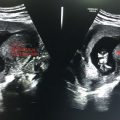
Aorta enters the abdomen through the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm, immediately anterior to T-12 vertebra.
Descends anterior to and slightly to the left of vertebral bodies.
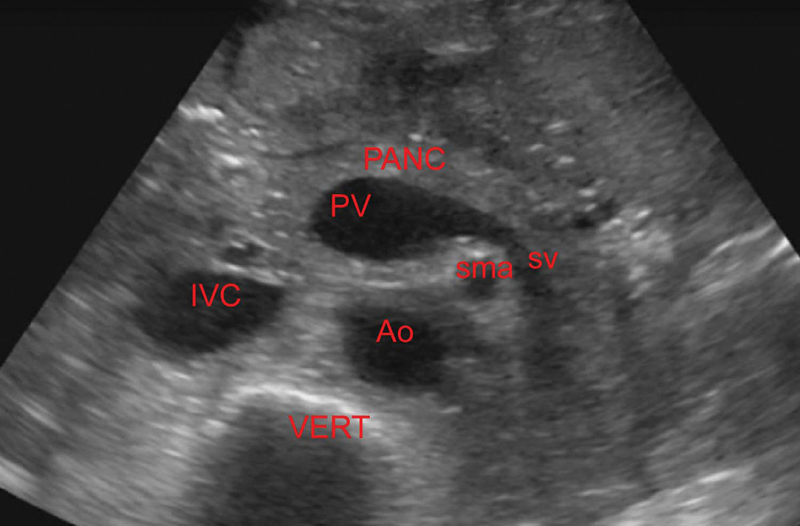
Main branches seen on USG.
Celiac artery, superior mesenteric artery (SMA), paired renal arteries, and common iliac arteries (Figure 9.1).
1. Inferior phrenic artery
2. Celiac artery
3. Suprarenal artery
4. Superior mesenteric artery
5. Renal artery
6. Gonadal artery
7. Inferior mesenteric artery
8. Median sacral artery
9. Common iliac artery
Figure 9.1 Depicting vascular anatomy after the origin of SMA.
Celiac artery demonstrates seagull sign and divides into (Figure 9.2)
1. Left gastric artery: Supplies curvature of stomach
2. Splenic artery: Supplies greater curvature, spleen, and pancreas
3. Common hepatic artery: Divides into gastric artery, hepatic artery and gastroduodenal artery
Superior mesenteric artery supplies most of the small intestine, ascending colon, and part of the transverse colon.
Inferior mesenteric artery supplies part of transverse colon, descending colon, and rectum.
1. Pulsatile abdominal mass
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree