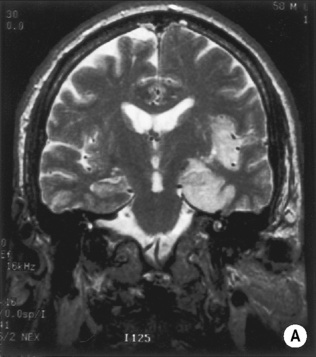
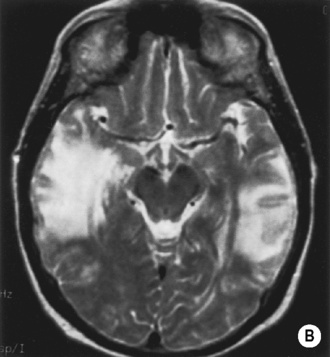
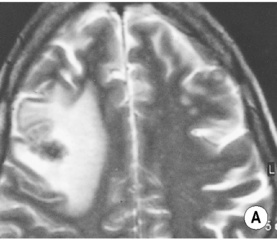
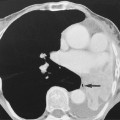
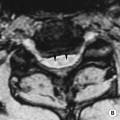
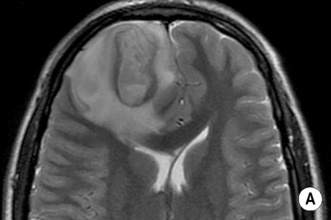
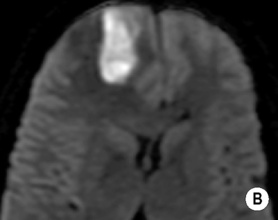
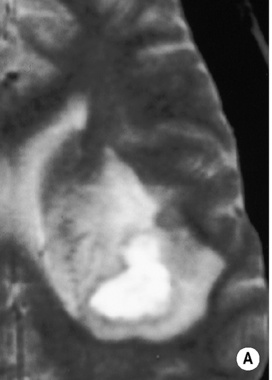
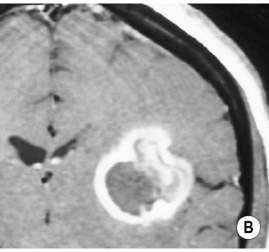
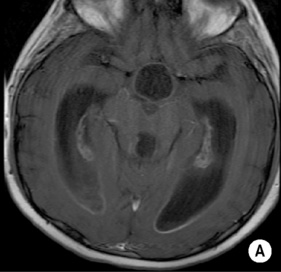
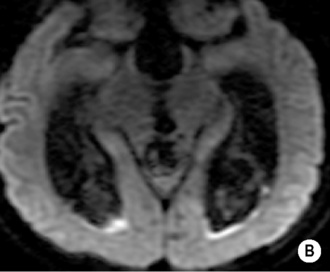
• A focal encapsulated pus-containing cavity • The abscess site depends on the cause: • Abscesses are frequently subcortical or periventricular in location • A rim-enhancing mass is a non-specific finding and may be mimicked by a metastasis, a glioblastoma, a resolving haematoma, or a subacute infarct There is a similar pattern of rim enhancement as seen with CT • Restricted diffusion techniques are unable to distinguish an abscess from a tumour • Dynamic contrast-enhanced perfusion MRI: abscesses have a lower relative cerebral blood volume within their enhancing rim than a glioma • Resolution post treatment: this is indicated by resolution of any rim enhancement or disappearance of the low SI rim (T2WI) *DWI: high SI (due to restricted diffusion within the viscous pus)
Brain infection, AIDS and demyelinating diseases
INTRACRANIAL INFECTION
BRAIN ABSCESS
DEFINITION
 in immunocompetent patients it is usually due to a streptococcal bacterial infection (and can be multiple in 10–50% of cases)
in immunocompetent patients it is usually due to a streptococcal bacterial infection (and can be multiple in 10–50% of cases)
 It usually arises by haematogenous dissemination
It usually arises by haematogenous dissemination  it can also occur following penetrating trauma or due to direct spread from a contiguous infection
it can also occur following penetrating trauma or due to direct spread from a contiguous infection
 Fungal cerebral abscesses: these typically affect immunocompromised patients
Fungal cerebral abscesses: these typically affect immunocompromised patients  they are similar to a pyogenic abscess but are more likely to demonstrate areas of haemorrhage
they are similar to a pyogenic abscess but are more likely to demonstrate areas of haemorrhage
RADIOLOGICAL FEATURES
MRI
 a low SI on DWI correlates with a good clinical response (increasing SI implies pus reaccumulation)
a low SI on DWI correlates with a good clinical response (increasing SI implies pus reaccumulation)
Abscess centre*
Abscess rim
Surrounding vasogenic oedema
T1WI
SI between CSF and white matter
Slightly higher SI than white matter
Low SI
T2WI
SI similar or slightly higher than CSF
Relatively low SI
High SI

 ADC map: low SI
ADC map: low SI
Radiology Key
Fastest Radiology Insight Engine




 headache
headache  a focal neurological deficit
a focal neurological deficit
 following IV contrast medium administration the ring of enhancement corresponds to the abscess capsule (and is surrounded by low attenuation vasogenic oedema)
following IV contrast medium administration the ring of enhancement corresponds to the abscess capsule (and is surrounded by low attenuation vasogenic oedema) it is more often subdural than extradural and is a neurosurgical emergency
it is more often subdural than extradural and is a neurosurgical emergency it is slightly denser than CSF and marginal enhancement is characteristic
it is slightly denser than CSF and marginal enhancement is characteristic there may be marked contrast enhancement
there may be marked contrast enhancement
 ADC: low SI
ADC: low SI periventricular and subependymal high SI or ventricular marginal enhancement is less commonly seen
periventricular and subependymal high SI or ventricular marginal enhancement is less commonly seen it is usually pyogenic in origin and can resolve or develop into a frank abscess
it is usually pyogenic in origin and can resolve or develop into a frank abscess there may be haemorrhagic transformation
there may be haemorrhagic transformation it is usually viral and often diffuse
it is usually viral and often diffuse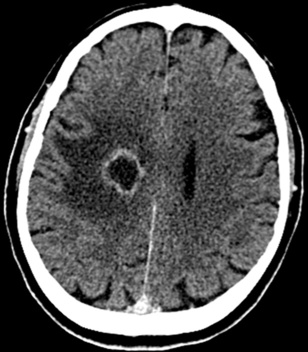
 it is often fatal without treatment
it is often fatal without treatment this is followed by low attenuation within the anteromedial temporal lobe (± involvement of the insula or the orbital surface of the frontal lobe)
this is followed by low attenuation within the anteromedial temporal lobe (± involvement of the insula or the orbital surface of the frontal lobe)  haemorrhage is not usually prominent and is a late feature
haemorrhage is not usually prominent and is a late feature  there can be patchy or gyriform enhancement
there can be patchy or gyriform enhancement the abnormal SI is mainly cortical (with secondary subjacent white matter involvement)
the abnormal SI is mainly cortical (with secondary subjacent white matter involvement)  it is more sensitive than CT for detecting haemorrhagic foci
it is more sensitive than CT for detecting haemorrhagic foci cortical areas of increased density (which are not limited to the temporal lobes)
cortical areas of increased density (which are not limited to the temporal lobes)  there can be lesion progression to a multicystic encephalomalacia
there can be lesion progression to a multicystic encephalomalacia CT is useful for detecting any complications (e.g. hydrocephalus, a subdural effusion, an abscess or a cerebral infarction)
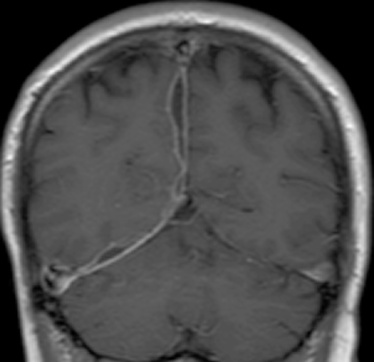
CT is useful for detecting any complications (e.g. hydrocephalus, a subdural effusion, an abscess or a cerebral infarction) FLAIR + Gad: meningeal enhancement (this may be more sensitive than T1WI + Gad)
FLAIR + Gad: meningeal enhancement (this may be more sensitive than T1WI + Gad) tuberculous meningitis is the most frequent manifestation (involving the basal leptomeninges)
tuberculous meningitis is the most frequent manifestation (involving the basal leptomeninges) a tuberculous abscess is a rare finding
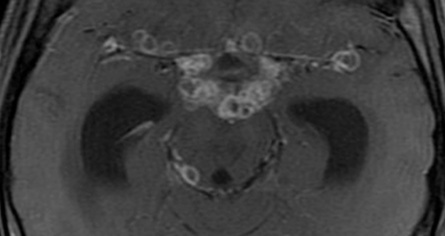
a tuberculous abscess is a rare finding there is avid enhancement of the basal meninges extending into the ambient, sylvian, pontine and chiasmatic cisterns
there is avid enhancement of the basal meninges extending into the ambient, sylvian, pontine and chiasmatic cisterns meningeal calcification is rarely seen with healing
meningeal calcification is rarely seen with healing neurosarcoid
neurosarcoid  carcinomatous meningitis
carcinomatous meningitis there is variable surrounding oedema
there is variable surrounding oedema  there is homogeneous enhancement (with solid lesions) or rim enhancement (with central caseation or liquefaction)
there is homogeneous enhancement (with solid lesions) or rim enhancement (with central caseation or liquefaction)  lesions rarely calcify with healing
lesions rarely calcify with healing  brainstem involvement is uncommon
brainstem involvement is uncommon T2WI: high SI (but low SI with caseation)
T2WI: high SI (but low SI with caseation)  T1WI + Gad: solid lesions demonstrate homogeneous enhancement
T1WI + Gad: solid lesions demonstrate homogeneous enhancement  ring enhancement is seen with caseation
ring enhancement is seen with caseation