© Springer International Publishing Switzerland 2017
Maria Carmen Garganese and Giovanni Francesco Livio D’Errico (eds.)Conventional Nuclear Medicine in Pediatrics10.1007/978-3-319-43181-9_1818. Gastroenterology: Focus on Children with Liver Problems
(1)
Pediatric Hepatology Gastroenterology Nuriition Unit, “Bambino Gesù” Children Hospital, Rome, Italy
18.1 Introduction
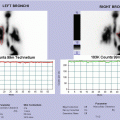
Hepatobiliary scintigraphy is a radionuclide diagnostic imaging study that evaluates hepatocellular function and the biliary system by tracing the production and flow of bile from the formative phase in the liver and its passage through the biliary system into the small intestine.
Sequential (or dynamic) images of the liver, biliary tree, and gut are obtained. Computed acquisition and analysis, including pharmacological interventions, are used according to varying indications and an individual patient’s needs.
Scintigraphy today works in combination with other methods of hepatobiliary imaging, mainly sonography and echocolor Doppler, magnetic resonance, and Colangio-RM, bringing the advantage of a dynamic display of the tracer extraction phases, concentration, and excretion in the bile duct.
In adult hepatobiliary disease, main indications of hepatobiliary scintigraphy are acute and chronic cholecystitis, evaluation of patency and integrity of biliary tree, dysfunction of the sphincter of Oddi, functional biliary pain syndromes, or chronic pain localized at the right hypochondrium. In case of ongoing surgical liver resection, hepatobiliary scintigraphy is employed for the functional preoperative evaluation. After liver transplant, it is used for the study of the biliary tree and of the functional hepatic reserve.
In childhood, the above indications are less frequent, while more often hepatobiliary scintigraphy is used in the differential diagnosis of neonatal cholestasis, in particular, to distinguish between obstructive jaundice depending on anatomical malformations (biliary atresia, choledochal cysts) and medical cholestatic jaundice resulting from a defective hepatocellular function (due to infectious, metabolic, hormonal causes). It also allows to evaluate the patency and the function of hepatic–jejunal anastomosis (Kasai surgery) after surgery for atresia and the possible presence of leak of the bile duct. Similar to adulthood, it has a role in anatomical and functional aspects of the transplanted liver.
Main hepatobiliary clinical problems and indications in pediatrics:
- 1.
Neonatal cholestasis and suspicion of biliary atresia:
Neonatal cholestasis has an incidence of 1:2500 newborns and is more common in premature babies. It can be recognized by various causes: infectious/septic, genetic/metabolic, endocrine, hematological. Liver and biliary congenital malformations must always be considered and excluded: among them, the most typical is biliary atresia. It is a progressive fibro-obliterative condition of extrahepatic and intrahepatic bile ducts, resulting in the obstruction of bile flow to the intestine, intrahepatic retention of bile and bile salts, leading to structural liver damage. From the clinical point of view, biliary atresia usually affects a full-term infant (of few weeks of age) generally in good clinical conditions and regular growth, who is referred for jaundice, hyperchromic urine, and hypo-acholic stools. In suspicion of biliary atresia (incidence 1:8000–15,000 births, depending on the ethnic groups), the differential diagnosis versus other causes of neonatal cholestasis is absolutely urgent, for the possibility in case of biliary atresia of an early surgical correction, before the development of biliary cirrhosis and portal hypertension. The sooner the surgery (Kasai portoenterostomy) is performed, better is the outcome and chances of an effective and lasting biliary drainage.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree