Fat Injury
KEY FACTS
Terminology
Imaging
 Localized mild swelling and increased echogenicity of subcutaneous fat
Localized mild swelling and increased echogenicity of subcutaneous fat
 Loss of normal subcutaneous fat striation
Loss of normal subcutaneous fat striation
 Irregular poorly defined margins without discrete mass
Irregular poorly defined margins without discrete mass
 Hypoechoic stranding extending into surrounding fat
Hypoechoic stranding extending into surrounding fat
 ± fluid accumulation within affected fat (liquefaction)
± fluid accumulation within affected fat (liquefaction)
 ± calcification of affected fat
± calcification of affected fat
 ± hypoechoic pseudocapsule
± hypoechoic pseudocapsule
 Usually mild or no hyperemia
Usually mild or no hyperemia
IMAGING
General Features
Ultrasonographic Findings
 Appearances vary depending on chronicity of lesion
Appearances vary depending on chronicity of lesion
 Earlier stages (within 1 year)
Earlier stages (within 1 year)
 Seen in subacute or chronic stage of fat necrosis
Seen in subacute or chronic stage of fat necrosis
 Varies from mild, speckled calcification to dense calcification
Varies from mild, speckled calcification to dense calcification
 Increasing calcification with increasing lesion chronicity
Increasing calcification with increasing lesion chronicity
 Shadowing artifact may impede full depiction of necrotic area
Shadowing artifact may impede full depiction of necrotic area
 Aggregations of fibrosis without calcification in chronic lesions can cast less severe shadowing artifact
Aggregations of fibrosis without calcification in chronic lesions can cast less severe shadowing artifact
 US more sensitive than radiographs at depicting milder degrees of calcification
US more sensitive than radiographs at depicting milder degrees of calcification
 Later stages
Later stages
 Usually normal fascia and muscle deep to affected area
Usually normal fascia and muscle deep to affected area






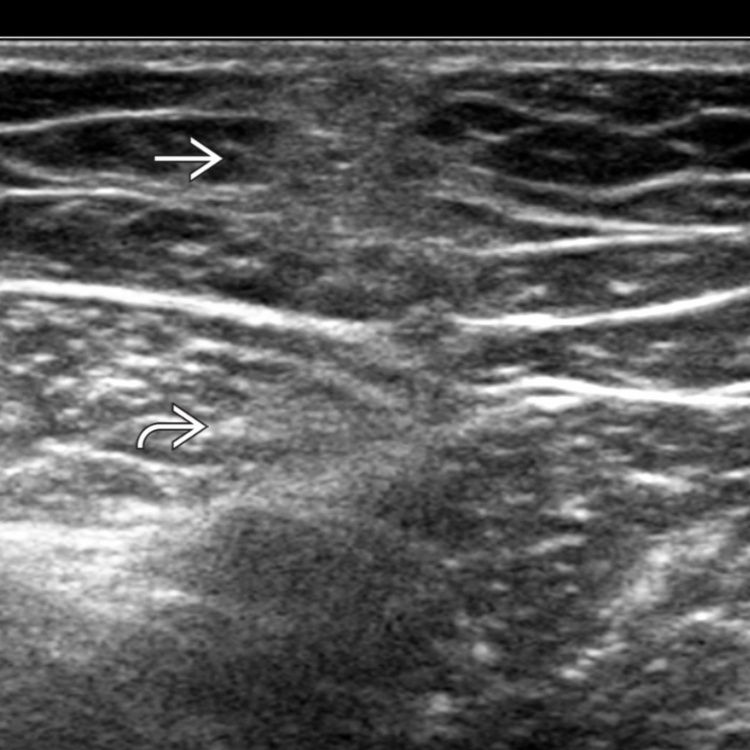
 due to fat injury. Note the mirror image artifact deep to the investing fascia
due to fat injury. Note the mirror image artifact deep to the investing fascia  .
.
 . The entire thickness of the subcutaneous fat down to the investing fascia is affected. The signal alteration deep to the investing fascia is artifactual
. The entire thickness of the subcutaneous fat down to the investing fascia is affected. The signal alteration deep to the investing fascia is artifactual  .
.
 in the subcutaneous fat due to chronic fat injury. Note the mild degree of posterior shadowing
in the subcutaneous fat due to chronic fat injury. Note the mild degree of posterior shadowing  due to fibrotic tissue.
due to fibrotic tissue.
 due to perilesional reparative change. Clinically, such lesions become smaller and firmer over time, possibly with some skin depression.
due to perilesional reparative change. Clinically, such lesions become smaller and firmer over time, possibly with some skin depression.