Base of Fifth Metatarsal Fracture
Andrew F. Barnes
Daniel B. Nissman
CLINICAL HISTORY
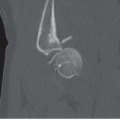
42-year-old female with lateral left foot pain following forced inversion injury while ballroom dancing.
FINDINGS
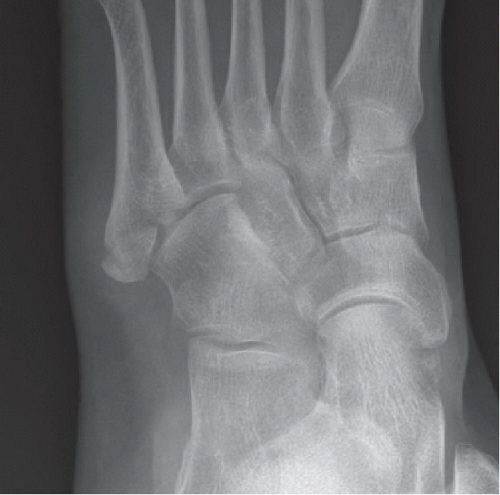
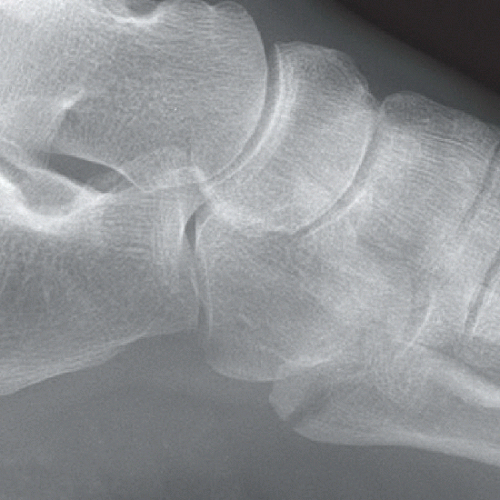
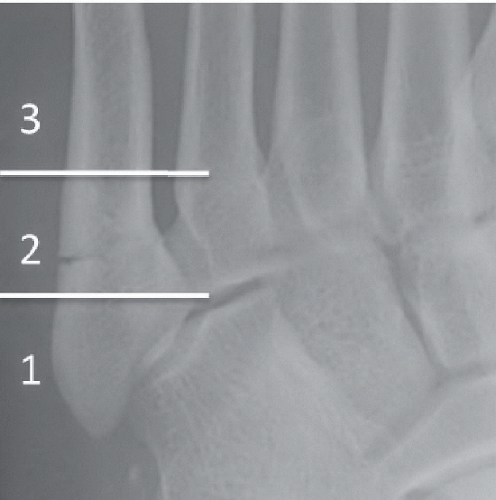
Oblique and lateral views of the left foot (Figs. 68A and 68B) reveal a transverse fracture of the fifth metatarsal base approximately 1.0 cm from the proximal tuberosity with mild posterior displacement of the proximal fragment. The fracture extends into the tarsometatarsal joint. Annotations on an oblique radiograph of the foot in another patient (Fig. 68C) demonstrate the zones of fracture in the fifth metatarsal base. Zone 1 = avulsion fractures. Zone 2 = Jones fractures. Zone 3 = stress fractures. A transverse fracture of the fifth metatarsal base extends into the intermetatarsal articulation and lies within Zone 2. The zoomed-in portion of a lateral foot radiograph in another patient (Fig. 68D) demonstrates
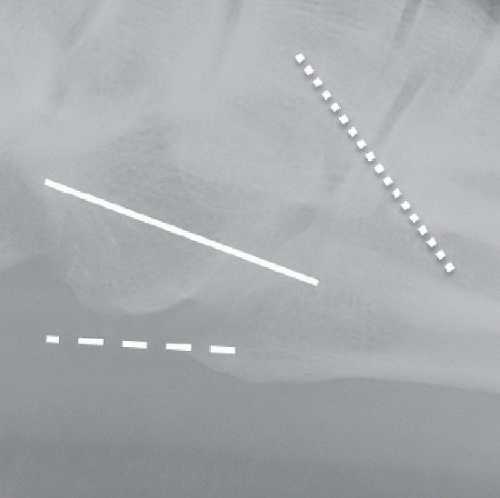
the important soft tissue attachment sites on the base of the fifth metatarsal: the solid white line represents the approximate course and attachment of the peroneus brevis tendon, the dashed white line represents the approximate course and attachment of the lateral bundle of the plantar fascia/aponeurosis, and the dotted white line represents the approximate course and attachment of the peroneus tertius tendon.
the important soft tissue attachment sites on the base of the fifth metatarsal: the solid white line represents the approximate course and attachment of the peroneus brevis tendon, the dashed white line represents the approximate course and attachment of the lateral bundle of the plantar fascia/aponeurosis, and the dotted white line represents the approximate course and attachment of the peroneus tertius tendon.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Jones fracture, avulsion fracture (a.k.a. pseudo-Jones or dancer’s fracture), unfused apophysis, os peroneum.