39 Echo Planar Imaging
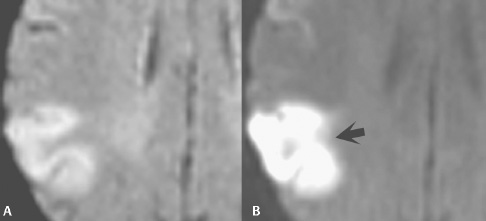
Fig. 39.1
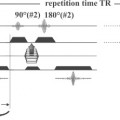
Echo planar imaging (EPI) is one of the fastest techniques for acquiring MRI data. This method incorporates rapid changes in readout gradient polarity and amplitude to refocus the signal of a single spin excitation, producing the required echoes for an entire image. The acquisition time for one slice is one TR period, which lasts as little as 40 msec, and the process is repeated for the number of slices desired.
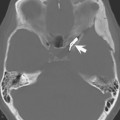
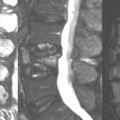
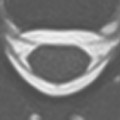
Echo planar imaging techniques are defined by the spin preparation method used. Gradient echo (GRE-EPI) consists of a single RF excitation creating a free induction decay (FID)-based image. A dual RF pulse train generates an RF echo, which is the basis for spin echo (SE-EPI) images. Inversion pulses (IR-EPI) can also be applied to obtain fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR)-like echo planar images. Figure 39.1 illustrates (A) FLAIR and (B
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree