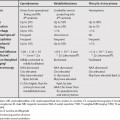
141 Focal vertebral lesions can be benign or malignant. Focal benign lesions include hemangiomas, focal fatty marrow, focal red marrow, bone islands and can also be the result of hematopoietic growth factors. Focal lesions can also occur as the result of treatment of aplastic anemia with transplant or immunosuppressive therapy and following bone marrow transplant for malignancy; however, the findings will be more diffuse. The main concern when encountering a focal lesion is malignancy, which can be metastatic or less commonly, primary. Metastases can be solitary, multiple, or diffuse. Many times, biopsy, bone scan, or additional follow-up studies will be required to separate malignant lesions from benign; nevertheless, there are some differentiating features between metastases and the relatively common, benign vertebral hemangioma (Table 141.1). The appearance of hemangiomas on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be variable, with lesions with more adipocytes being hyperintense on T1-weighted MR images (T1WI) and intermediate on T2-weighted MR images (T2WI), and lesions with high vascularity/interstitial edema are intermediate signal on T1WI and T2 hyperintense. Hemangiomas can also have varying degrees of heterogeneity reflecting their histology. Occasionally, hemangiomas can be hypointense and enhance significantly and then can be confused with malignant lesions. On computed tomography (CT) and x-rays, hemangiomas have a characteristic appearance (Table 141.1
Focal Vertebral Lesions
Hemangiomas
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree