and LI Ning2
(1)
Radiology Department, Capital Medical University Beijing You’an Hospital, Beijing, China, People’s Republic
(2)
Capital Medical University Beijing You’an Hospital, Beijing, China, People’s Republic
Abstract
History of Present Illness. A 53-year-old woman, complained of cough for 7 days and fever for 6 days, with a body temperature of 40 °C. She suffered from no chills, sore throat, shortness of breath, headache, spasmodic breathing and expectoration of pink foamy phlegm. Death occurred with following autopsy.
Case 12.1
History of Present Illness. A 53-year-old woman, complained of cough for 7 days and fever for 6 days, with a body temperature of 40 °C. She suffered from no chills, sore throat, shortness of breath, headache, spasmodic breathing and expectoration of pink foamy phlegm. Death occurred with following autopsy.
Past History. None.
Contact History. Denied history of contacting with any Influenza A (H1N1) patient.
Physical Signs. Pharyngeal congestion, tonsils not swollen, moist rales in both lungs.
Laboratory Tests. By throat swabs, universal gene of influenza A virus (gene M) positive, universal gene of H1N1 swine flu (gene NP) positive, specific gene of Influenza A (H1N1) virus (gene HA) positive.
On Nov. 11th, 2009, the liver function tests found ALT 81.3 U/L, AST 166.6 U/L.
On Nov. 23rd, 2009, the liver function tests found ALT 63.1 U/L, AST 55.1 U/L, Cr 137.5 mmol/L, UREA 9.67 mmol/L.
On Nov. 24th, 2009, the liver function tests found ALT 40 U/L, AST 32 U/L, Cr 115.9 mmol/L, UREA 16.73 mmol/L; blood gas analysis found pH 7.33, PaCO2 54 mmHg, PaO2 85 mmHg; routine blood tests found leukocytes count 17.89 × 109/L, lymphocytes 5.5 %, neutrophils 90.7 %.
On Oct. 28th, 2009, routine blood tests found leukocytes count 7.8 × 109/L, neutrophils 88.4 %, lymphocytes 8.2 %; blood gas analysis found pH 7.512, PaO2 48.8 mmHg, PaCO2 32.16 mmHg; the liver functions tests found ALT 166.8 U/L, AST 270.5 U/L.
Diagnostic Imaging. By diagnostic imaging on Nov. 19th, 2009 (Fig. 12.1a–f), liver volume increased; the outer boundaries full.
Pathological Analysis and Autopsy. Figure 12.1g–j: the liver cords detached; visible portal structure; no apparent damage to the liver cells; blurry nucleus of liver cells; self-solution changes of the liver cells.
Diagnosis. Hepatic impairments complicating Influenza A (H1N1).
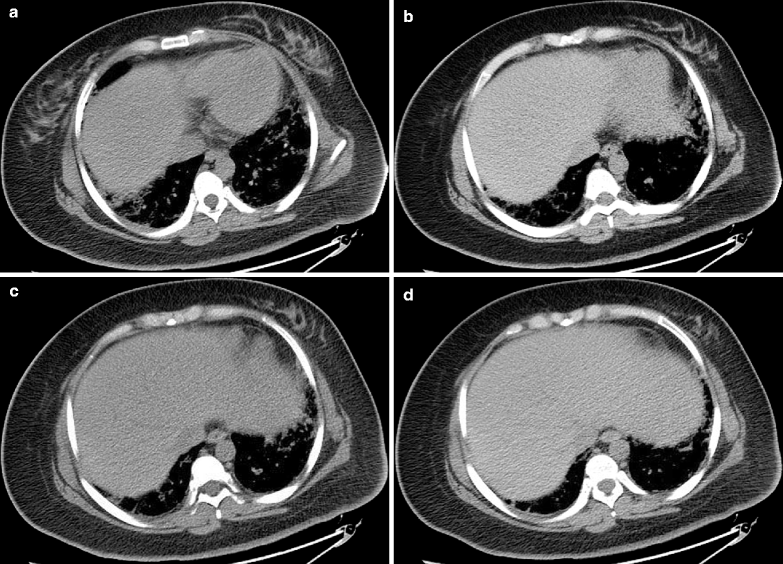
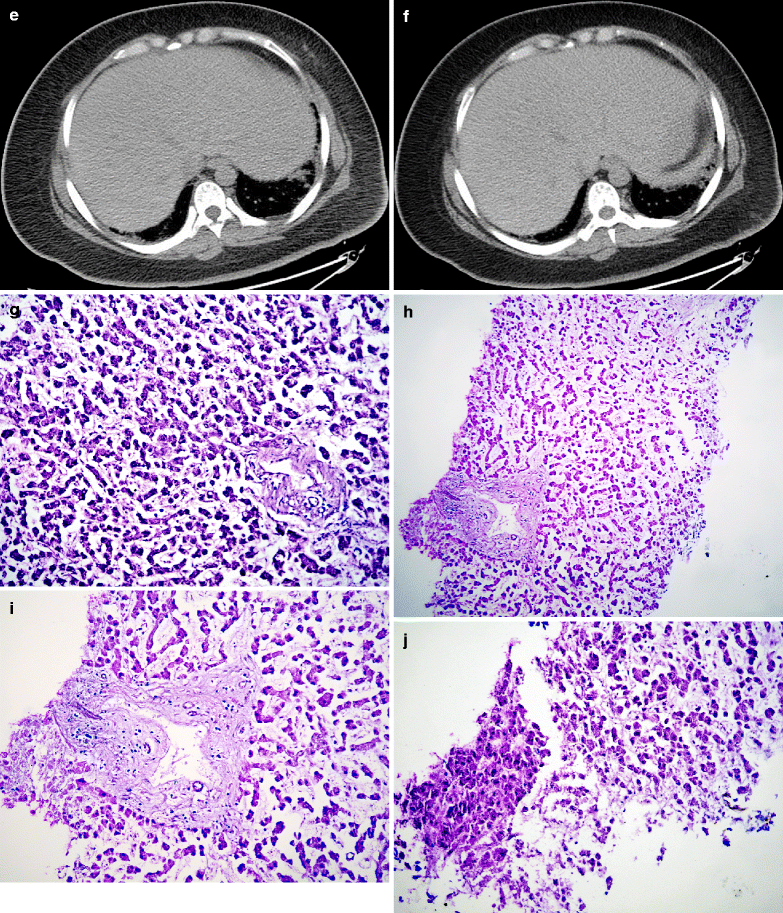


Fig. 12.1
Case 12.2
History of Present Illness. A 74-year-old man, complained of fever and cough for 4 days and was hospitalized.
Past History. Hypertension for 8 years with the highest blood pressure of 200/100 mmHg, usual blood pressures of about 180/90 mmHg, and oral intake of Bovis Hypertension Relieving Pills to maintain the blood pressure normal; type II diabetes mellitus for 2 years and oral intake of Metformin but no monitoring of his blood sugar; chronic bronchitis for more than 10 years.
Contact History. None.
Physical Signs. Body temperature 39.4 °C. Unconscious, in deep coma and no responses to verbal commands. Heart rate 120 beats/min with regular rhythms. Respiration rate 24 times/min. Trachea cannulation and a respirator were applied to assist his pulmonary ventilation. Breath sounds of both lungs low, with rare moist rales from the bottoms of both lungs. Abdominal sounds negative. No edema in both lower extremities.
Laboratory Tests.
By throat swabs, the nucleic acid of Influenza A (H1N1) virus positive.
On Dec. 3rd, 2009, routine blood tests found leukocytes count 9.51 × 109/L, neutrophils 80.6 %, hemoglobin 102 g/L, platelets count 154 × 109/L; blood gas analysis found pH 7.3, PaO2 144 mmHg, PaCO2 70 mmHg, 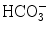 33.4 mmol/L, BE 5.4 mmol/L, SaO2 98.8 %; the renal and liver functions tests found ALT 46.6 U/L, AST 56.3 U/L, TBIL 6.9 μmol/L, Cr 85.6 μmmol/L, K+ 4.14 mmol/L, Na+ 150.5 mmol/L.
33.4 mmol/L, BE 5.4 mmol/L, SaO2 98.8 %; the renal and liver functions tests found ALT 46.6 U/L, AST 56.3 U/L, TBIL 6.9 μmol/L, Cr 85.6 μmmol/L, K+ 4.14 mmol/L, Na+ 150.5 mmol/L.
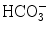 33.4 mmol/L, BE 5.4 mmol/L, SaO2 98.8 %; the renal and liver functions tests found ALT 46.6 U/L, AST 56.3 U/L, TBIL 6.9 μmol/L, Cr 85.6 μmmol/L, K+ 4.14 mmol/L, Na+ 150.5 mmol/L.
33.4 mmol/L, BE 5.4 mmol/L, SaO2 98.8 %; the renal and liver functions tests found ALT 46.6 U/L, AST 56.3 U/L, TBIL 6.9 μmol/L, Cr 85.6 μmmol/L, K+ 4.14 mmol/L, Na+ 150.5 mmol/L.On Dec. 3rd, 2009, routine blood tests found leukocytes count 10.83 × 109/L, neutrophils 79.8 %, hemoglobin 105 g/L, platelets count 140 × 109/L; by blood gas analysis, pH 7.31, PO2 93 mmHg, PaCO2 71 mmHg, 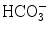 34.7 mmol/L, BE 7 mmol/L, SaO2 96 %; by the renal and liver functions tests, ALT 46.2 U/L, AST 46.1 U/L, TBIL 6.9 μmol/L, Cr 112 μmmol/L, K+ 3.45 mmol/L, Na+ 154 mmol/L.
34.7 mmol/L, BE 7 mmol/L, SaO2 96 %; by the renal and liver functions tests, ALT 46.2 U/L, AST 46.1 U/L, TBIL 6.9 μmol/L, Cr 112 μmmol/L, K+ 3.45 mmol/L, Na+ 154 mmol/L.
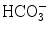 34.7 mmol/L, BE 7 mmol/L, SaO2 96 %; by the renal and liver functions tests, ALT 46.2 U/L, AST 46.1 U/L, TBIL 6.9 μmol/L, Cr 112 μmmol/L, K+ 3.45 mmol/L, Na+ 154 mmol/L.
34.7 mmol/L, BE 7 mmol/L, SaO2 96 %; by the renal and liver functions tests, ALT 46.2 U/L, AST 46.1 U/L, TBIL 6.9 μmol/L, Cr 112 μmmol/L, K+ 3.45 mmol/L, Na+ 154 mmol/L.Pathological Analysis
Figure 12.2a–c: By H&E staining, severe hepatic portal congestion; obvious congestions of the central veins and the peripheral hepatic sinus; hepatocellular congestions; bubble liked fat infiltration of the hepatic cells; inflammatory cells infiltration in the hepatic portal areas.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree