Asthma
Brian C. Allen, MD
Tan-Lucien H. Mohammed, MD, FCCP
Key Facts
Terminology
Reactive airway disease
Intermittent reversible obstruction to air flow in lungs due to hyperreactivity and inflammation
Imaging Findings
Asthma typically involves mainly small and medium-sized bronchi
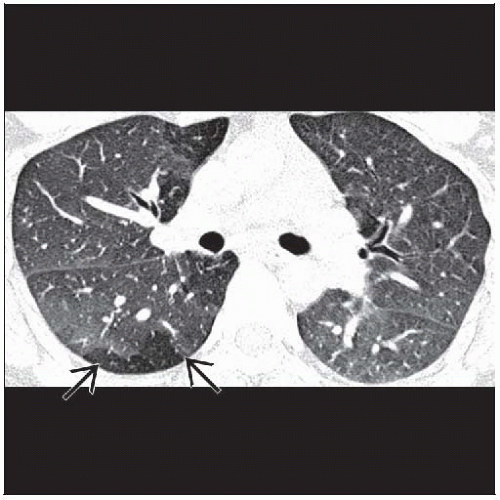
Air-trapping on expiratory scans most common finding
Bronchial wall thickening (50-90%)
Decreased lung attenuation (50%)
Mosaic lung attenuation
Degree of mosaic attenuation correlates with degree of asthma
HRCT useful to evaluate for bronchiectasis
Perform expiratory scans to visualize air-trapping
CXR: Limited role in diagnosis, important for complications of and processes that mimic asthma, alters treatment in few patients with acute asthma (5%)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Asthma Mimics
Airway Foreign Bodies
Cardiac asthma (edema of airway narrows lumen)
Recurrent Aspiration
Recurrent Pulmonary Embolus
Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Churg-Strauss Syndrome
Sarcoidosis
Bronchocentric Granulomatosis
Bronchiolitis Obliterans
Vocal cord dysfunction (factitious asthma)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations and Synonyms
Reactive airway disease
Definitions
Intermittent reversible obstruction to air flow in lungs due to hyperreactivity and inflammation
Status asthmaticus: Medical emergency in which asthmatic attack is refractory to bronchodilator therapy
IMAGING FINDINGS
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Air-trapping on expiratory scans
Bronchial wall thickening
Patient position/location
Segmental and distal bronchi
Nonuniform distribution through both lungs
CT Findings
More sensitive than chest radiography but not usually indicated
Used to assess for complications such as allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, presence of emphysema in smokers, or to identify asthma mimics
Heterogeneous distribution of bronchial and lung parenchymal findings typical
Airways
Mainly small and medium-sized bronchi
Bronchial wall thickening (50-90%)
Degree of thickening correlates with severity of disease and airflow obstruction
Will improve with treatment
Bronchial artery ratio (normal approximately 1:1)
75% of asthmatics (35% of bronchi) have bronchial artery ratio > 1 (but < 1.5)
Bronchial dilatation (30%)
Subsegmental bronchi larger than adjacent artery or nontapering airway morphology (typically cylindrical)
Bronchiectasis consider: APBA, irreversible airway remodeling, artifactual (from hypoxic vasoconstriction), or physiologic (from ventilation at large lung volumes)
Centrilobular micronodules or branching opacities (10-20%)
Finding most likely to be seen in patients with near-fatal asthma
Lung parenchyma
Decreased lung attenuation (50%)
Air-trapping (total volume > 1 segment) 50%
Mosaic lung attenuation
Degree of mosaic attenuation correlates with degree of asthma
Emphysema rare
Debatable whether secondary to asthma, usually only seen in those who smoke
Radiographic Findings
Limited role in diagnosis, important for complications of and processes that mimic asthma, alter treatment in few patients with acute asthma (5%)
Normal radiographs (75%) because
Obstruction to airflow is nonuniform throughout lungs
Large segments receive small fraction of each breath (hypoventilated)
Small segments receive most of air (hyperventilated)
Summation of hypo- and hyperventilated lung often results in normal chest radiograph
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree