| SKULL BASE REGION | Petroclival |
| HISTOPATHOLOGY | Meningioma, transitional type, WHO grade I |
| PRIOR SURGICAL RESECTION | Yes |
| PERTINENT LABORATORY FINDINGS | N/A |
Case description
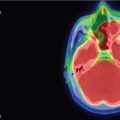
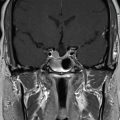
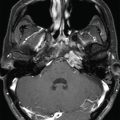
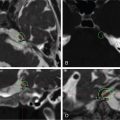
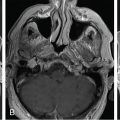
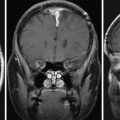
The patient is a woman who was diagnosed at the age of 54 with a left petroclival meningioma causing atypical trigeminal neuralgia. The tumor extended into the cerebellopontine angle (CPA) and cavernous sinus. She was initially treated with oral carbamazepine, which was not tolerated. Surgery was indicated to remove the posterior portion of the tumor and decompress the trigeminal nerve root entry zone ( Figure 6.27.1 ). Postoperatively, she suffered from mild diplopia and dizziness, but fully recovered over a 6-month period. Histology revealed a transitional meningioma, WHO grade I. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) of the residual tumor in the cavernous sinus was planned and administered at 3 months after surgery ( Figure 6.27.2 ). The tumor remained stable for 5 years. The patient then reported new trigeminal symptoms. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) confirmed progression of the posterior portion of the tumor extending into the CPA ( Figure 6.27.3 ). The patient underwent SRS of the recurring tumor in the posterior fossa ( Figure 6.27.4 ).
| Radiosurgery Machine | CyberKnife |
| Radiosurgery Dose (Gy) |
|
| Number of Fractions |
|




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree