KEY FACTS
Imaging
- •
US for initial detection and characterization, CECT or MR for preoperative assessment and staging
- •
3 main morphological types
- ○
Large soft tissue mass infiltrating gallbladder (GB) fossa/replacing GB, ± invading liver ( most common )
- ○
Diffuse or focal GB wall thickening: Asymmetric, irregular, extensive thickening
- ○
Polypoid intraluminal mass: > 1 cm, thickened base, irregular margins
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
GB polyp
- •
Chronic or xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis
- •
Hyperplastic cholecystoses
- •
Diffuse GB thickening from portal hypertension, heart failure
Pathology
- •
Most are adenocarcinoma; mean 5-year survival: 5-10%
- •
Chronic irritation of GB mucosa by gallstones (GS)
- •
Malignant degeneration of adenomatous polyps less common
- •
Spreads by local invasion or hematogenous spread to liver, nodal spread to porta hepatis and paraaortic nodes
Clinical Issues
- •
Most common malignancy of biliary tree; prevalence: 3-7%
- •
F:M = 3:1; mean age: 65 years
- •
Risk factors: GS, chronic infection and inflammation
- •
Preoperative diagnosis occurs in < 20% of patients, found at cholecystectomy for stones/cholecystitis
- •
Right upper quadrant pain, weight loss, anorexia, fever
- •
Jaundice occurs when tumor invades bile ducts
Scanning Tips
- •
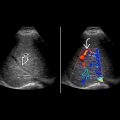
Look for asymmetric mass infiltrating liver
 : Direct tumor infiltration to liver parenchyma
: Direct tumor infiltration to liver parenchyma  and retrograde spread along biliary tree
and retrograde spread along biliary tree  .
.
 filled with solid tumor proven to be adenocarcinoma. Color Doppler would be useful to confirm that this is a tumor and not sludge.
filled with solid tumor proven to be adenocarcinoma. Color Doppler would be useful to confirm that this is a tumor and not sludge.
 surrounded by tumor
surrounded by tumor  . The interface
. The interface  between the gallbladder and the liver is indistinct, indicating local invasion.
between the gallbladder and the liver is indistinct, indicating local invasion.
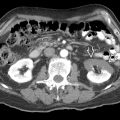
 and kidney
and kidney  in the same patient shows liver metastases
in the same patient shows liver metastases  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree