Abstract
Anomalies of pulmonary venous return are rare conditions characterized by abnormal drainage of pulmonary venous blood. Its prenatal diagnosis is challenging but vital these conditions are usually pediatric cardiology emergencies.
Keywords
congenital heart disease, abnormal drainage of pulmonary veins, pulmonary collector, heterotaxy
Disease
Definition
APVR is defined as abnormal drainage of pulmonary venous blood into the systemic venous system. Total APVR is characterized by the anomalous drainage of all the pulmonary veins, whereas partial APVR is characterized by the anomalous drainage of one, two, or three of the four pulmonary veins.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
The incidence of APVR has been reported to be 1 : 10,000 live births, with an incidence of approximately 2.2% of patients with congenital heart disease (CHD).
Etiology and Pathophysiology
The main consequence of APVR is interruption of the normal circulation of blood that enters the left atrium after closure of the foramen ovale. In total APVR, there is virtually no oxygenated blood return to the left atrium, left ventricle, and aorta. Immediate and increasing hypoxemia and acidosis are the rule, which can be reversed only by emergency postnatal cardiac surgery.
APVR can be classified by the location of the abnormal drainage and further designated as being with or without obstruction, as follows :
- •
Type I: supracardiac (50%). The four pulmonary veins drain into a venous collector located behind the left atrium, from which a vertical vein runs up to reach the innominate vein, and this terminates in the right superior vena cava and right atrium. It has been reported that the vertical vein may be obstructed, but this is rarely severe in the perinatal period.
- •
Type II: cardiac (25%). The pulmonary veins drain through the coronary sinus or directly into the right atrium. Usually, there is no obstruction.
- •
Type III: infracardiac or infradiaphragmatic (20%). The pulmonary veins converge into a descending vertical vein that reaches the abdomen through the diaphragm. It usually drains into the portal vein or, more rarely, into the ductus venosus or the inferior vena cava. Almost always, the vertical vein is significantly obstructed.
- •
Type IV: mixed (5%). The pulmonary veins drain separately to different sites.
Manifestations of Disease
Clinical Presentation
If APVR is isolated, the prenatal course is uneventful. Postnatal clinical signs are variable and depend on any associated cardiac anomaly, but total APVR commonly represents a neonatal emergency. In contrast, partial APVR usually has a very good prognosis and often remains asymptomatic with no need of surgery.
Imaging Technique and Findings
Ultrasound.
Prenatal diagnosis generally is quite challenging, and the condition is often missed in utero . Total APVR can be diagnosed in the fetus by indirect indicators on an echocardiogram, such as the following :
- •
Lack of a visible connection of the pulmonary veins to the atrium.
- •
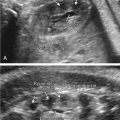
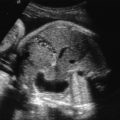
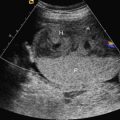
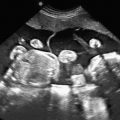
The presence of a chamber or collector of the pulmonary venous confluence behind the left atrium ( Figs. 91.1 and 91.2 , ).

Fig. 91.1
Vein collector of the pulmonary venous confluence behind the left atrium.