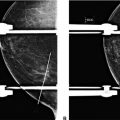
A. Described as cigar shaped
B. Present in males and females
C. Seen on the CC and true lateral projections only
D. Associated with tubular carcinoma
3a A 61-year-old female presents for a screening mammogram. Patient’s most recent prior mammogram from 2 years ago was negative. What is the most appropriate BI-RADS classification based on this single right MLO view?
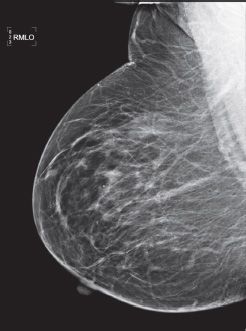
A. 0
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
3b Additional views were performed. What is the most appropriate description of these calcifications?
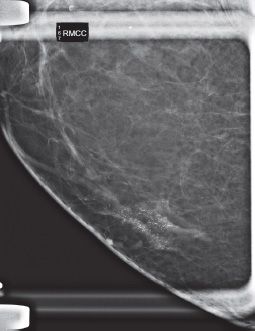
A. Fat necrosis (dystrophic, rim, and lucent centered)
B. Pleomorphic, fine linear branching
C. Skin calcifications
D. Coarse/popcorn-like
E. Rod-like/secretory
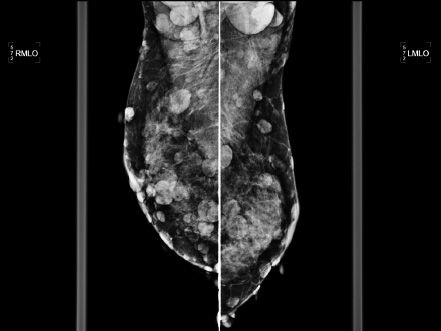
4 A 62-year-old female presents for her annual routine screening mammogram. The interval between the two studies is 13 months. The patient has no current complaints. Comparing the current study with the prior, what is the MOST likely cause of the change in her mammogram in the interval?
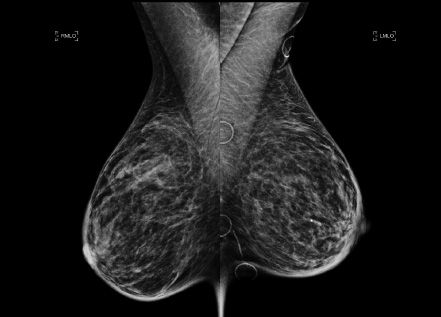
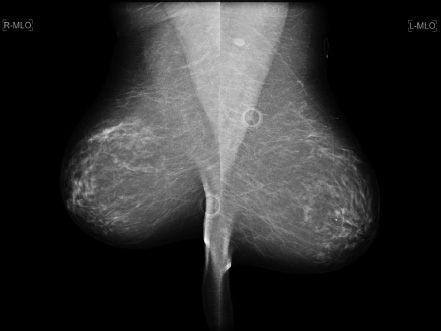
A. Hormone replacement therapy
B. Weight loss
C. Inflammatory breast cancer
D. Breast edema from congestive heart failure
5 A 57-year-old female presents for an annual routine screening mammogram. Which of the following statements is correct regarding this patient’s prior breast surgical history?
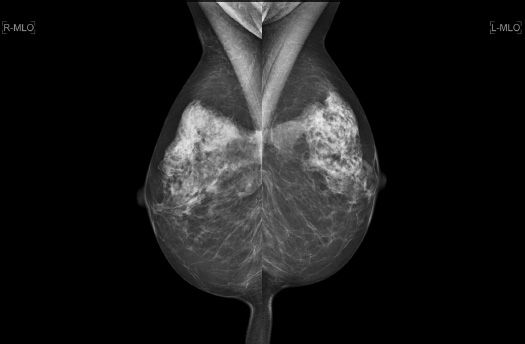
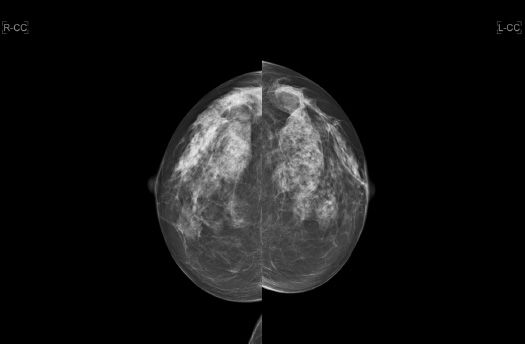
A. If fat necrosis is to occur mammographically, it typically occurs within the 1st year.
B. Nipple elevation occurs because there is more skin inferior to the nipple than superior.
C. Architectural distortion commonly presents as a swirled fibroglandular pattern in the inferior and lateral breast.
D. There is parenchymal redistribution of the fibroglandular tissue, as the residual breast tissue is shifted from the upper outer breast to the upper inner breast.
6 A 30-year-old female has a family history of breast cancer in her mother at age 45 and her sister at age 42. She undergoes genetic testing and discovers she is a carrier of the BRCA2 mutation. At what age should she begin screening mammography?
A. 30
B. 32
C. 35
D. 40
7 Breast MRI has proven to be a powerful adjunct to screening mammography in women considered to be at increased risk for breast cancer. Current guidelines recommend screening breast MRI to begin at the age of 30 for which of the following groups?
A. Proven carriers of the BRCA mutation
B. Women with >10% lifetime risk for breast cancer on the basis of family history
C. Women with history of chest irradiation
D. Women with a personal history of biopsy proven atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH)
8 Which of the following is correct regarding performing periodic mammographic surveillance of a BI-RADS 3 (probably benign) lesion versus performing tissue biopsy?
A. Decreased call-back rates
B. Increased costs
C. Increased false positives
D. Increased morbidity
E. Increased positive predictive value
9 Which one of the following breast lesions can be appropriately categorized as a BI-RADS 3 (probably benign) lesion?
A. A nonpalpable, circumscribed mass on a baseline mammogram
B. A nonpalpable, circumscribed mass, new since the last mammogram
C. A nonpalpable, circumscribed mass, unchanged for 2 years
D. A nonpalpable, noncircumscribed mass on a baseline mammogram
E. A palpable, noncircumscribed mass, new since last mammogram
10 Which statement is correct regarding computer-aided detection (CAD) in mammography?
A. CAD sensitivity is greater for masses than calcifications.
B. Breast cancer detection rate increases with CAD.
C. Use of CAD decreases the recall rate.
D. CAD can be used as a primary tool in reading mammograms.
E. CAD makes no false-positive or false-mark findings.
11 Which statement is correct regarding male breast cancer?
A. Gynecomastia is a known risk factor.
B. Male breast cancer is about 10% of all male cancers in the United States.
C. Female relatives of men with breast cancer have no increased risk of breast cancer.
D. It has no associations with BRCA2 gene mutation.
E. Testicular diseases such as undescended testes and testicular injury are considered risk factors for male breast cancer.
12 Which is the most common cancer found in men?
A. Invasive ductal carcinoma
B. Invasive lobular carcinoma
C. Paget disease of the nipple
D. Atypical ductal hyperplasia
13 Which BI-RADS assessment category is inappropriate to assign to a screening mammogram?
A. 0
B. 1
C. 3
D. 5
14 A 43-year-old female presents for a screening mammogram. No prior studies are available. Based on these images, what would be a possible associated finding in this patient?
A. Bilateral acoustic neuromas
B. Increased risk for meningiomas
C. Ependymomas
D. Lisch nodules
15 A 46-year-old Asian female presents for a screening mammogram. Patient recently moved to the United States and prior imaging studies were not available for comparison. Ultrasound demonstrates diffuse shadowing. Which of the following is correct?
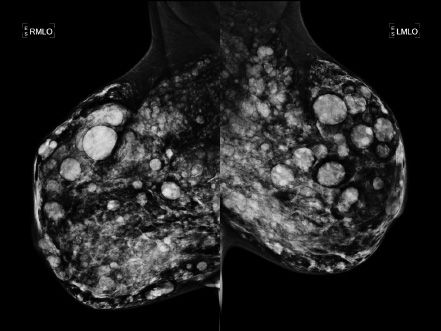
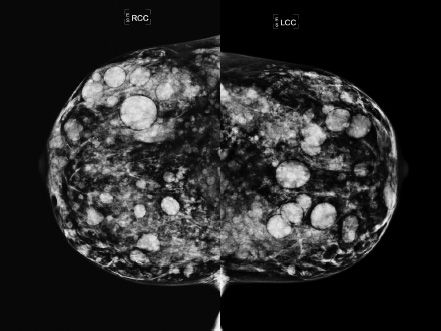
A. Patient has cafe au lait spots and similar mammographic imaging findings in family members.
B. Patient experiences cyclic breast pain predominantly during her premenstrual phase.
C. Patient has a history of prior malignant skin lesion on the sole of her foot.
D. Patient has a history of prior breast procedure.
E. Patient has a history of renal transplant with cyclosporin A therapy.
16a A 42-year-old female requests contrast-enhanced MRI of the breasts. The patient’s medical history includes a history of fibromyalgia, which makes mammograms very uncomfortable. The patient has a family history of breast cancer affecting her maternal aunt and cousin. The patient’s last screening mammogram demonstrated heterogeneously dense breasts. She has a history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma as a teenager, in complete remission since. Surgical history includes bilateral silicone breast implant placement at 27 years of age. Which of the following is correct?
A. The test is not indicated, and advise the patient to consult with her primary care physician for follow-up, including a clinical breast exam.
B. The test is not indicated, and recommend routine annual screening mammogram.
C. The test is indicated, and advise the patient to schedule her MRI during days 4 to 11 of her menstrual cycle.
D. The test is indicated, and advise the patient to schedule her MRI during days 21 to 28 of her menstrual cycle.
16b Which of the following is an indication for contrast-enhanced screening MRI in this patient?
A. Her family history of breast cancer
B. Heterogenously dense breasts
C. History of fibromyalgia, making mammograms very uncomfortable
D. History of non-Hodgkin lymphoma
E. Bilateral silicone breast implants
17 An 82-year-old female asks her internist if she needs to have a yearly screening mammogram done. What are the ACS guidelines?
A. No need to have a screening mammogram done after age 75.
B. She should have a screening mammogram done, but once every 2 years.
C. Continue having yearly screening mammograms until age 90, then stop.
D. Continue having yearly screening mammograms done as long as she is in otherwise good health.
18 A 45-year-old female presents for a screening mammogram. A mass is noted and after further imaging and biopsy proves to represent an invasive ductal carcinoma. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the location of this mass?
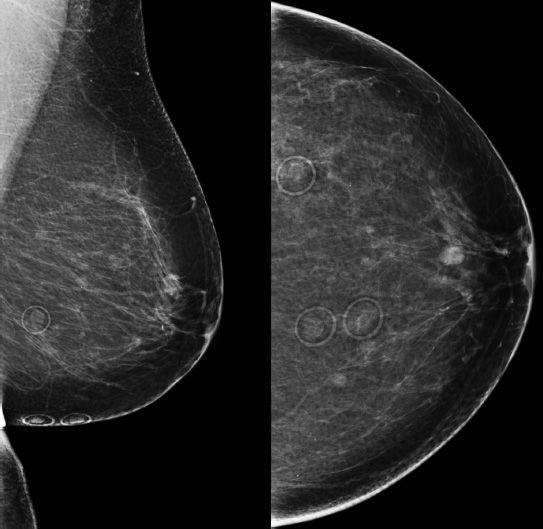
A. Approximately 10% of all breast cancers occur in the subareolar location.
B. Breast cancers in the subareolar location are more common in women than in men.
C. Breast cancers in the subareolar region are easy to detect, due to a lack of superimposed breast tissue in this location.
D. Breast cancers in this location are associated with earlier lymphatic spread via the retroareolar Sappey plexus.
19 A 55-year-old female presents for a screening mammogram. A mass is detected, which after further evaluation and biopsy proves to be invasive ductal carcinoma. What percentage of breast cancers in females is detected in this location?
A. 7%
B. 17%
C. 27%
D. 37%
20 A 60-year-old female presents for a mammogram. A mass is detected at the site of the palpable abnormality in the upper outer quadrant. What percentage of breast cancers in females occurs in the upper outer quadrant?
A. 21%
B. 41%
C. 61%
D. 81%
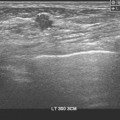
21 A 29-year-old female presents with a palpable abnormality in the right breast. Given the ultrasound image below, what is the most likely diagnosis?
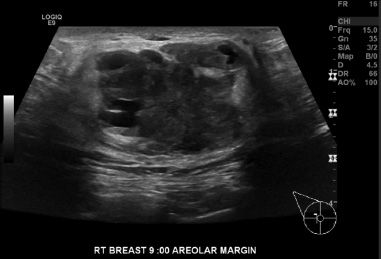
A. Galactocele
B. Lipoma
C. Hamartoma
D. Lymph node
22 A 56-year-old female presents for a baseline screening mammogram. What is the appropriate BI-RADS classification?
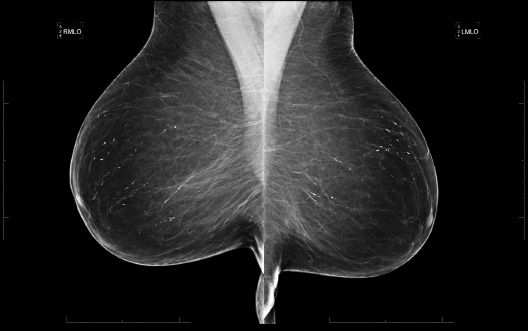
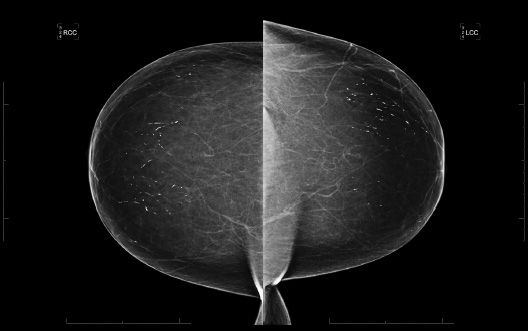
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4A
23 A 62-year-old female presents for an annual screening mammogram.
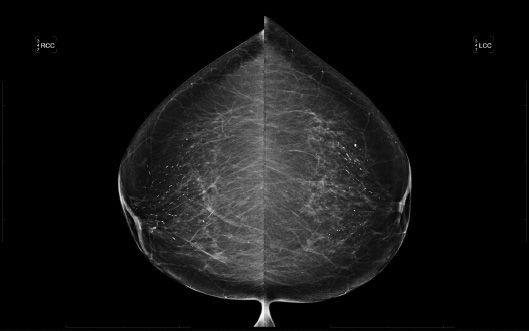
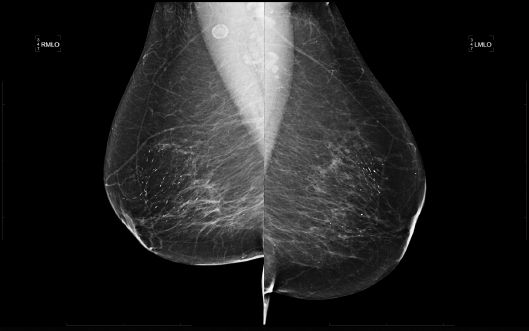
23a Based on the images, what is the BI-RADS Category assessment?
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
23b Based on the images, what is the recommendation?
A. Incomplete—Needs additional workup
B. Benign—Recommend annual screening in 1 year
C. Probably benign—Follow-up in 6 months
D. Suspicious—Recommend biopsy under stereotactic guidance.
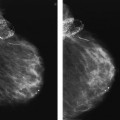
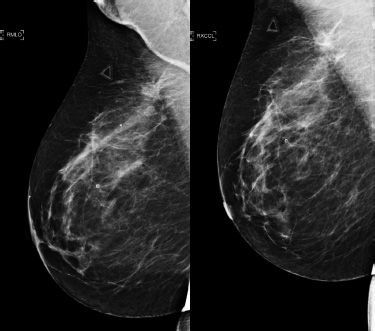
24a Mammograms from 2011 are on the left and those from 2012 are on the right. The first pair represents CC projections, and the second pair represents MLO projections. The images are magnified to show the area of interest. What is the name of the radiologic sign that these images demonstrate?
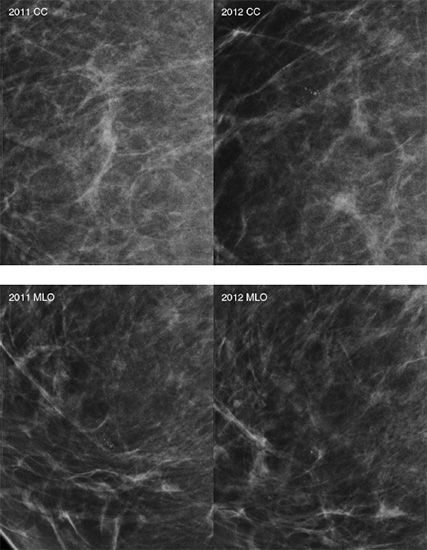
A. Cord sign
B. Cluster sign
C. Mirror sign
D. Tattoo sign
24b What type of calcifications is represented in the above images?
A. Secretory calcifications
B. Fibroadenoma calcifications
C. Dermal calcifications
D. Milk of calcium calcifications
E. Fat necrosis calcifications
25 A 45-year-old asymptomatic female presents for a screening mammogram. craniocaudal (CC) and mediolateral oblique (MLO) views are shown below:
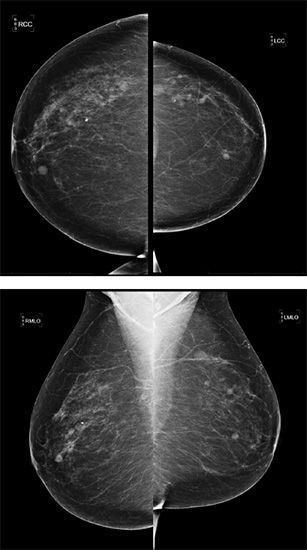
What BI-RADS assessment would you give?
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 2
C. BI-RADS 3
D. BI-RADS 4
26 Based on the location of the lesion in the left breast shown below, how do you expect the lesion to shift on a mediolateral (ML) view?
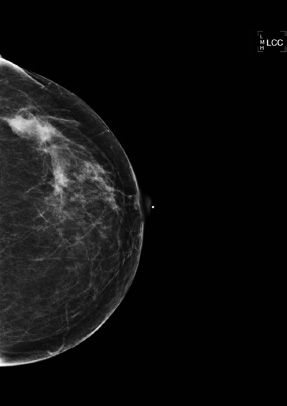
A. Inferior
B. Lateral
C. Medial
D. Superior
27 Which of the following is correct about human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)?
A. HER2 positive breast cancers usually demonstrate rapid growth and spread.
B. HER2 negative breast cancers are more aggressive than HER2 positive cancers.
C. Approximately 60% of newly diagnosed breast cancer is HER2 positive.
D. ER negative, PR negative, and HER2 negative cancers have a better prognosis.
E. HER2 positive breast cancers are more responsive to hormonal treatment.
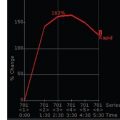
28a Screening breast MRI was performed on a high-risk patient with history of right breast cancer and mastectomy. Based on the following images, what is the best BI-RADS assessment to assign this patient’s breast MRI?
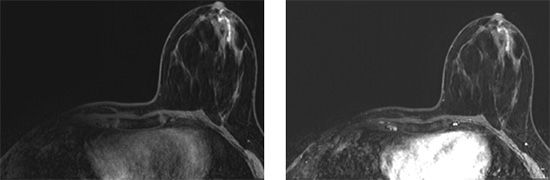
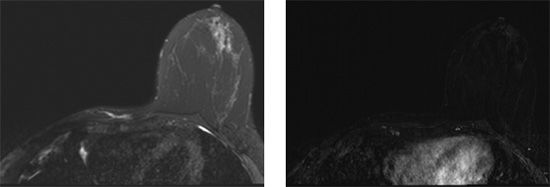
A. 0
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
28b What is the best follow-up recommendation for this patient?
A. Focused ultrasound
B. Surgical referral
C. MRI-guided biopsy
D. 6-month follow-up MRI
E. Annual follow-up MRI
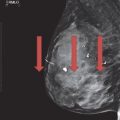
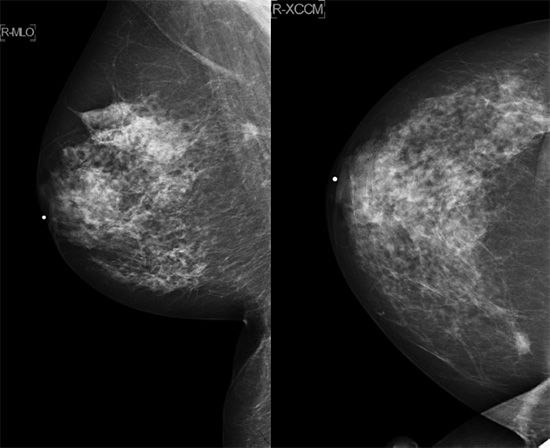
29 A 52-year-old female presents with a painless, swollen, and erythematous left breast.
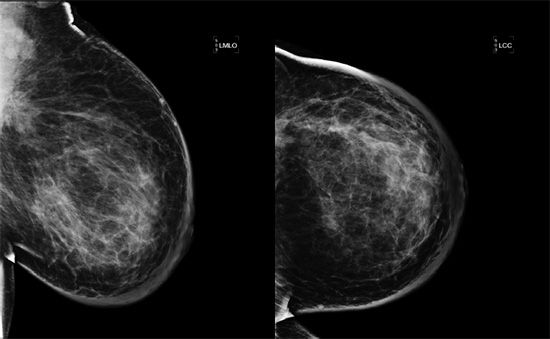
Based on the images above, what is the most appropriate next step?
A. Recommend follow-up imaging after antibiotic treatment
B. Biopsy
C. Breast MRI
D. Annual screening mammography
30 Which of the following is true regarding breast-specific gamma imaging (BSGI)?
A. BSGI is less sensitive in women with dense breasts.
B. BSGI cannot distinguish and differentiate between scar tissue and recurrence in a patient with a history of breast cancer with lumpectomy.
C. BSGI uses technetium-99m-sestamibi.
D. BSGI has lower lifetime attributable risk of mortality when compared to radiation exposure from a four-view screening digital mammogram.
E. BSGI does not involve whole body radiation exposure.
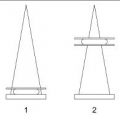
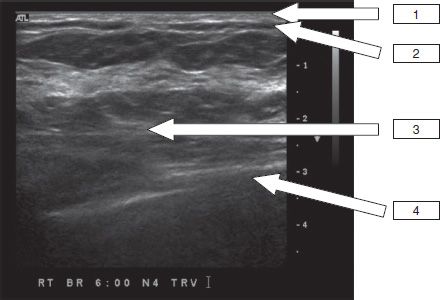
31 Match the anatomic structure to the appropriate numerical location on the sonographic image of a normal breast.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree