Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma
Nayela Keen, MD
Christine M. Glastonbury, MBBS
Key Facts
Terminology
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL)
Uncommon group and spectrum of lymphomas arising in skin
80% of cutaneous lymphomas are T cell; most are mycosis fungoides (MF)
Imaging
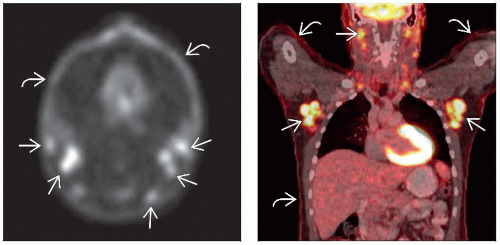
Skin plaques and tumors evident on CECT/MR/PET
Evaluate for enlarged, abnormally enhancing nodes
CT/MR/PET may not be able to distinguish reactive from involved nodes
Very high nodal SUV concerning for transformation
Top Differential Diagnoses
Benign dermatosis
Drug reaction
Idiopathic erythroderma
Pathology
Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome (SS) have own ISCL/EORTC classification system
Clinical Issues
Many variants of CTCL defined by pathologic and serum criteria with variable prognoses
MF confined to skin is chronic indolent disease, normal survival
Characterized by skin patches, plaques, and tumors
Poorer prognosis if skin tumors, extracutaneous spread, > 60 years of age, ↑ LDH
SS is leukemic variant with very poor prognosis, 10-20% 5-year survival
Diagnostic Checklist
Imaging has no role in diagnosis, used for staging
Look for nodal and visceral disease
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL)
Synonyms
Mycosis fungoides (MF)
Sézary syndrome (SS)
Cutaneous CD30(+) T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder (CC-TCLPD)
Cutaneous anaplastic large cell lymphoma (C-ALCL)
Lymphomatoid papulosis (LyP)
Cutaneous peripheral T-cell lymphoma (C-PTCL)
Definitions
Uncommon group of extranodal T-cell lymphomas arising in skin
80% of cutaneous lymphomas are T-cell
≥ 50% mycosis fungoides, 30% CC-TCLPD, < 5% SS
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Multiple, diffusely distributed skin lesions ± lymphadenopathy
Location
70% CTCL have cutaneous and nodal lesions in H&N
Folliculotropic MF has particular predilection for involvement of head and neck
Abnormal T-cells infiltrate hair follicles → alopecia
Morphology
Variable: Plaques (not evident on imaging) to thickened patches to tumor masses > 1 cm
CT Findings
Focal or diffuse, confluent areas of skin thickening
May be subtle patches or thicker, ≥ 1 cm tumors
May show solid adenopathy ± enhancement
MR Findings
Plaques and tumor generally low T1 and variable T2 signal
Enhancement variable: Mild → marked homogeneity
Nuclear Medicine Findings
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree