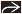Cutaneous Melanoma
Nayela Keen, MD
Christine M. Glastonbury, MBBS
Key Facts
Terminology
Cutaneous malignancy arising from melanocytes of neural crest origin
5% of skin cancers but ˜ 65% of skin cancer deaths
Imaging
On whole body: Females most often extremities, males on trunk
25-35% arise in H&N; most often face
CT/MR: Primary site may not be evident; small or previously resected
Radiologist’s role is to search for deep invasion, perineural tumor, nodal and distant metastases
PET: Melanoma has high FDG avidity
Top Differential Diagnoses
Cutaneous SCCa
Merkel cell carcinoma
Cutaneous basal cell carcinoma
Pathology
Associated with ultraviolet radiation
Increased incidence in genetic syndromes
Clinicopathologically > 95% are superficial spreading, nodular, lentigo maligna or acral lentiginous type
Multiple distinct variants, which may behave differently
Clinical Issues
Incidence increasing at faster rate than any other cancer
Wide local excision performed for early-stage disease
Regional lymph nodes most frequent site of metastasis (stage III)
Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) &/or complete regional lymphadenectomy
Stage III (nodal metastases) 5-year survival = 40-78%
Stage IV (distant metastases) 1-year survival = 40-60%
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Cutaneous malignancy arising from melanocytes
Originates in neural crest
Widely distributed in skin
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
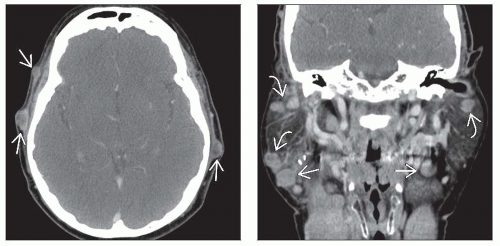
Multiple nodal masses
Location
In females most often extremities, in males on trunk
25-35% arise in H&N, most often face
Increased sun exposure
2-3x higher melanocytic content
Size
Variable, both in superficial and deep extent
Tumor thickness (in mm) important for T stage
Morphology
Infiltrative lesion of skin ± ulceration of overlying epidermis
Ulceration is predictor of reduced survival
CT Findings
Most widely used modality for staging, surveillance, and assessment of treatment response
Primary site may not be evident: Small or previously resected
Look for deep extent to bone and soft tissues
Some melanomas have propensity for perineural spread
Expansion or erosion of skull base foramina
Nodal metastasis round, often necrotic
MR Findings
T1WI
Heterogeneous; may be hyperintense if melanin content high
T2WI FS
Heterogeneous; may be T2 hypointense if melanin content high
T1WI C+ FS
Moderate to marked enhancement
Nuclear Medicine Findings
PET/CT
Melanoma has high avidity for FDG
May alter clinical management by detecting unsuspected distant metastases
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree