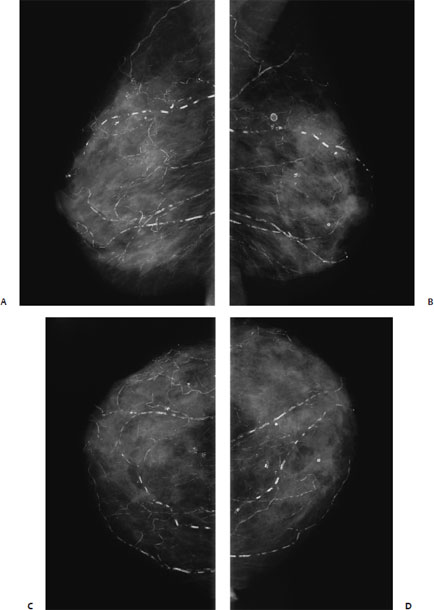
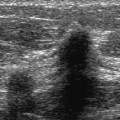
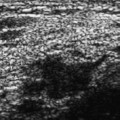
9 Calcifications: Large Linear A 61-year-old woman presents for screening mammogram. • Normal exam Calcifications (Fig. 9.1) • Type: vascular • Distribution: diffuse/scattered Fig. 9.1 Both breasts exhibit numerous linear vascular calcifications. (A) Right MLO mammogram. (B) Left MLO mammogram. (C) Right CC mammogram. (D) Left CC mammogram. • Atherosclerosis • BI-RADS assessment category 1, negative • Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of vascular calcifications in the breast. These calcifications are linear and generally are easy to differentiate from malignant calcifications. Vascular calcifications may be increased in patients with renal failure. Occasionally, vessels that are poorly calcified may appear worrisome, but, generally, magnification views clarify the etiology of the calcification. Cooper RA, Berman S. Extensive breast calcification in renal failure. J Thorac Imaging 1988;3:81–82 Kemmeren JM, Beijerinck D, van Noord PA, et al. Breast arterial calcifications: association with diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular mortality. Work in progress. Radiology 1996;201:75–78 Meybehm M, Pfeifer U. Vascular calcifications mimicking grouped microcalcifications on mammography. Breast Dis 1990;3:81–86 Sommer G, Kopsa H, Zazgornik J, Salomonowitz E. Breast calcifications in renal hyperparathyroidism. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1987;148:855–857
Case 9.1: Vascular
Case History
Physical Examination
Mammogram
Pathology
Management
Pearls and Pitfalls
Suggested Reading
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree