KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Need for dialysis or failure of serum creatinine to halve in 1st week after transplantation
Imaging
- •
Clinical diagnosis with no specific imaging findings
- •
Renal transplant may be edematous
- •
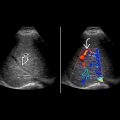
Ultrasound with Doppler serves to exclude other causes of renal transplant dysfunction
- ○
Look for hemorrhage, vascular thrombosis, or hydronephrosis
- ○
- •
Resistive indices may be elevated or there may be absence of diastolic flow
Pathology
- •
21% incidence in deceased donor transplantation
- •
2-5% after living donor transplantation
- •
Most common cause is acute tubular necrosis: 70-90%
- •
Risk factors
- ○
Donor age, harvest injury, preservation
- ○
Injury at procurement, organ preservation methods, warm and cold ischemia time
- ○
Clinical Issues
- •
Present with oliguria, lack of renal function
- •
Delayed graft function has significant impact on long-term graft and patient survival
- •
Increased incidence of acute rejection
- •
May be complicated by vascular thrombosis
- •
Treatment is supportive with dialysis as indicated
Scanning Tips
- •
Determine vascular patency, exclude ureteral obstruction and collections
- •
Use ultrasound to guide renal transplant biopsy