Distal occlusion balloons
−Theron triple coaxial catheter
−PercuSurge GuardWire
(Medtronic Vascular, Santa Rosa, CA)
Distal filters
−AngioGuard RX/AngioGuard XP
(Cordis Endovascular, Miami Lakes, FL)
−RX Accunet
(Guidant, Indianapolis, IN)
−FilterWire EZ/FilterWire EX
(Boston Scientific, Santa Clara, CA)
−MedNova NeuroShield/MedNova EmboShield
(Abbott Vascular Devices, Abbott Park, IL)
−Spider/SpideRX
(ev3, Plymouth, MA)
−FiberNet Embolic Protection System (EPS)
(Lumen Biomedical Inc., Plymouth, MN)
Proximal occlusion devices with or without reversal of flow
−Flow Reversal System
(W.L. Gore & Associates, Flagstaff, AZ)
−MO.MA
(Invatec, Roncadelle, Italy)
2 PercuSurge GuardWire (Fig. 11.1)

Fig. 11.1
Distal Occlusion Device
The PercuSurge GuardWire device (Medtronic Vascular, Santa Rosa, CA) provides temporary occlusion of the internal carotid artery (ICA) and aspiration of particles after CAS. The device has three components: an exchange guidewire, a microseal adapter, and a monorail aspiration catheter. The wire is a 0.014- or 0.018-in. angioplasty-style device with a segment that consists of a hollow hypotube made of nitinol. The distal segment of the wire is shapeable, radiopaque, and steerable. Just proximal to the distal segment is an elastomeric latex balloon capable of occluding blood flow when inflated. The proximal end of the hypotube wire incorporates a moveable seal that allows inflation and deflation of the balloon by means of the detachable adapter. After the distal tip is shaped, the guidewire is advanced through the guide catheter under fluoroscopic guidance. The wire is steered through the carotid stenosis and advanced at least 3 cm beyond the target lesion. The predilatation balloon is then passed over the wire into the distal guiding catheter. The microseals’ adapter is attached, and the balloon is inflated to a diameter of 5.5 mm. Contrast is injected to confirm complete occlusion of distal blood flow [2, 3].
If flow is observed, an additional 0.5 ml of diluted contrast agent is added to enlarge the balloon until complete occlusion is achieved. The microseal is then closed and the adapter removed. The predilatation balloon is passed across the lesion, inflated, deflated, and removed. The carotid stent is placed over the guidewire and deployed in the lesion. The stent delivery system is removed, and the post dilatation balloon is passed over the guidewire into the lesion, inflated, deflated, and removed. An Export aspiration catheter with a monorail design (Medtronic Vascular) is inserted up to the level of the distal occlusion balloon. Blood (15–45 mL) is aspirated from the area between the carotid artery bifurcation and the balloon. The aspiration catheter is then removed, and the occlusion balloon is deflated, restoring antegrade flow (Table 11.2).
Table 11.2
Distal occlusion balloon
Pros: | •Low Crossing Profile |
Cons: | •No protection during initial passage |
•Interruption of flow during protection | |
•Inability to perform angiography during procedure | |
•Difficulties in crossing tight and/or tortuous lesions | |
•Potential to cause spasm and dissection in the distal ICA | |
•Potential for particles to embolize to the brain via patent external carotid circulation. | |
•Intolerance |
3 Filters (Fig. 11.2)
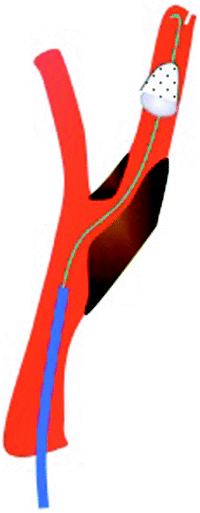
Fig. 11.2
Filters
Filtering cerebral protection devices are the most commonly used systems to prevent cerebral embolism during carotid stenting procedures [4]. The devices are, in general, sophisticated in construction, but the protection is based on a simple concept of trapping downstream larger particles of debris capable of causing cerebral ischemia. Most of the devices are calibrated to filter particles larger than 100 μm, allowing blood flow to continue during the procedure. At the time of this document being written, there are six FDA-approved filtering devices for carotid stenting in the United States: