Abstract
Atrial isomerism is a very rare condition defined as symmetric development of normally asymmetric organs or organ systems. The combination of situs ambiguus and congenital heart disease is the main clue for the diagnosis. It associates poor prognosis due to its high in utero and neonatal mortality.
Keywords
isomerism, heterotaxy, situs ambiguus, cardiosplenic syndrome
Introduction
Heterotaxy (or situs ambiguus ) is defined as the abnormal arrangement of thoracic or abdominal organs, or both, across the left-right axis ( ); it is different from complete situs inversus, which involves all organs. The term isomerism refers to the symmetric development of normally asymmetric organs or organ systems; this is the main feature of heterotaxy syndromes. These syndromes comprise a combination of cardiac, vascular, and visceral abnormalities. The terms heterotaxy syndrome, cardiosplenic syndrome, right and left isomerism, and situs ambiguus are often used to describe these defects.
Atrial isomerism manifests as a varied spectrum of corporeal and cardiac malformations. It is associated with a very poor prognosis owing to high in utero and neonatal mortality.
Disease
Definition
Isomerism is defined as symmetric development of normally asymmetric organs or organ systems. The combination of situs ambiguus and congenital heart disease is the main clue for the diagnosis.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
Atrial isomerism is very rare, accounting for 4% of congenital heart anomalies.
Etiology and Pathophysiology
Atrial isomerism manifests with a varied spectrum of cardiac malformations with viscerocardiac heterotaxy occurring in most cases. Although there is wide variation in the range of anomalies that may be present, isomerism is classified as follows.
- •
Right isomerism: paired right-side viscera; left-sided structures may be absent. Typical features include asplenia, bilateral trilobed lungs, intestinal malrotation, abnormal drainage of the pulmonary veins, persistence of the left superior vena cava, aorta and inferior vena cava located on the same abdominal side, atrioventricular septal defect, and ductus-dependent pulmonary flow.
- •
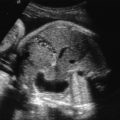
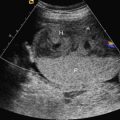
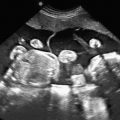
Left isomerism: paired left-side viscera; right-sided structures may be absent. Fetal anomalies include bilateral morphologic left atrial appendages, bilobed lungs, multiple splenules, and malrotation of the intestines. Interruption of the inferior vena cava with azygos continuation is an almost universal echocardiographic finding ( Figs. 90.1 and 90.2 ). Heart block, atrioventricular septal defect, double-outlet right ventricle, right or left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, total anomalous pulmonary vein drainage, persistence of left superior vena cava, and aorta and inferior vena cava located on the same abdominal side may also be present.

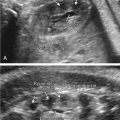
Fig. 90.1
Dilated azygos vein parallel to the thoracic aorta, secondary to interruption of the inferior vena cava.

Fig. 90.2
Color Doppler in the same case as shown in Fig. 90.1 clearly shows the opposite direction of the flow.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree