Bone Tumor
IMAGING
General Features
Radiographic Findings
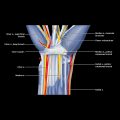
 Centrally or eccentrically located within bone
Centrally or eccentrically located within bone
 Expansile or nonexpansile
Expansile or nonexpansile
 Osteolytic, osteosclerotic, or mixed pattern
Osteolytic, osteosclerotic, or mixed pattern
 Well-defined margin (narrow zone of transition)
Well-defined margin (narrow zone of transition)
 Ill-defined margin (wide zone of transition)
Ill-defined margin (wide zone of transition)
 ± cortical breach
± cortical breach
 ± extraosseous tumor expansion
± extraosseous tumor expansion
 ± periosteal ± tumoral new bone formation
± periosteal ± tumoral new bone formation
 Many types of periosteal or tumoral new bone formation
Many types of periosteal or tumoral new bone formation
 Type of periosteal reaction is not highly sensitive discriminator of tumor aggressiveness
Type of periosteal reaction is not highly sensitive discriminator of tumor aggressiveness
 Spiculated, “sunburst,” and “hair-on-end” tumoral new bone are highly specific for aggressive tumor
Spiculated, “sunburst,” and “hair-on-end” tumoral new bone are highly specific for aggressive tumor
Ultrasonographic Findings
 US appearances generally mirror radiographic appearances
US appearances generally mirror radiographic appearances
 Bone metastases are most common bone tumor encountered in routine clinical practice
Bone metastases are most common bone tumor encountered in routine clinical practice
 Can be done for all tumors irrespective of whether primary tumor is visible on US
Can be done for all tumors irrespective of whether primary tumor is visible on US
 Flow velocities can be calculated
Flow velocities can be calculated
 Normal arterial flow is triphasic with reversal of flow in diastole
Normal arterial flow is triphasic with reversal of flow in diastole
 Metabolically active tumors may show substantial ↑ in antegrade diastolic flow
Metabolically active tumors may show substantial ↑ in antegrade diastolic flow
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree















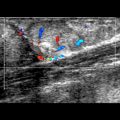
 of the distal radial metaphysis indicative of an aggressive bone lesion. There is a faint periosteal reaction
of the distal radial metaphysis indicative of an aggressive bone lesion. There is a faint periosteal reaction  .
.
 of the distal radial metaphysis with a surprisingly large extraosseous component. The tumor clearly extends beyond the physis.
of the distal radial metaphysis with a surprisingly large extraosseous component. The tumor clearly extends beyond the physis.
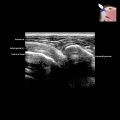
 of new bone suggestive of an osteogenic tumor. There is an ultrasonic Codman triangle
of new bone suggestive of an osteogenic tumor. There is an ultrasonic Codman triangle  at the proximal end of the tumor.
at the proximal end of the tumor.
 . This finding is seen in various bone tumors and is not unique for osteosarcoma, though US-guided biopsy did reveal osteosarcoma in this case.
. This finding is seen in various bone tumors and is not unique for osteosarcoma, though US-guided biopsy did reveal osteosarcoma in this case.