• Cysts occur more frequently within the jaw than in any other bone due to the numerous epithelial cell residues left after tooth formation • This arises from reduced enamel epithelium surrounding the crown of an unerupted tooth (therefore it is only found on buried teeth) • A malignant osteoid-producing bone tumour • Maxillary lesions tend to arise from the alveolar ridge • A locally invasive benign tumour arising from the odontogenic epithelium • Usually found within the molar or ramus mandibular region (commonly centred on the 3rd molar) • It is locally aggressive (requiring a wide excision margin) and can potentially involve the infratemporal fossa, orbit or skull base
Dental radiology
MANDIBULAR/MAXILLARY CYSTIC LESIONS
GENERAL FEATURES
DEFINITION
 these cysts are slow growing and painless (unless they become infected)
these cysts are slow growing and painless (unless they become infected)
DENTIGEROUS CYST (FOLLICULAR CYST)
DEFINITION
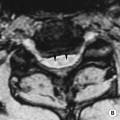
TUMOURS OF BONE
JAW OSTEOMA
OSTEOSARCOMA
Definition
 it is uncommon in the jaw and tends to be slower growing and occurs about 10 years later than seen with a long bone osteosarcoma
it is uncommon in the jaw and tends to be slower growing and occurs about 10 years later than seen with a long bone osteosarcoma  the mandible is more commonly affected than the maxilla
the mandible is more commonly affected than the maxilla
 mandibular lesions tend to arise from the body
mandibular lesions tend to arise from the body
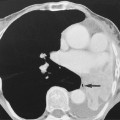
AMELOBLASTOMA
Definition
 the commonest odontogenic tumour (11%)
the commonest odontogenic tumour (11%)  30–50 years of age
30–50 years of age
 it can rarely undergo malignant transformation with lung metastases
it can rarely undergo malignant transformation with lung metastases
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

 dentigerous cysts
dentigerous cysts  odontogenic keratocysts
odontogenic keratocysts raised intracystic pressures and expansion by tissue fluid transudation results in its circular or oval shape (except for an odontogenic keratocyst)
raised intracystic pressures and expansion by tissue fluid transudation results in its circular or oval shape (except for an odontogenic keratocyst)  if the lesion is sufficiently large, then the cortex may become thinned, expanded and then perforated
if the lesion is sufficiently large, then the cortex may become thinned, expanded and then perforated  there is displacement of any adjacent structures (e.g. the tooth roots)
there is displacement of any adjacent structures (e.g. the tooth roots) however, many regress without treatment
however, many regress without treatment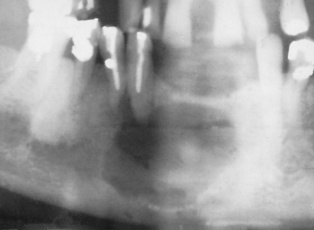
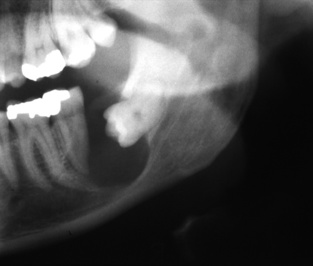
 it demonstrates a higher mitotic activity than the oral mucosa and so behaves like a benign neoplasm
it demonstrates a higher mitotic activity than the oral mucosa and so behaves like a benign neoplasm  recurrences are common
recurrences are common it lacks the more ballooning characteristics of other odontogenic cysts (which is an important diagnostic feature)
it lacks the more ballooning characteristics of other odontogenic cysts (which is an important diagnostic feature)  it frequently occurs within the lower 3rd molar or ramus region (and may displace an unerupted wisdom tooth where it can resemble a dentigerous cyst)
it frequently occurs within the lower 3rd molar or ramus region (and may displace an unerupted wisdom tooth where it can resemble a dentigerous cyst)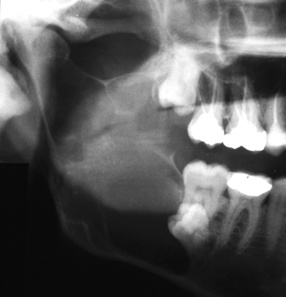
 tooth displacement and root resorption is uncommon
tooth displacement and root resorption is uncommon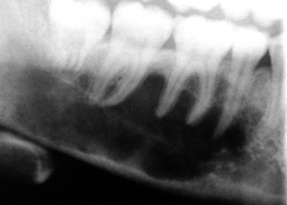
 it is rare and occurs mainly in the young (< 30 years old)
it is rare and occurs mainly in the young (< 30 years old) there is often marked cortical expansion
there is often marked cortical expansion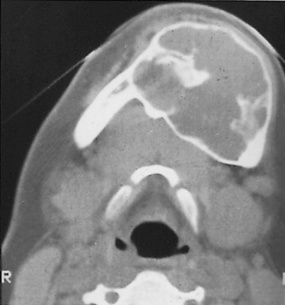
 usually slow growing and painless
usually slow growing and painless  affects the mandible more commonly than the maxilla (usually located posteromedially)
affects the mandible more commonly than the maxilla (usually located posteromedially)
 the tumour can be radiolucent, patchily radio-opaque or sclerotic
the tumour can be radiolucent, patchily radio-opaque or sclerotic  a ‘hair-on-end’, ‘sunray’ or ‘onion skin’ appearance (due to an elevated periosteum)
a ‘hair-on-end’, ‘sunray’ or ‘onion skin’ appearance (due to an elevated periosteum) it is also seen with other sarcomas (e.g. fibrosarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma)
it is also seen with other sarcomas (e.g. fibrosarcoma and Ewing’s sarcoma) heterogeneous SI
heterogeneous SI T2WI: high SI
T2WI: high SI  there may be areas of low SI due to mineralization
there may be areas of low SI due to mineralization it typically contains septa and locules of variable size producing a honeycombed ‘bubbly’ appearance
it typically contains septa and locules of variable size producing a honeycombed ‘bubbly’ appearance  a well-defined margin and often corticated
a well-defined margin and often corticated  a large mass will cause jaw expansion with cortical perforation
a large mass will cause jaw expansion with cortical perforation  there can be knife-edge resorption of tooth roots by the tumour
there can be knife-edge resorption of tooth roots by the tumour T2WI: moderate-to-high SI
T2WI: moderate-to-high SI  T1WI + Gad: enhancement of the septae and solid regions
T1WI + Gad: enhancement of the septae and solid regions usually located within the mandible (premolar or molar region)
usually located within the mandible (premolar or molar region)  a well-defined, unilocular mass with coarse internal trabeculations
a well-defined, unilocular mass with coarse internal trabeculations middle-aged patients (M>F)
middle-aged patients (M>F)  a well-defined mass with variable amounts of focal mineral deposits
a well-defined mass with variable amounts of focal mineral deposits females during the 2nd decade of life
females during the 2nd decade of life  associated with an unerupted tooth
associated with an unerupted tooth  a well-defined mass with variable amounts of focal mineral deposits
a well-defined mass with variable amounts of focal mineral deposits rare (affecting young males)
rare (affecting young males)  an encapsulated radio-opaque mass attached to a root (usually of a lower posterior tooth)
an encapsulated radio-opaque mass attached to a root (usually of a lower posterior tooth)