• These result from failure of the normal closure of the communication between the bladder urachus and allantois (which normally forms the median umbilical ligament) • Cystitis cystica: hyperplastic submucosal urothelial cells occurring in response to chronic infection (central necrosis can give a pseudocystic appearance) • Cystitis glandularis: glandular proliferation within the mucosa and lamina propria • Leukoplakia: developing squamous metaplasia in response to chronic inflammation
Bladder
MISCELLANEOUS BLADDER CONDITIONS
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES
Urachal anomalies
 an adenocarcinoma can arise within the urachal remnant
an adenocarcinoma can arise within the urachal remnant
 Patent urachus: the entire channel fails to close
Patent urachus: the entire channel fails to close  it presents with urine leakage at the umbilicus
it presents with urine leakage at the umbilicus
 Urachal cyst: the umbilical and bladder ends of the channel are closed but a mid portion remains patent
Urachal cyst: the umbilical and bladder ends of the channel are closed but a mid portion remains patent  it usually affects the lower ⅓ of the tract and may present as a cystic mass on imaging
it usually affects the lower ⅓ of the tract and may present as a cystic mass on imaging
 Urachal diverticulum: urachal dilatation only involving the bladder component
Urachal diverticulum: urachal dilatation only involving the bladder component
 Urachal sinus: urachal dilatation only involving the umbilical component
Urachal sinus: urachal dilatation only involving the umbilical component
INFLAMMATORY DISEASE
Chronic cystitis
AXR/CT
 it is characterized by granulomatous nodular cystic cavities
it is characterized by granulomatous nodular cystic cavities
 white patches are commonly seen on the trigone and bladder base
white patches are commonly seen on the trigone and bladder base
BLADDER TUMOURS
BLADDER TUMOURS
DEFINITION
Bladder

 there is marked upper tract dilatation and renal dysplasia which is incompatible with life
there is marked upper tract dilatation and renal dysplasia which is incompatible with life

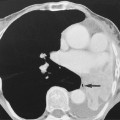
 they are usually multiple and may contain calculi (25%) or tumour (<5%)
they are usually multiple and may contain calculi (25%) or tumour (<5%)
 bladder outlet obstruction
bladder outlet obstruction  bladder diverticulae
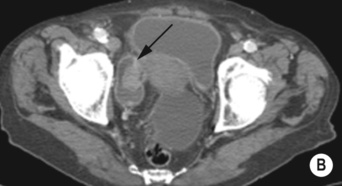
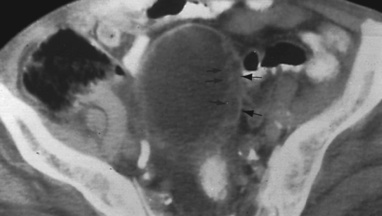
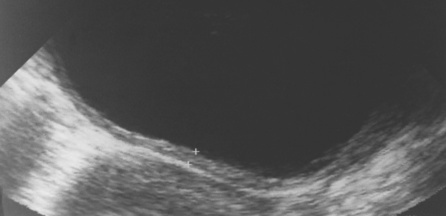
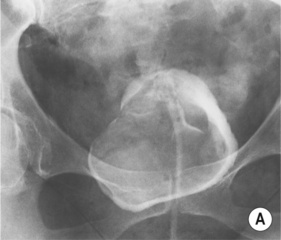
bladder diverticulae bladder wall irregularity associated with trabeculation
bladder wall irregularity associated with trabeculation  a diminished bladder capacity
a diminished bladder capacity
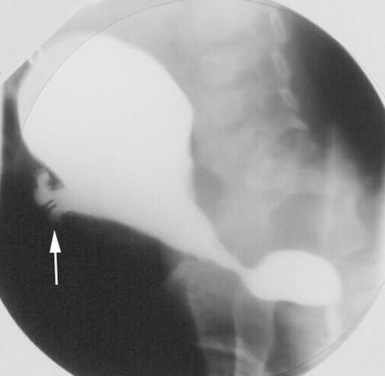
 gas within the bladder wall and appearing as a ‘ring’ within the pelvis
gas within the bladder wall and appearing as a ‘ring’ within the pelvis blood clot
blood clot  cellular debris
cellular debris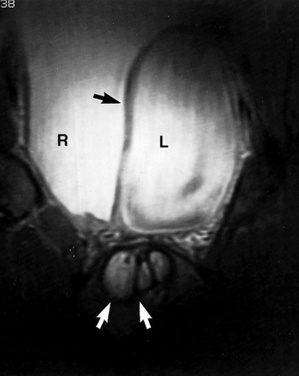
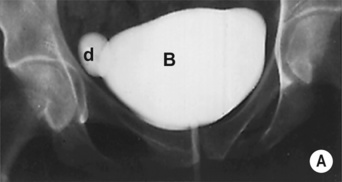
 carcinoma in situ is associated with an increased risk of developing invasive disease
carcinoma in situ is associated with an increased risk of developing invasive disease