• Acute phase: deposition of islets of osteoid tissue • Subacute phase: remodelling and osteoclastic bone resorption • Chronic phase: new osteoblast-induced sclerotic bone formation • Fenestral: this initially starts at the anterior margin of the oval window • Retrofenestral (cochlear): this initially starts within the pericochlear bony labyrinth • Identification of congenital variations: a deviated nasal septum • Identification of disease extent: which sinuses are involved or spared • Identification of bone destruction: this may indicate malignancy • Identification of complications: e.g. an orbital or intracranial abscess
Ear, nose and throat radiology
SELECTED DISORDERS OF THE EAR
EXTERNAL EAR
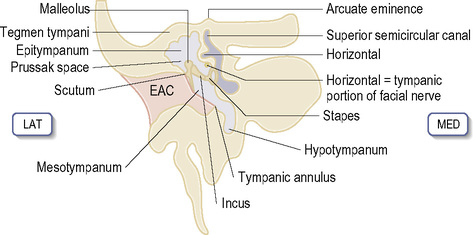
MIDDLE EAR
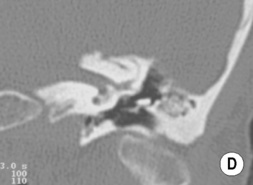
Otosclerosis
Definition
 it can lead to fusion of the stapes foot plate to the oval window (causing a conductive hearing loss)
it can lead to fusion of the stapes foot plate to the oval window (causing a conductive hearing loss)
 it can lead to a sensorineural hearing loss
it can lead to a sensorineural hearing loss
Parameter
Longitudinal fractures (middle ear fracture)
Transverse fractures (inner ear fracture)
Frequency
80%
20%
Fracture line
Parallel to long axis
Perpendicular to long axis
Labyrinth
Spared
Involved: vertigo, sensorineural hearing loss
Ossicles
Involved: conductive hearing loss
Tympanic membrane
Involved
Spared
Facial paralysis
20%
50%
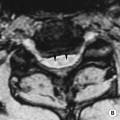
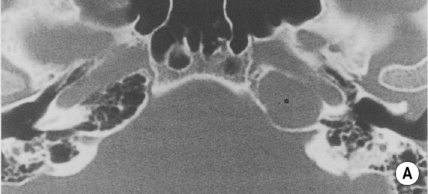
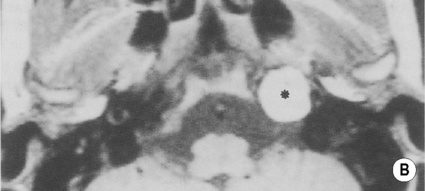
Congenital cholesteatoma
Cholesterol granuloma
T1WI
Low SI
High SI (cholesterol content)
T2WI
High SI
High SI
NOSE AND PARANASAL SINUSES
CT ASSESSMENT OF THE NOSE AND PARANASAL SINUSES
 hypoplasia and enlargement of the normal structures
hypoplasia and enlargement of the normal structures  anomalous air cells (e.g. Haller and Agger nasi air cells)
anomalous air cells (e.g. Haller and Agger nasi air cells)
 if there is involvement of the osteomeatal complex or sphenoethmoidal recess
if there is involvement of the osteomeatal complex or sphenoethmoidal recess  if there is disease extension into the orbit or cranium
if there is disease extension into the orbit or cranium

 Pseudomonas is a typical initiating organism
Pseudomonas is a typical initiating organism if any desquamating epithelium from the tympanic membrane cannot be cleared by the natural processes of ear toilet, the desquamated skin accumulates and forms a ball of skin which is known as a keratoma (cholesteatoma)
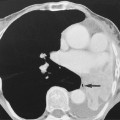
if any desquamating epithelium from the tympanic membrane cannot be cleared by the natural processes of ear toilet, the desquamated skin accumulates and forms a ball of skin which is known as a keratoma (cholesteatoma)  this can subsequently enlarge and cause bone destruction
this can subsequently enlarge and cause bone destruction ossicular erosion (commonly affecting the long process of the incus) with medial displacement of the ossicles
ossicular erosion (commonly affecting the long process of the incus) with medial displacement of the ossicles T2WI: high SI
T2WI: high SI  T1WI + Gad: there is little enhancement
T1WI + Gad: there is little enhancement it commonly erodes the ossicles with lateral displacement of the ossicles
it commonly erodes the ossicles with lateral displacement of the ossicles T2WI: high SI
T2WI: high SI  T1WI + Gad: there is little enhancement
T1WI + Gad: there is little enhancement it can be differentiated from a congenital cholesteatoma with MRI
it can be differentiated from a congenital cholesteatoma with MRI it rarely extends below the level of the hyoid bone
it rarely extends below the level of the hyoid bone T1WI + Gad: there is intense enhancement
T1WI + Gad: there is intense enhancement T1WI + Gad: pathological nerve enhancement is well described
T1WI + Gad: pathological nerve enhancement is well described they are important to identify because (1) there may be an associated CSF leak, (2) the facial nerve may be damaged and (3) the ossicular chain may be disrupted.
they are important to identify because (1) there may be an associated CSF leak, (2) the facial nerve may be damaged and (3) the ossicular chain may be disrupted.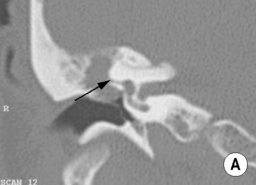
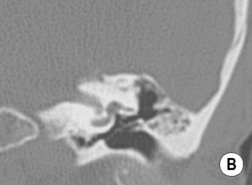
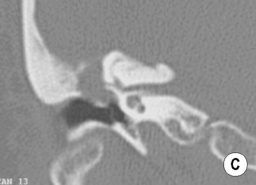
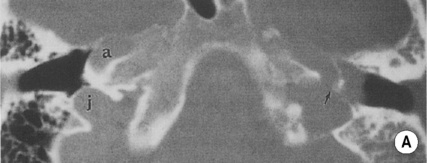
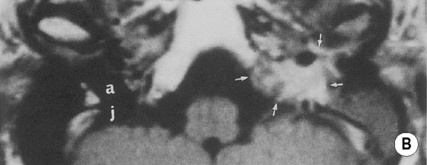
 its infundibulum leads to its opening (the hiatus semilunaris)
its infundibulum leads to its opening (the hiatus semilunaris)