobe arteries in a 53-year-old woman. Axial CT maximum-intensity projection (MIP) image demonstrates the medial and lateral segmental pulmonary arteries arising individually from the right interlobar pulmonary artery (arrows).
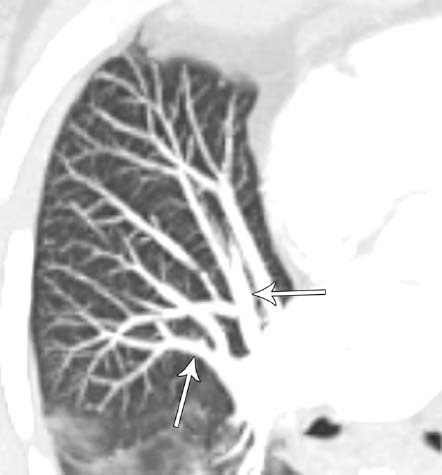
Fig. 1.7 High lingular artery in a 64-year-old man. Oblique sagittal reformatted CT image demonstrates the lingular artery arising from the left upper lobe artery (arrow).
Right Pulmonary Artery
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree